Session Information
Session Type: Poster Session (Tuesday)
Session Time: 9:00AM-11:00AM
Background/Purpose: Patients with rheumatoid arthritis (RA) suffer a high susceptibility to infection, and many inflammatory cytokines are prognostic in RA, but currently the role of cytokines in identifying infection individuals is rarely studied. We assessed the performance of serum inflammatory cytokines to discriminate bacteria infection from non-infections in RA, and setted up a bioscore system to evaluate the significance of these biomarkers in identifying bacterial infection.
Methods: A total of 168 RA patients were enrolled and divided into the bacterial infection (INFE) group and non-INFE group from January 2018 through January 2019, and were quantitatively measured the expression level of cytokines by flow cytometry. The discriminating value of C-reactive protein (CRP), erythrocyte sedimentation rate (ESR), white blood cell count (WBC), lymphocyte subsets, complement C3 and complement C4 also were assessed. Bacterial infection was confirmed through bacterial culture, image study, response to antibiotic therapy and typical clinical symptom. The diagnostic value for bacterial infection was evaluated by the areas under the receiver operating characteristic (ROC) curves (AUC) and a novel bioscore system combining multiple biomarkers.
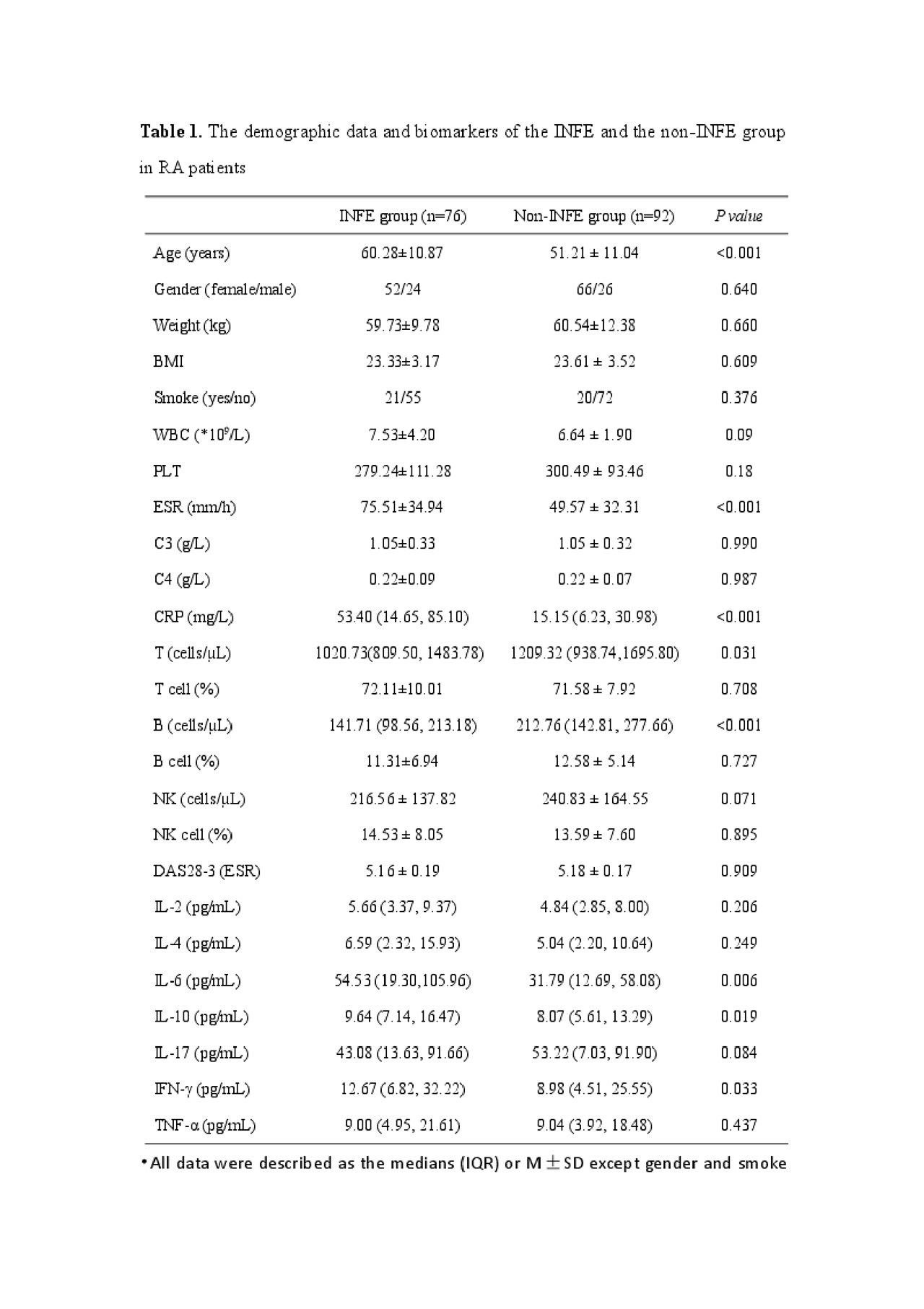
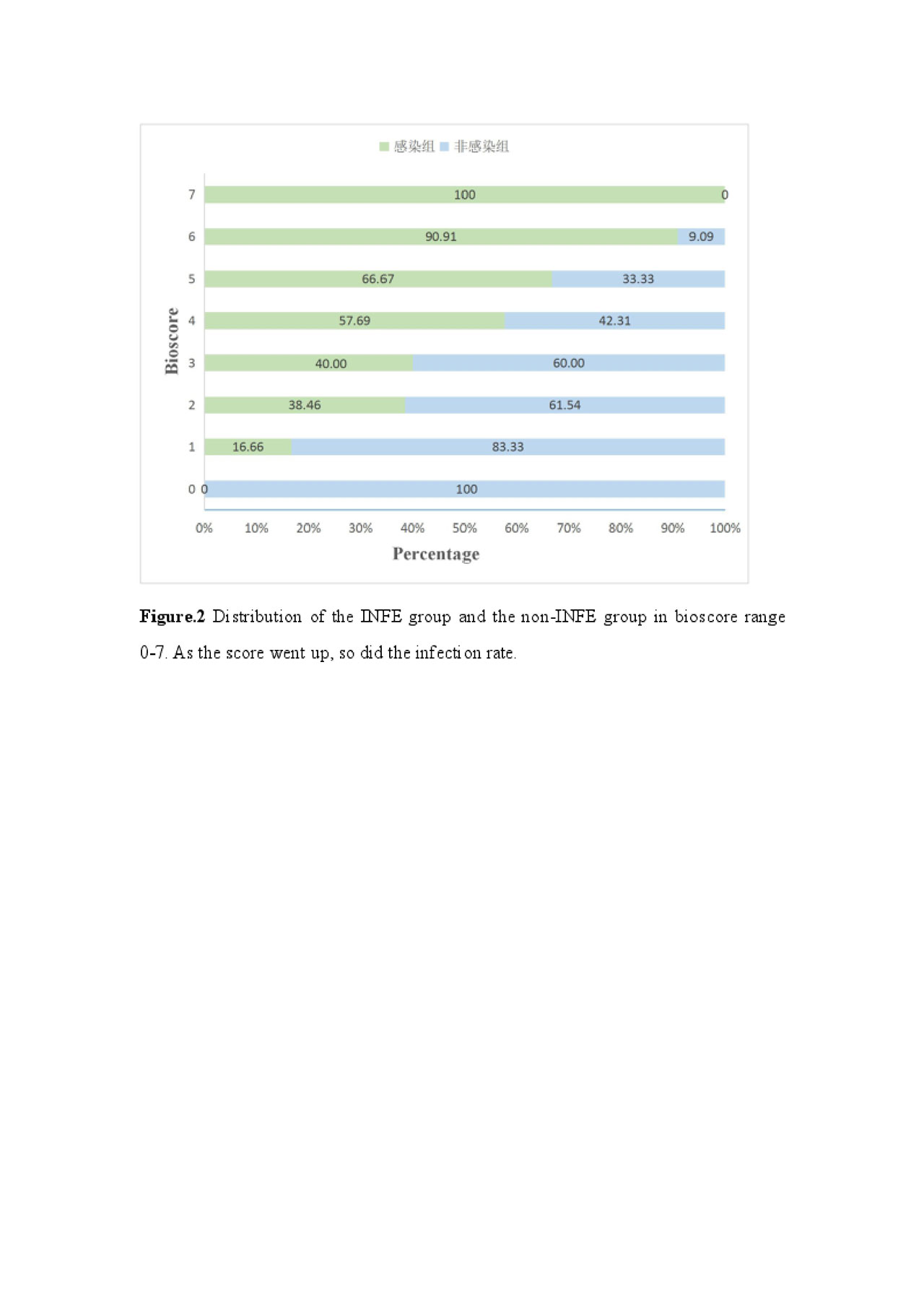
