Session Information
Date: Tuesday, October 28, 2025
Title: (2338–2376) Spondyloarthritis Including Psoriatic Arthritis – Treatment Poster III
Session Type: Poster Session C
Session Time: 10:30AM-12:30PM
Background/Purpose: Psoriatic arthritis (PsA) is a chronic immune-mediated disease which involves joints, skin, and nails, leading to deformities, decreased function, lower quality of life, and in many cases higher mortality. While traditional synthetic DMARDs and TNF inhibitors(TNFi), such as adalimumab, are effective existing treatments, they both have their shortcomings. Despite this, most patients with PsA do not achieve complete disease remission with synthetic DMARDs, and TNFi may be ineffective for skin, and lose efficacy over time, or be limited for long-term use due to safety concerns. IL-17 inhibitors target a separate inflammatory pathway and have demonstrated greater skin clearance and comparable joint improvement compared with TNFi in clinical trials at 52 weeks. This meta-analysis compares IL-17i versus adalimumab in biologic-naive PsA populations to evaluate safety and efficacy of using IL-17i in PsA patients.
Methods: We systematically searched PubMed, Embase, Cochrane for English-language studies involving comparison of treatment effects between IL-17i and Adalimumab, and reported at least one relevant outcome. Three studies met inclusion criteria. Data were pooled using the inverse variance weighting method with a random-effects model in R Studio. Confidence intervals and heterogeneity were assessed, and forest plots were generated to visualise the pooled effect estimates.
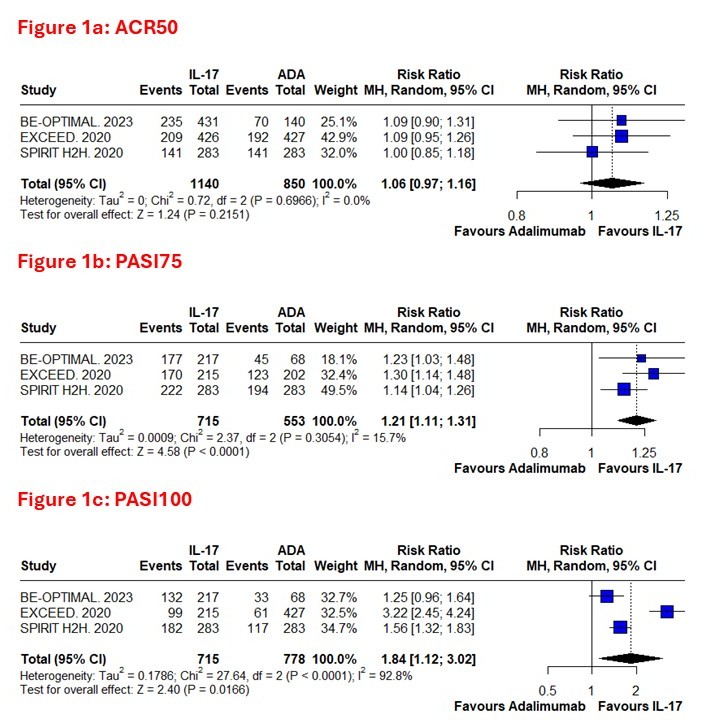
Results: Three studies(Randomized controlled trials) involving 1990 patients were included. Analysis of IL-17i versus Adalimumab revealed comparable ACR50 responses (RR=1.06, 95% CI: 0.97–1.16, p=0.22) but significantly higher PASI75 achievement with IL-17i (RR=1.21, 95% CI: 1.11–1.31, p< 0.0001). The primary composite outcome (ACR50+PASI100) strongly favored IL-17i (RR=1.49, 95% CI: 1.26–1.78, p< 0.01). Serious adverse events were slightly less in IL-17i group but that change is not significant (RR=0.72, 95% CI: 0.35–1.50, p=0.38), and also IL-17i demonstrated significantly lower discontinuation rates due to adverse events (RR=0.56, 95% CI: 0.38–0.82, p< 0.01).
Conclusion: In biologically naive PsA patients, IL-17i showed comparable joint response, but has higher skin clearance compared to Adalimumab. IL-17i also has fewer discontinuations due to drug adverse events and overall it showed to be a great treatment option. Future Research should direct towards long-term outcomes and combination therapies to improve treatment algorithms.
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Chirumamilla P, Medarametla R, Cherukuri A, Sunkara S, Bandarupalli P, Nimmagadda R, Erasani G, Sakhamuri P, Lindsey S. Comparative Efficacy and Safety of IL-17 Inhibitors Versus Adalimumab in Biologic-Naive Psoriatic Arthritis Patients: A Meta-Analysis of Randomized Controlled Trials [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2025; 77 (suppl 9). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/comparative-efficacy-and-safety-of-il-17-inhibitors-versus-adalimumab-in-biologic-naive-psoriatic-arthritis-patients-a-meta-analysis-of-randomized-controlled-trials/. Accessed .« Back to ACR Convergence 2025
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/comparative-efficacy-and-safety-of-il-17-inhibitors-versus-adalimumab-in-biologic-naive-psoriatic-arthritis-patients-a-meta-analysis-of-randomized-controlled-trials/

.jpg)