Session Information
Date: Sunday, October 21, 2018
Title: Rheumatoid Arthritis – Treatments Poster I: Strategy and Epidemiology
Session Type: ACR Poster Session A
Session Time: 9:00AM-11:00AM
Background/Purpose: Tofacitinib is an oral Janus kinase inhibitor for the treatment of RA, in combination with MTX or other non‑biologic (nb)DMARDs, or as monotherapy. Two pooled open-label long-term extension studies previously showed that patients (pts) discontinuing concomitant MTX or glucocorticoids (GC) could maintain favorable treatment response.1 This analysis of real world data assessed characteristics of pts who discontinued MTX after tofacitinib treatment.
Methods: This retrospective cohort study included pts aged ≥18 years in the Truven MarketScan™ US Commercial and Medicare Supplemental claims database with ≥2 tofacitinib claims (first = index) with <60-day gap between 1/1/2014–1/31/2017, ≥2 oral MTX claims (one ≤90 days post-index) with <60-day gap, and an RA diagnosis on or within 12 months pre‑index. Pts were continuously enrolled for ≥12 months pre-/post-index with no prior claim for tofacitinib 12 months pre‑index. Pts were assigned to mutually exclusive cohorts for analysis by 12‑month post-index MTX persistence: “persistent” (MTX‑P; ≤60‑day gap), “discontinued” (MTX-D; >60-day gap) and “interrupted” (MTX‑I; >60-day gap with ≥1 subsequent MTX claim 12 months post-index). Outcomes at 12 months post‑index were tofacitinib persistence (<60-day gap), adherence (proportion of days covered), effectiveness (composite measure; defined in Table)2,3 and RA-related costs. Two sample tests (t-test, chi-squared) were applied separately to MTX-P vs combined MTX-D and MTX-I, and pair-wise among the 3 cohorts, with no adjustment for multiple comparisons or imbalances in baseline covariates.
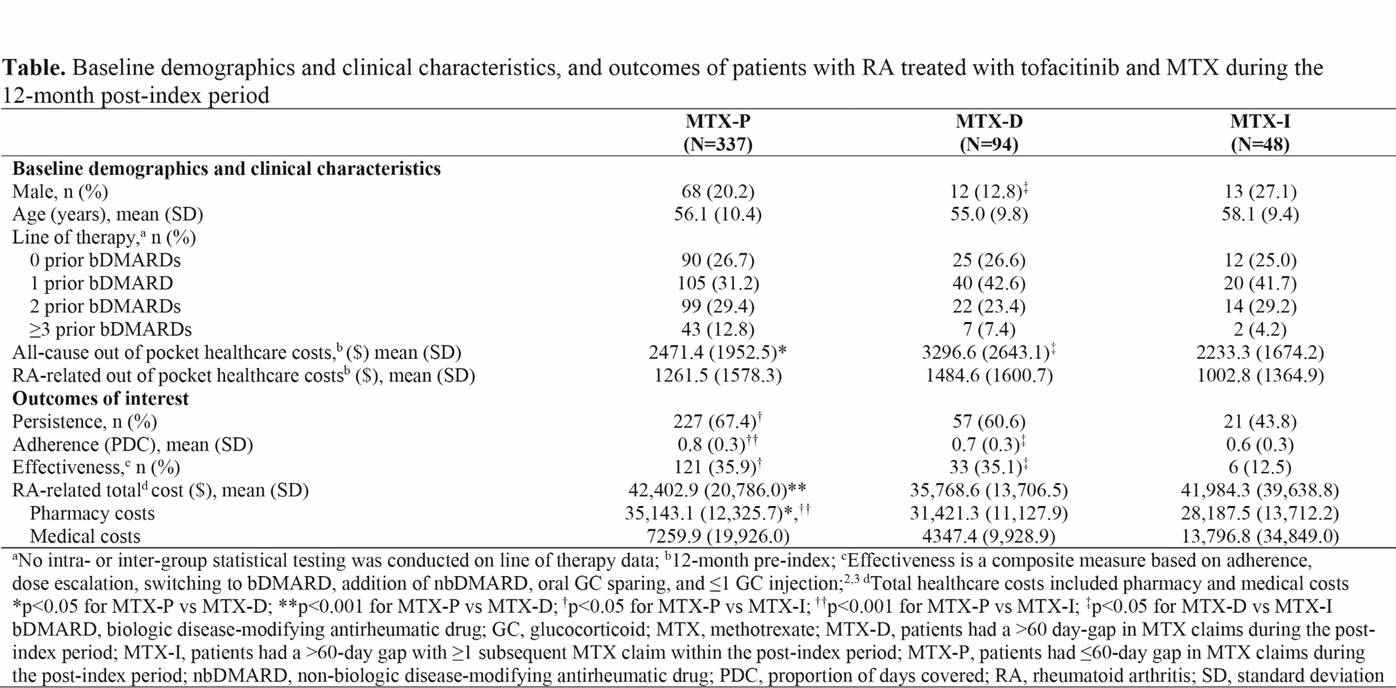
Results: 479 pts met inclusion criteria (MTX-P: 337 [70%]; MTX-D: 94 [20%]; MTX-I: 48 [10%] in the 12-month post-index period). Demographic and baseline clinical characteristics were similar among cohorts, aside from differences in the proportion of males and all-cause out-of-pocket costs (p<0.05; Table).
Tofacitinib persistence, adherence and effectiveness over 12 months were similar between MTX-D and MTX-P. RA-related total and pharmacy costs were lower in MTX-D vs MTX-P (p<0.001 and p<0.05, respectively).
Conclusion: This analysis of US-based claims data showed that pts who initiate tofacitinib with oral MTX can discontinue MTX with similar persistence, adherence and effectiveness, and lower RA-related total/pharmacy costs 12‑months post-index vs MTX‑persistent pts. Further analysis with a larger sample size is needed to confirm the robustness of these findings; further investigation is also needed regarding the MTX-I group as interpretation of this group is limited by the small sample size. Findings are limited by the use of claims data which may reflect MTX discontinuation/interruption related to pt choice without physician knowledge.
References:
1. Fleischmann R et al. Rheumatol Ther 2018; 5: 203-14.
2. Curtis JR et al. Arthritis Res Ther 2011; 13: R155.
3. Oladapo A et al. J Manag Care Spec Pharm 2014; 20: 657-67.
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Cohen S, Haraoui B, Curtis JR, Smith T, Woolcott J, Gruben D, Murray CW, Iikuni N, Koenig A, Harnett J. Comparative Analysis of Outcomes Among Patients with Rheumatoid Arthritis Initiating Tofacitinib in Combination with Oral MTX Who Discontinue, Interrupt, or Persist with MTX [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2018; 70 (suppl 9). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/comparative-analysis-of-outcomes-among-patients-with-rheumatoid-arthritis-initiating-tofacitinib-in-combination-with-oral-mtx-who-discontinue-interrupt-or-persist-with-mtx/. Accessed .« Back to 2018 ACR/ARHP Annual Meeting
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/comparative-analysis-of-outcomes-among-patients-with-rheumatoid-arthritis-initiating-tofacitinib-in-combination-with-oral-mtx-who-discontinue-interrupt-or-persist-with-mtx/