Session Information
Date: Sunday, November 7, 2021
Title: Spondyloarthritis Including PsA – Treatment Poster I: Axial Spondyloarthritis (0908–0939)
Session Type: Poster Session B
Session Time: 8:30AM-10:30AM
Background/Purpose: Tumor necrosis factor (TNF) inhibitors are the mainstay treatment for NSAID refractory axial spondyloarthritis (axSpA). However, few data exist on their use during routine clinical practice. The primary aim of this study was to evaluate the effectiveness and treatment survival of different TNF blocking agents within a cohort of patients with axSpA.
Methods: We obtained data from patients who fulfilled the ASAS 2011 classification criteria for axSpA, who were treated with a TNF inhibitor and had clinical follow-up from 2003 to 2019. Effectiveness was evaluated based on the BASDAI50 response at 6 months of therapy. Multivariable linear regression models were used to estimate the predictors of improvement in BASDAI. Treatment persistence was analyzed using Kaplan-Meier survival analysis and Cox proportional hazards model.
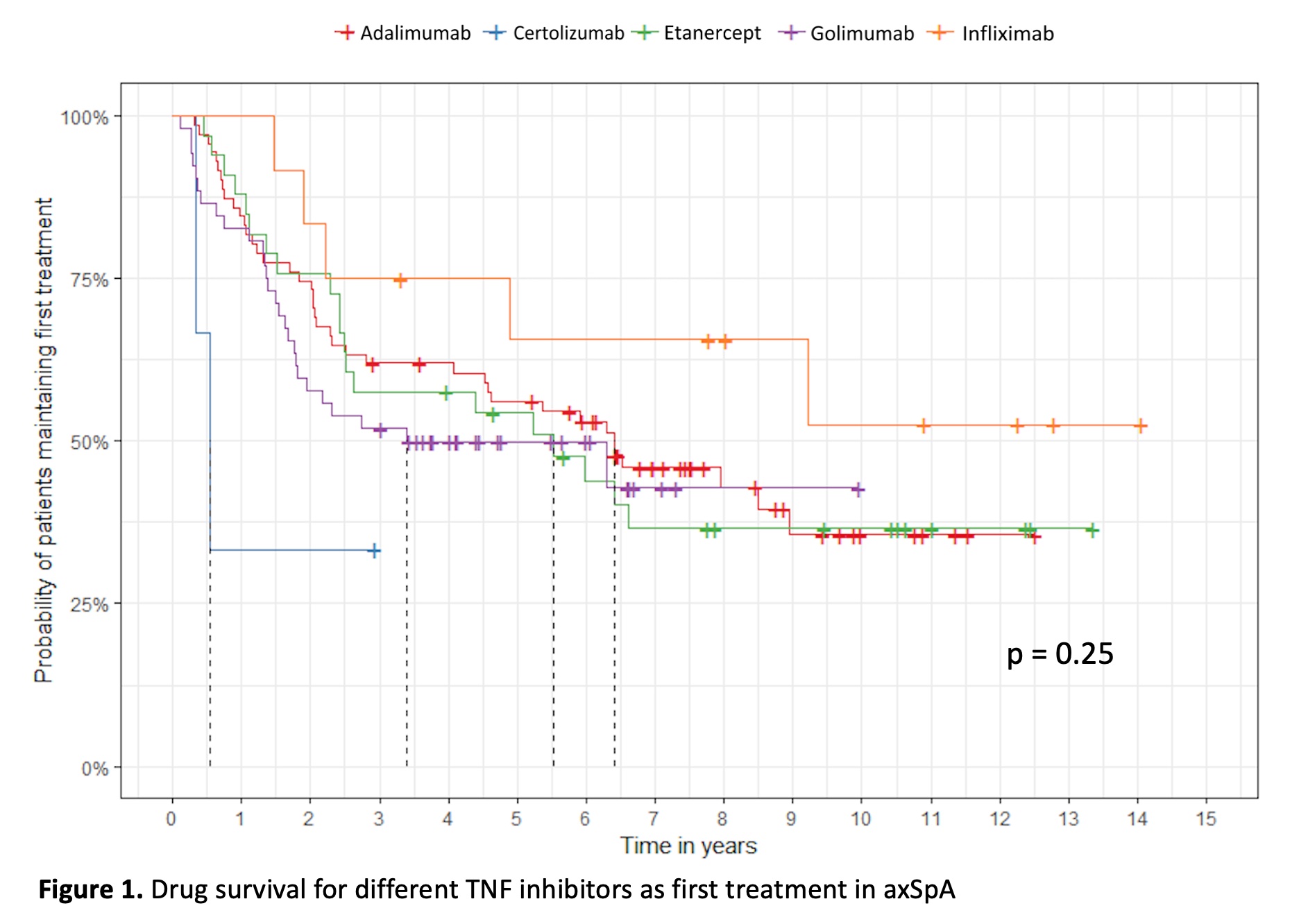
Results: The study comprised 171 patients. The median age was 45 years and 57% were males. Mean baseline BASDAI and BASFI were 6.1 and 5.5 respectively. At 6 months, 50.9% reached a BASDAI50 response and no differences were observed within the different TNF inhibitors (Table 