Session Information
Date: Tuesday, November 9, 2021
Title: Spondyloarthritis Including PsA – Treatment Poster III: Psoriatic Arthritis II (1801–1835)
Session Type: Poster Session D
Session Time: 8:30AM-10:30AM
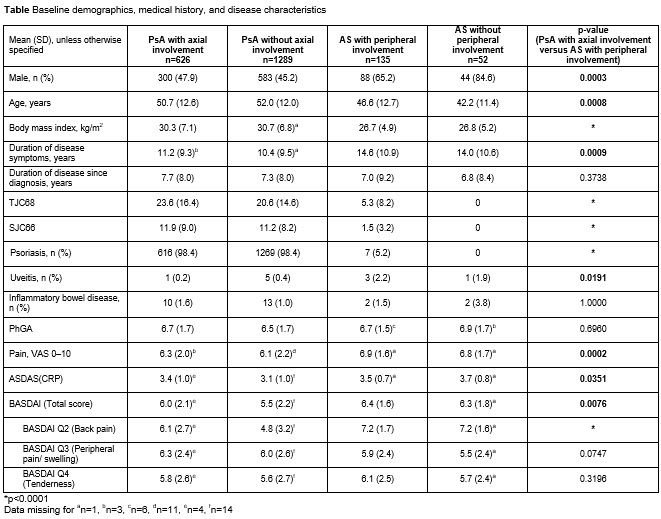
Background/Purpose: Axial, peripheral, and other disease manifestations often overlap between psoriatic arthritis (PsA) and ankylosing spondylitis (AS). Upadacitinib (UPA) is an oral Janus kinase inhibitor under evaluation for the treatment of PsA and AS. The objective of this analysis was to describe and compare baseline characteristics and UPA efficacy across 4 subgroups of patients (pts) from clinical trials: active PsA (with/without axial involvement) and active AS (with/without peripheral involvement).
Methods: Baseline characteristics and efficacy of UPA in reducing axial and peripheral signs and symptoms were assessed via an integrated analysis across the 4 pt subgroups from the SELECT-PsA 1,1 SELECT-PsA 2,2 and SELECT-AXIS3 studies. Analyses of baseline characteristics included pts in the UPA 15 mg once daily (QD), UPA 30 mg QD, and placebo (PBO) groups; efficacy analyses included pts in the UPA 15 mg QD group only. Axial involvement in PsA (axial PsA) was determined by investigator assessment. Peripheral involvement in AS was defined based on presence of tender or swollen joints (TJC68 >0 or SJC66 >0), or presence of enthesitis at baseline (Maastricht Ankylosing Spondylitis Enthesitis Score >0).
Results: 2102 pts (UPA 15 mg; UPA 30 mg; PBO) were evaluated across the 4 subgroups (PsA [with/without axial involvement]: 626/1289; AS [with/without peripheral involvement]: 135/52). 33% of pts with PsA had axial PsA; 72% of pts with AS had peripheral symptoms. Pts with axial PsA had higher peripheral joint (TJC68 and SJC66) and skin (psoriasis) burden than pts with AS with peripheral involvement (p< 0.0001). Pts with AS with peripheral involvement had significantly greater overall pain (pt’s assessment of pain; p=0.0002) and back pain (BASDAI Q2; p< 0.0001) scores, and higher total BASDAI (p=0.0076) and ASDAS (p=0.0351) scores than pts with axial PsA; physician’s global assessment of disease activity, and peripheral pain and tenderness (BASDAI Q3 and Q4) were numerically similar for these 2 subgroups (Table). The efficacy of UPA 15 mg (measured using ASDAS and BASDAI) was generally consistent across the 4 pt subgroups regardless of peripheral or axial involvement (Figure).
Conclusion: Pts with PsA with axial involvement and pts with active AS showed some differences in baseline characteristics but similar improvements versus placebo with UPA 15 mg QD.
References: 1. McInnes I, et al. Ann Rheum Dis 2020;79(Suppl 1):16–17; 2. Genovese MC, et al. Ann Rheum Dis 2020;79(Suppl 1):139; 3. van der Heijde D, et al. Lancet 2019;394:2108–17.
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Baraliakos X, Deodhar A, Ranza R, Rednic S, Ciccia F, Ganz F, Gao T, Lertratanakul A, Song I, Ostor A, Coates L. Comparison of Axial and Peripheral Manifestations in Patients with Psoriatic Arthritis and Ankylosing Spondylitis in Upadacitinib Clinical Trials [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2021; 73 (suppl 9). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/comparison-of-axial-and-peripheral-manifestations-in-patients-with-psoriatic-arthritis-and-ankylosing-spondylitis-in-upadacitinib-clinical-trials/. Accessed .« Back to ACR Convergence 2021
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/comparison-of-axial-and-peripheral-manifestations-in-patients-with-psoriatic-arthritis-and-ankylosing-spondylitis-in-upadacitinib-clinical-trials/