Session Information
Session Type: Poster Session (Monday)
Session Time: 9:00AM-11:00AM
Background/Purpose: Clinical studies have demonstrated the efficacy of tocilizumab (TCZ) administered with methotrexate (MTX) in improving rheumatoid arthritis (RA) disease activity in patients who have had an inadequate response to tumor necrosis factor inhibitors (TNFis). The objective of this study was to compare the effectiveness of TCZ + MTX with that of TNFis + MTX in patients with RA who had prior exposure to TNFis in routine clinical practice.
Methods: Eligible participants were TCZ-naïve patients from the Corrona RA registry who initiated TCZ + MTX or a TNFi + MTX after January 1, 2010 and had a 6-month follow-up visit. Patients in both groups must have used ≥ 1 TNFi, had a Clinical Disease Activity Index (CDAI) score available at initiation (baseline) and 6 months and had a CDAI score > 10 at baseline. The primary outcome was mean change in CDAI from baseline to 6 months. Secondary outcomes included achievement of low disease activity (LDA; CDAI ≤ 10) and mean change in modified Health Assessment Questionnaire (mHAQ) at 6 months. Patients were grouped by baseline MTX dose (≤ 10 mg; > 10 to ≤ 15 mg; > 15 to ≤ 20 mg; > 20 mg); outcomes were compared between patients initiating TCZ and those initiating a TNFi overall and within each MTX dose group using propensity score (PS)-trimmed populations. As a sensitivity analysis, TCZ and TNFi initiators in each group were PS-matched 1:1 and outcomes were assessed in the matched populations. Linear and logistic regression models were estimated in the trimmed and matched populations, adjusting for covariates not balanced after PS trimming or matching, respectively.
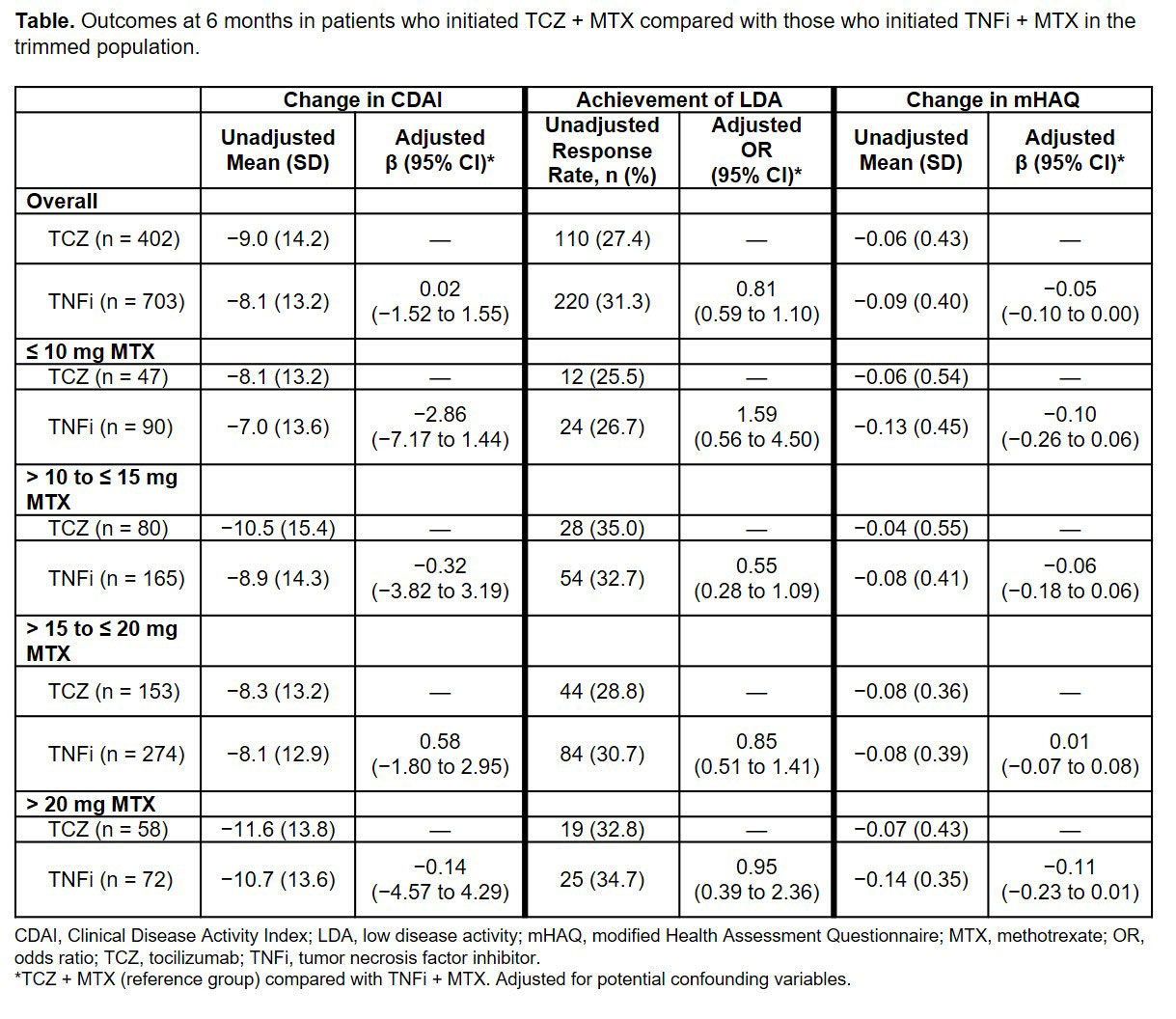
Results: A total of 415 TCZ + MTX initiators and 725 TNFi + MTX initiators met the inclusion criteria prior to PS trimming or matching. The overall trimmed population included 402 TCZ + MTX initiators and 703 TNFi + MTX initiators. In the trimmed population, patient demographics were generally comparable between TCZ + MTX and TNFi + MTX initiators; the mean age was 57.1 years in the TCZ + MTX group and 57.7 years in the TNFi + MTX group, the