Session Information
Date: Sunday, November 13, 2022
Title: Spondyloarthritis Including PsA – Diagnosis, Manifestations, and Outcomes Poster III
Session Type: Poster Session C
Session Time: 1:00PM-3:00PM
Background/Purpose: Psoriatic Arthritis (PsA) is a complex, heterogeneous disease with chronic inflammation. Disease manifestations include the peripheral joint inflammation, dactylitis, enthesitis and skin psoriasis. Chronic inflammation is associated with structural damage, which jeopardize long-term functional ability. Sensitive biomarkers reflecting disease activity in various disease domains are lacking.
The aim of the study was to define the molecular basis of inflammation in different disease domains through comparative profiling of serum proteins
Methods: This is a cross-sectional study in patients with PsA. Clinical assessment of inflammation in the peripheral joint (clinical Disease Activity in Psoriatic Arthritis [cDAPSA] and swollen joint count), dactylitis digit count, skin (Psoriasis Activity and Severity Index [PASI]) and enthesis (Leeds enthesitis index) were performed. Blood samples were collected for biomarker assay including 48 cytokines, chemokines, growth and angiogenic factors using the Bio-Rad Bioplex assay1 (Table 1). Levels of selected serum proteins were compared between different disease activity scores across various domains using adjusted linear regression with least absolute shrinkage and selection operator (LASSO) modeling.
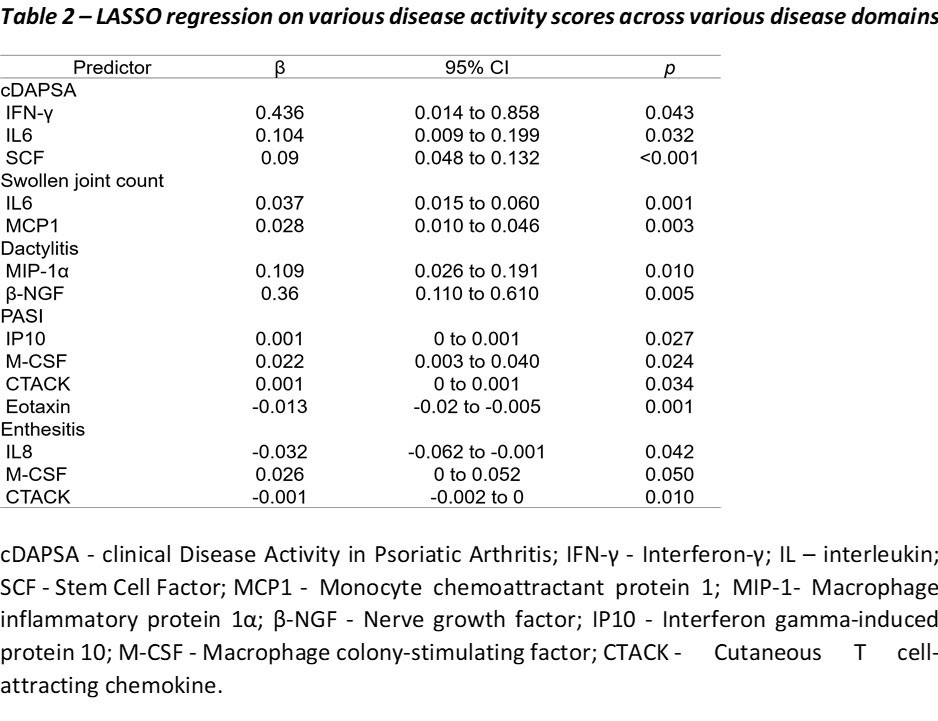
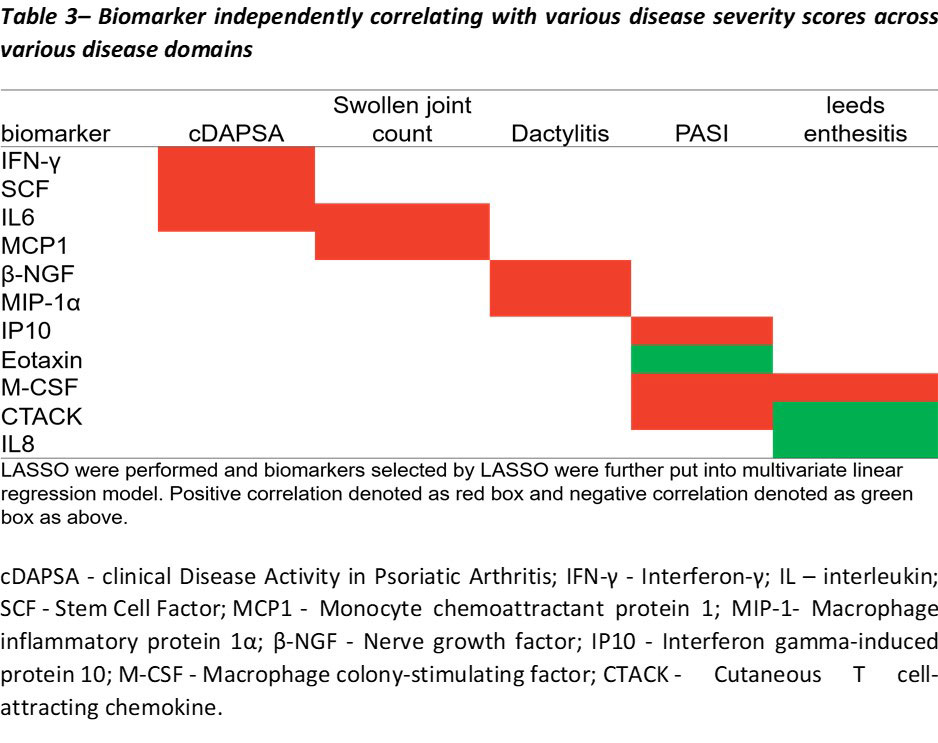
Results: 100 PsA patients were recruited (age: 51±11 years, male: 52 (52%), disease duration: 9.0±3 years). The cohort had moderate disease activity (DAPSA: 24.4±14.6; PASI: 6.0±7.2). 53 (53%) and 11 (11%) patients were using conventional synthetic disease modifying anti-rheumatic drugs (csDMARDs) and biologic DMARDs (bDMARDs) respectively. Using LASSO regression analysis, biomarkers correlating with peripheral joint inflammation were IFN-γ, IL6, SCF and MCP1, while MIP-1α and β-NGF were related to dactylitis. Biomarkers correlating with skin severity were IP10, M-CSF and eotaxin, while IL8, M-CSF and CTACK were related to enthesitis. Details of biomarkers independent predicting various disease severity are listed in table 2-3.
Conclusion: Comparative serum protein biomarker profiling represents a viable method for distinguishing active inflammation in the various disease domains which may be a step forward towards personalized medicine.
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Cheng I, Li M, SO H, Lee J, Wong C, Tam L. Comparative Profiling of Serum Protein Biomarkers and Disease Activity Across Various Disease Domains in Patients with Psoriatic Arthritis (PsA) [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2022; 74 (suppl 9). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/comparative-profiling-of-serum-protein-biomarkers-and-disease-activity-across-various-disease-domains-in-patients-with-psoriatic-arthritis-psa/. Accessed .« Back to ACR Convergence 2022
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/comparative-profiling-of-serum-protein-biomarkers-and-disease-activity-across-various-disease-domains-in-patients-with-psoriatic-arthritis-psa/