Session Information
Session Type: Poster Session B
Session Time: 9:00AM-11:00AM
Background/Purpose: Treatment safety, particularly malignancy and infections, is an important issue for biologics; hence, surveillance and analyses comparing biosimilar versus bio-originator use in the real world are needed. We aimed to compare malignancy and serious infections among initiators of etanercept originator (ETA-O) versus biosimilar (ETA-B), all users and rheumatoid arthritis (RA) specific.
Methods: CAN-AIM is a team funded to do high-priority research projects for Health Canada and other stakeholders. We used data from the National Prescription Drug Utilization Information System (NPDUIS), which contains pan-Canadian (except Quebec) claims-level data on prescriptions dispensations paid from public drug programs, linked to the hospital Discharge Abstract Database (DAD) and the National Ambulatory Care Reporting System (NACRS). We studied adults (≥18 years), initiating ETA between January 2015 and December 2019, further restricted to RA (ICD-10 M05, M06, M45, M70, M71, M72, M73andL40). Those with ICD diagnostic codes indicating malignancy, HIV or organ transplant one year before ETA/INF initiation (baseline) were excluded. For infection, follow-up began at treatment initiation and ended at end of data or 90 days after discontinuation or end of study; and for malignancy, 365 days after treatment initiation up to 365 days after discontinuation. Serious infections were defined as the first hospitalization with ICD-10 indicating infectious disease, observed from treatment initiation up to end of data or 90 days after treatment discontinuation. Malignancy was defined by the first record of neoplasm except non-melanoma skin cancer, from 365 days after treatment start up to 365 days after discontinuation. We compared originator and biosimilar using Cox regression models. We presented the adjusted hazard ratio (aHR) – potential confounders or effect modifiers included sex at birth, age at ETA initiation, prior corticosteroids or other biologics, region (Ontario vs other), and calendar year. Kaplan-Meier curves were plotted to compare time to first event between both treatment groups.