1). In the adjusted analysis, smokers were less likely to achieve a BASDAI50 response compared with nonsmokers HR 0.15 (95% CI 0.059 – 0.375) p < 0.0001. In contrast, patients with a higher baseline BASDAI score were more likely to reach a BASDAI50 at 6 months HR 1.29 (95% CI 1.072 - 1.564) p = 0.007. No other variables demonstrated an association with BASDAI50. The median survival for the first TNF inhibitor therapy was 5.9 years (95% CI 4.5-7.4) without significant difference in treatment survival between TNF inhibitors. There was a trend for a better survival with infliximab, but this was not statistically significant (Figure 1). In the non-radiographic (nr-axSpA) group (n=51), 57% reached a BASDAI50 response, compared to 48% in the ankylosing spondylitis (AS) group (n=119) (p=0.28) during the first TNF inhibitor treatment. The median survival, for the first TNF blocking therapy, was 5.3 years (95% CI 1.58-9.15) in the nr-axSpA group and 6,3 years in the AS group (95% CI 4.58-8.01).
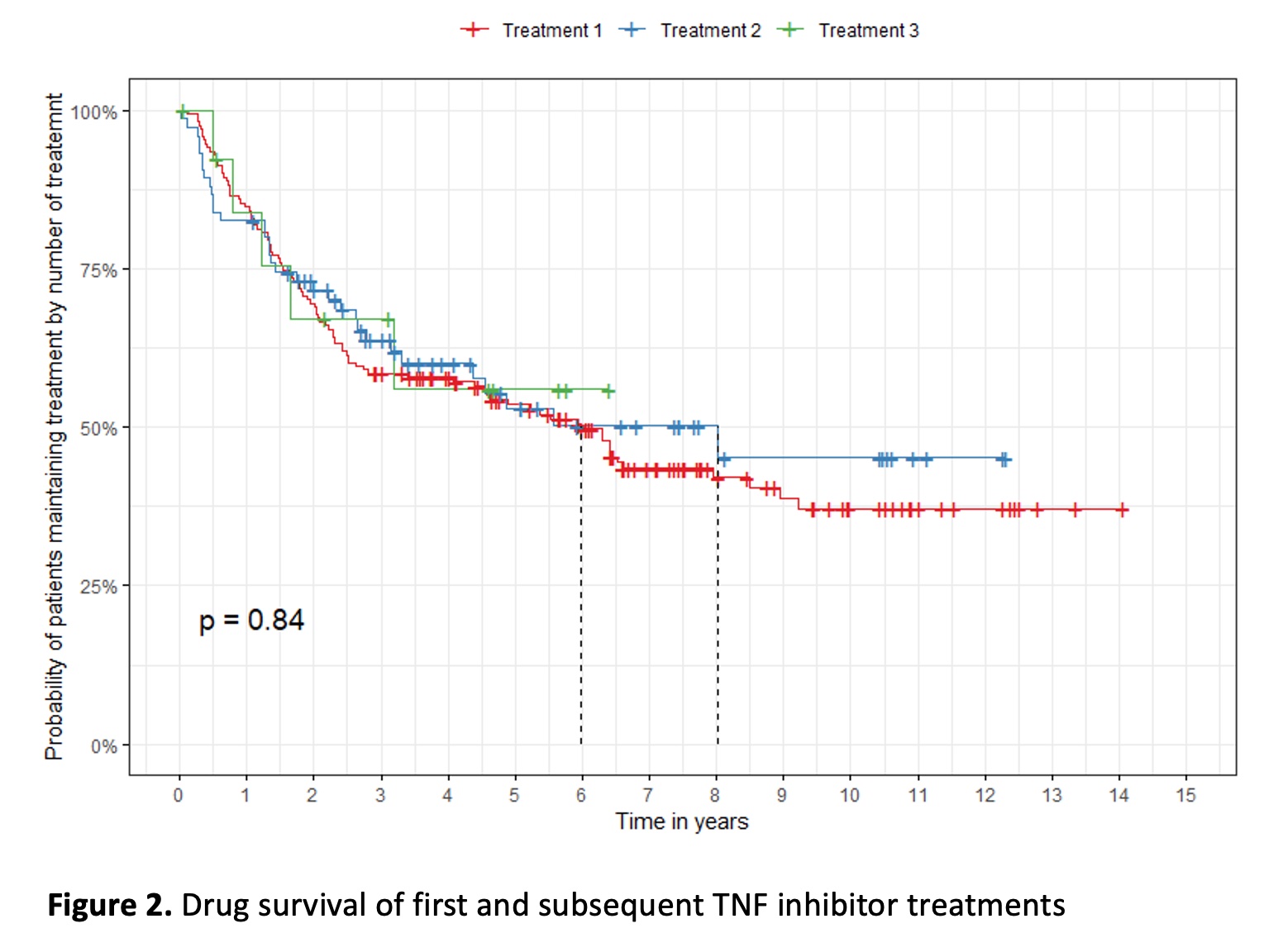
After a first TNF inhibitor failure, the BASDAI50 response for subsequent second and third TNF inhibitor therapies, was 48.7% and 38.5% respectively, with no significant difference in treatment survival (Figure 2). The reasons for discontinuation of the first TNF inhibitor were primary failure 14.7%, secondary failure 61.1%, adverse events 14.7%, and others 9.5%.
Conclusion: Most patients who received TNF blocking agents for axSpA during routine clinical care showed improvement in disease activity. TNF inhibitor effectiveness and drug survival were comparable to published data. There were no significant differences in effectiveness or treatment survival among the different TNF inhibitors. Effectiveness and drug survival was not different between nr-axSpA and AS. Failure to a first TNF inhibitor did not diminish effectiveness or drug survival of subsequent TNF inhibitor treatments. The main reason for treatment discontinuation was secondary failure.
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Marrugo J, Bonin M, Boire G, Bessette L, Masetto A. Comparative Effectiveness and Treatment Survival of Different TNF Inhibitors for Axial Spondyloarthritis in Real-World Clinical Practice [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2021; 73 (suppl 9). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/comparative-effectiveness-and-treatment-survival-of-different-tnf-inhibitors-for-axial-spondyloarthritis-in-real-world-clinical-practice/. Accessed .« Back to ACR Convergence 2021
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/comparative-effectiveness-and-treatment-survival-of-different-tnf-inhibitors-for-axial-spondyloarthritis-in-real-world-clinical-practice/