Session Information
Date: Saturday, November 7, 2020
Title: RA – Treatments Poster II: Comparative Effectiveness, Biosimilars, Adherence & the Real World
Session Type: Poster Session B
Session Time: 9:00AM-11:00AM
Background/Purpose: AWARE (Comparative and Pragmatic Study of Golimumab IV Versus Infliximab in Rheumatoid Arthritis) is a Phase 4, prospective, noninterventional, observational, multicenter (88 sites), 3-year US study providing real-world assessment of intravenous golimumab (GLM) and infliximab (IFX) in patients with rheumatoid arthritis. Treatment decisions, including prescribed dose and dosing interval, are made by the treating rheumatologists. This analysis of 52-week results from AWARE explored patterns of dose escalation among IFX patients and compared changes in Clinical Disease Activity Index (CDAI), comparing IFX and GLM.
Methods: AWARE enrolled patients initiating GLM or IFX treatment. Prescribed dose was recorded at the time of infusion. IFX patients had dose-escalation when ≥1 normalized prescribed dose exceeded the baseline dose. Normalized prescribed dose = ([prescribed dose] x [scheduled time interval] / [actual time interval]). CDAI was determined at baseline and Months 3, 6, and 12. See table for statistical methods.
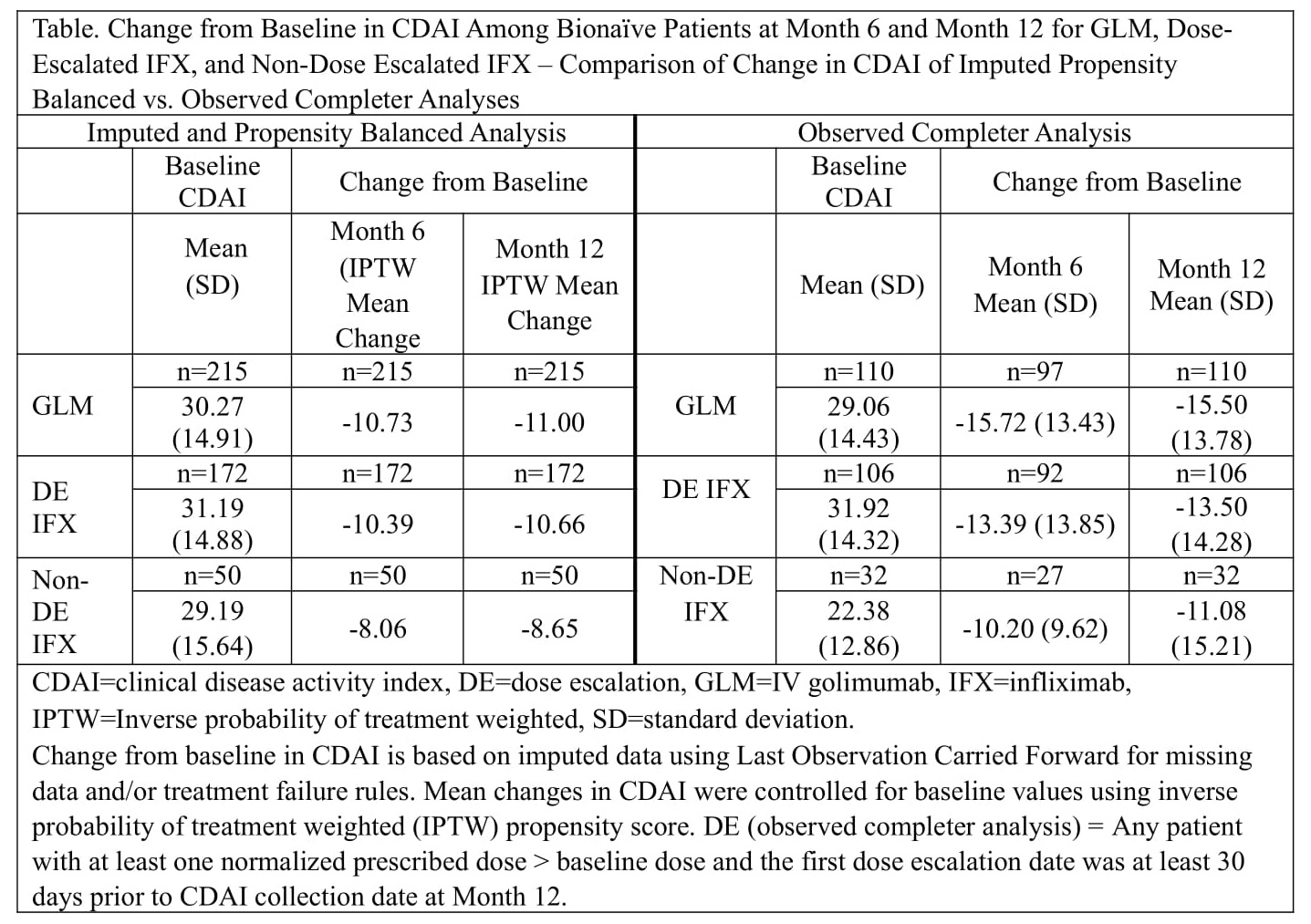
Results: Baseline demographics were generally similar between 685 GLM and 585 IFX patients (including 425 dose-escalated IFX patients), although mean ± SD disease duration was 9.20 ± 9.97 years for GLM and 6.87 ± 9.28 years for dose-escalated IFX patients. Among bionaïve and non-bionaïve GLM patients with an imputed CDAI measure, the mean prescribed dose was 2.0 mg/kg from infusion 1 through 9. The mean normalized prescribed dose among bionaïve dose-escalated IFX patients with CDAI data as 3.25 mg/kg and increased at each infusion through infusion 9 (5.14 mg/kg). The mean normalized prescribed dose among non-bionaïve dose-escalated IFX patients with CDAI data was 3.29 mg/kg and increased at each infusion through infusion 9 (5.48 mg/kg). Based on the definition of normalized dose, 75.9% of all IFX patients were dose-escalated (72.4% of bionaïve IFX and 78.7% of non-bionaïve IFX patients). The percent of bionaïve IFX patients prescribed at least 1 dose ≥8 mg/kg increased with each infusion through infusion 12. At the 10th and 12th infusions, respectively, 15.1% (39/258) and 19.1% (36/188) of IFX patients had received at least 1 IFX dose ≥8 mg/kg. Mean changes from baseline in CDAI for GLM, dose-escalated IFX, and non-dose-escalated IFX patients at Months 6 and 12 are shown in the Table.
Conclusion: The majority of IFX patients were dose-escalated, evident in the increasing mean normalized dose and the proportion of patients prescribed at least 1 IFX dose ≥8 mg/kg. The mean changes from baseline in CDAI scores were similar between GLM patients and dose-escalated IFX patients, although numerically lower for non-dose-escalated IFX patients.
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Schwartzman S, Kafka S, Conaway D, Broadwell A, Black S, Xu S, Langholff W, Curtis J. Comparative Effectiveness of Intravenous Golimumab vs Dose-Escalated Infliximab in a Real World Population of Rheumatoid Arthritis Patients: 52-Week Data from the AWARE Study [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2020; 72 (suppl 10). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/comparative-effectiveness-of-intravenous-golimumab-vs-dose-escalated-infliximab-in-a-real-world-population-of-rheumatoid-arthritis-patients-52-week-data-from-the-aware-study/. Accessed .« Back to ACR Convergence 2020
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/comparative-effectiveness-of-intravenous-golimumab-vs-dose-escalated-infliximab-in-a-real-world-population-of-rheumatoid-arthritis-patients-52-week-data-from-the-aware-study/