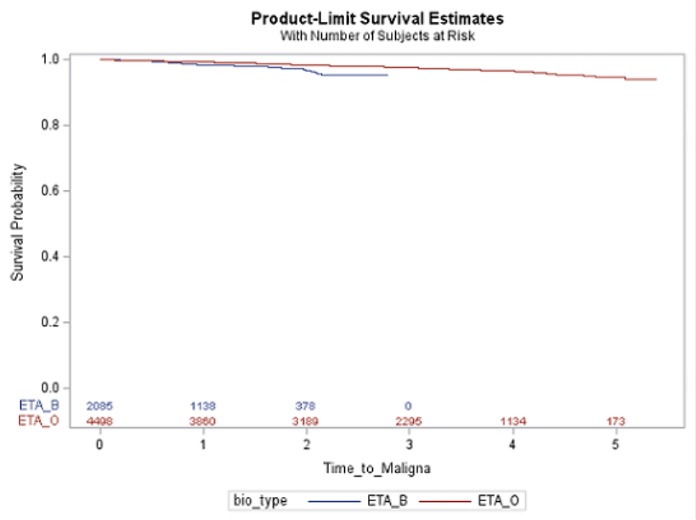
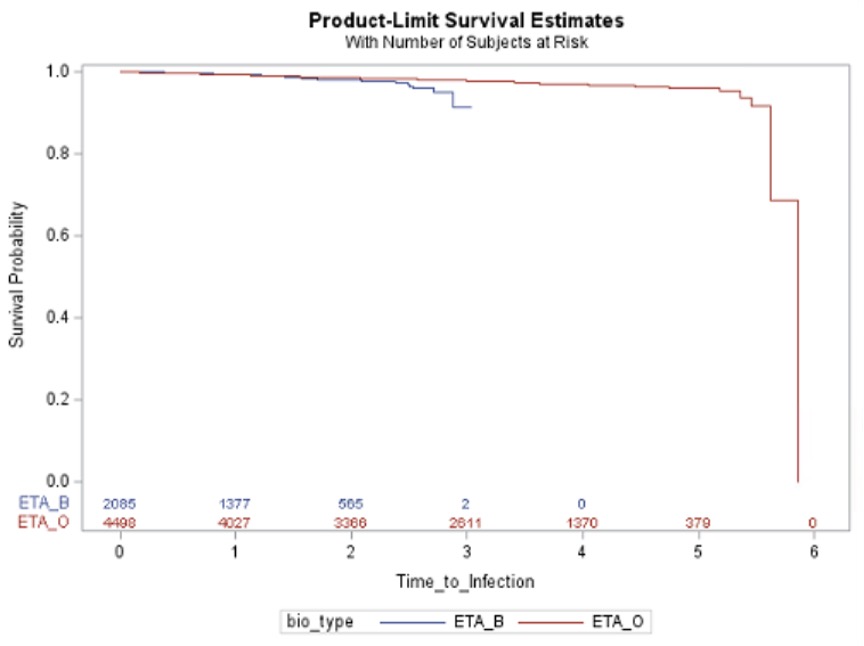
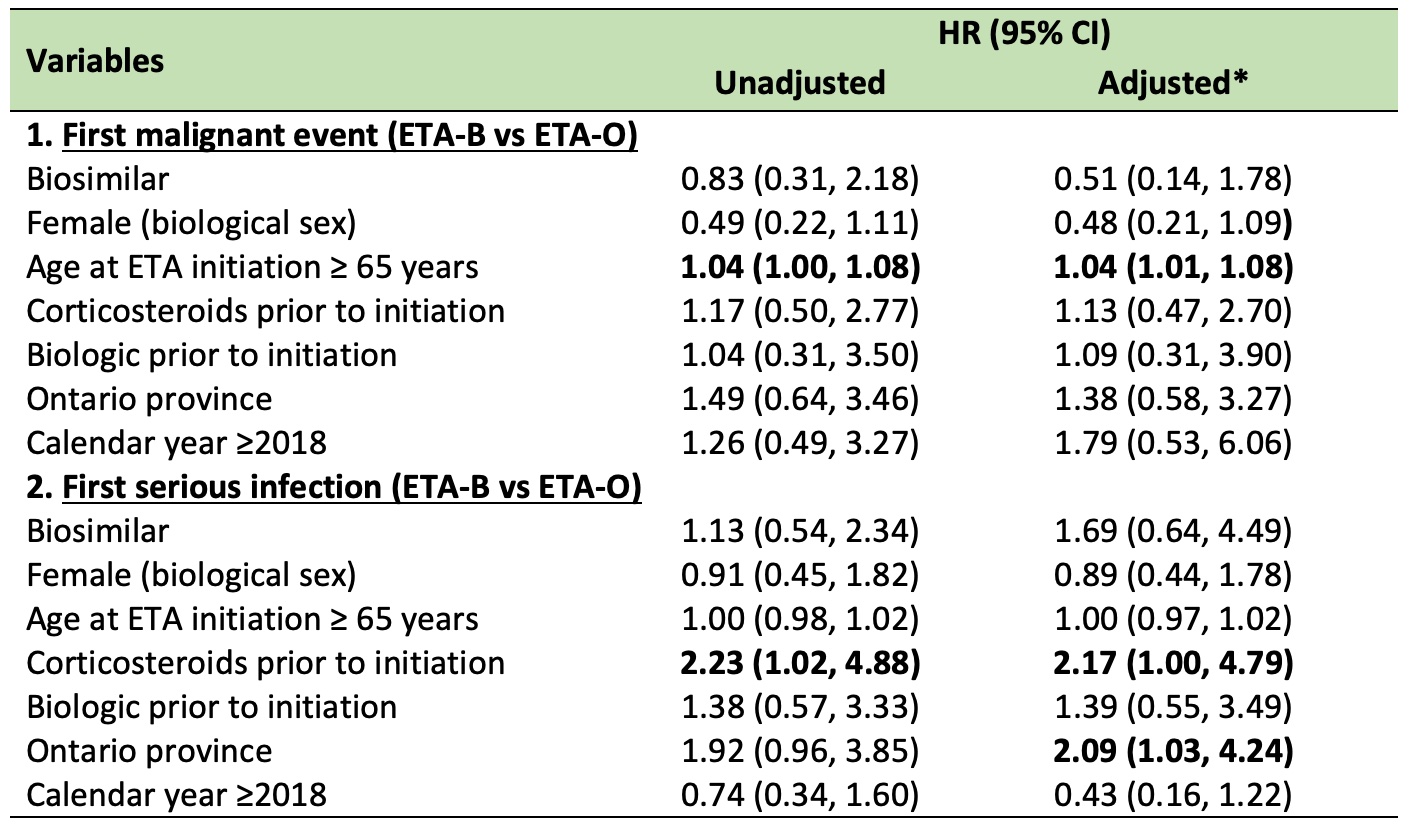
Results: The cohort (6,583 users, 695 RA, 31.7% on ETA-B) was mostly female (65%), with a median age (interquartile range, IQR) of 62 (50-69) at treatment initiation. Overall, malignancy incidence was 10.3 (95%CI 8.8-12.1), and infection rate was 8.9 (95%CI 7.5-10.4) per 1,000 person-year. Time to first event between ETA-B and ETA-O is presented in Figures 1-2. The aHR for ETA-B versus ETA-O (reference) was 1.14 (95%CI 0.68-1.91) for malignancy and 1.33 (95%CI 0.77-2.30) for infection. Non-significant results were also found when restricted to RA (Table 1).
Conclusion: In this real-world dataset, we were unable to identify clear differences in serious infections and malignancy comparing biosimilar and originator of etanercept, all users and RA-specific. Limitations include inability to control for residual confounders (e.g., disease severity), potential outcome misclassification and selection bias and short follow-up or treatment exposure to detect malignancy.
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Birck M, Lukusa L, Abrahamowicz M, Boire G, Choquette D, Maksymowych W, Bernatsky S. Comparison of Malignancies and Serious Infections Between Etanercept Biosimilar and Bio-Originator Initiators: Population-Based Analyses [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2023; 75 (suppl 9). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/comparison-of-malignancies-and-serious-infections-between-etanercept-biosimilar-and-bio-originator-initiators-population-based-analyses/. Accessed .« Back to ACR Convergence 2023
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/comparison-of-malignancies-and-serious-infections-between-etanercept-biosimilar-and-bio-originator-initiators-population-based-analyses/