Results: In INFE group, the levels of IL-6 (p=0.006), IL-10 (p=0.019), IFN-γ (p=0.033), CRP (p< 0.001), ESR (p< 0.001), B cell (p< 0.001) and T cell (p=0.031) were higher than in non-INFE group. The IL-2, IL-4 and TNF-α also increased in INFE group, but no statistical significance (IL-2, p=0.206; IL-4, p=0.249; TNF-α, p=0.437), IL-17 decreased (p=0.084). However, it was remarkable that the AUC yielded 0.820 (95%CI: 0.753, 0.876), with sensitivity of 64.38% and specificity of 88.03%, when combined with IL-6, IL-10, IFN-γ, ESR, CRP, B and T cell. The above seven biomarkers were included in the bioscore system, the whole of patients with bioscore of 0 (n=18) were in the non-INFE group. When the score was 7, all patients (n=6) were in the INFE group.
Conclusion: Serum cytokines are markers for detection of bacterial infection in RA. The combination of ESR, CRP, IL-6, IL-10, IFN-γ, B and T cell may be a valuable diagnostic score to early diagnose infection in RA, and provide certain reference basis for clinical treatment and prognosis evaluation.
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Qin Y, Zhao X, Luo J. Combined Detection of Cytokines and Biomarkers Improve the Diagnostic Performance of Bacteria Infection in Rheumatoid Arthritis [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2019; 71 (suppl 10). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/combined-detection-of-cytokines-and-biomarkers-improve-the-diagnostic-performance-of-bacteria-infection-in-rheumatoid-arthritis/. Accessed .« Back to 2019 ACR/ARP Annual Meeting
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/combined-detection-of-cytokines-and-biomarkers-improve-the-diagnostic-performance-of-bacteria-infection-in-rheumatoid-arthritis/