majority of patients in both groups were female ( > 79%) and white ( > 82%) and the mean duration of RA was 11.8 and 10.5 years in the TCZ + MTX and TNFi + MTX groups, respectively. Higher proportions of patients initiating TCZ had received ≥ 2 prior biologics (66.0% to 76.3%) compared with those initiating a TNFi (33.2% to 42.2%) across all MTX dose groups. Patients initiating TCZ had higher mean baseline CDAI scores (26.5 to 29.3) than those initiating a TNFi (24.7 to 27.5). Patients in both cohorts had improvement in CDAI scores at 6 months regardless of baseline MTX dose. Improvement in CDAI and mHAQ and the odds of achieving LDA were comparable between TCZ and TNFi initiators across all MTX groups in the trimmed population after adjustment for potential confounding variables (Table). Similar results were observed in the PS-matched cohorts.
Conclusion: In this real-world population of US patients with RA who had prior TNFi exposure, there was no statistically significant or clinically meaningful difference in the effectiveness of therapy in patients who initiated TCZ + MTX compared with TNFi + MTX.
Acknowledgments: Support for third-party writing assistance, furnished by Health Interactions, Inc, was provided by Genentech, Inc.
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Pappas D, Blachley T, Zlotnick S, Best J, Emeanuru K, Kremer J. Comparative Effectiveness of Tocilizumab in Combination with Methotrexate versus Tumor Necrosis Factor Inhibitors (TNFis) in Combination with Methotrexate in Patients with Rheumatoid Arthritis with Prior Exposure to TNFis [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2019; 71 (suppl 10). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/comparative-effectiveness-of-tocilizumab-in-combination-with-methotrexate-versus-tumor-necrosis-factor-inhibitors-tnfis-in-combination-with-methotrexate-in-patients-with-rheumatoid-arthritis-with-pr/. Accessed .« Back to 2019 ACR/ARP Annual Meeting
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/comparative-effectiveness-of-tocilizumab-in-combination-with-methotrexate-versus-tumor-necrosis-factor-inhibitors-tnfis-in-combination-with-methotrexate-in-patients-with-rheumatoid-arthritis-with-pr/