Session Information
Date: Monday, November 8, 2021
Title: Spondyloarthritis Including PsA – Treatment Poster II: Psoriatic Arthritis I (1329–1363)
Session Type: Poster Session C
Session Time: 8:30AM-10:30AM
Background/Purpose: Psoriatic arthritis (PsA) is characterized by inflammation of synovial membranes and entheseal sites leading to pain, structural damage, impairment of physical function and quality of life.1 2 ULTIMATE (NCT02662985) was the first large, randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled phase IIIb study in PsA, using the Global OMERACT EULAR Synovitis Score (GLOESS), an ultrasound score at patient level, to demonstrate that secukinumab (SEC) rapidly and significantly decreased synovitis.2 However, little is known about the heterogeneity of PsA related to the distribution of ultrasound detected synovitis in PsA and its impact on treatment response. We report exploratory analyses to identify clusters of patients (pts) based on baseline ultrasound distribution and severity of synovitis [power doppler and greyscale alone and combined power doppler ultrasound (PDUS)] and their longitudinal treatment trajectory with SEC versus Placebo over 12 weeks.
Methods: ULTIMATE was a 52-week study with a 12-week double-blind, placebo-controlled period followed by 12-week open-label (OL) treatment and 6-month OL extension period. Factor analysis and clustering methods were applied post hoc to identify groups of PsA pts with similar baseline composite PDUS-detected synovitis characteristics. Aggregation of baseline demographics, clinical and ultrasound characteristics were explored through cluster analysis using descriptive statistics. Nonlinear mixed models for change in GLOESS (primary endpoint of the study) from baseline to Week 12 across clusters were used to explore the treatment difference between SEC and placebo up to Week 12.
Results: The baseline demographics, clinical and ultrasound characteristics have been reported previously.3 One hundred and sixty-six pts could be categorized in 3 different clusters (N1=63, N2=49 and N3=54) at baseline. The heatmap in Figure 1 shows the differences in the distribution of PDUS-detected synovitis at the joint level across the 3 clusters. The baseline ultrasound characteristics showed higher disease activity, more severe synovitis and enthesitis in clusters 3 and 1 vs. cluster 2 (Table). Cluster 3 showed a trend toward increased clinical activity (TJC, SJC, pain and PGA VAS). The longitudinal trajectories of the 3 clusters up to Week 12 showed a treatment difference in favor of SEC, compared with placebo, in clusters 3 and 1 but not in cluster 2 (Figure 2).
Conclusion: The cluster analysis in the ULTIMATE trial highlights the heterogeneity of PsA. Interestingly, only clusters 1 and 3, with evidence of higher amounts of PDUS-detected inflammation had disease activity that responded to secukinumab treatment. Ultrasound may help in identifying different levels of inflammation of synovitis and enthesitis at tissue level in patients with similar clinical phenotype and could support a more rigorous selection of patients with active disease in future clinical trials.
References:
1. Coates LC, et al. Arthritis Res Ther 2019;21(1):266.
2. D’Agostino M-A, et al. Arthritis Rheumatol 2020;72 (suppl 10)
3. D’Agostino M-A, et al. Ann Rheum Dis 2021;80 (suppl 1)
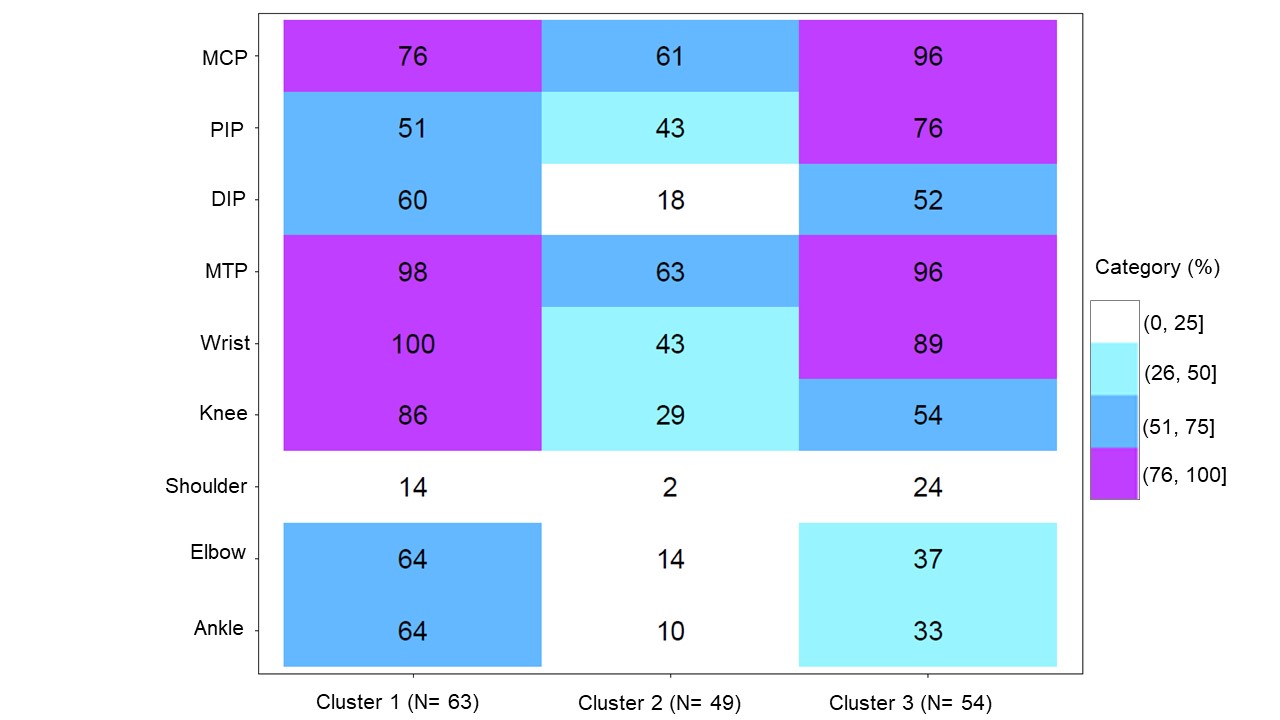 Figure 1: Heat map reporting the distribution of ultrasound detected synovitis for each cluster. Ultrasound detected synovitis was defined as PDUS ≥ 1 DIP, distal interphalangeal; MCP, metacarpophalangeal; MTP, metatarsophalangeal; PIP, proximal interphalangeal
Figure 1: Heat map reporting the distribution of ultrasound detected synovitis for each cluster. Ultrasound detected synovitis was defined as PDUS ≥ 1 DIP, distal interphalangeal; MCP, metacarpophalangeal; MTP, metatarsophalangeal; PIP, proximal interphalangeal
 Figure 2. Non linear mixed model for change in GLOESS from baseline to week 12 by US cluster and treatment. GLOESS, global EULAR-OMERACT synovitis score; US, ultrasound
Figure 2. Non linear mixed model for change in GLOESS from baseline to week 12 by US cluster and treatment. GLOESS, global EULAR-OMERACT synovitis score; US, ultrasound
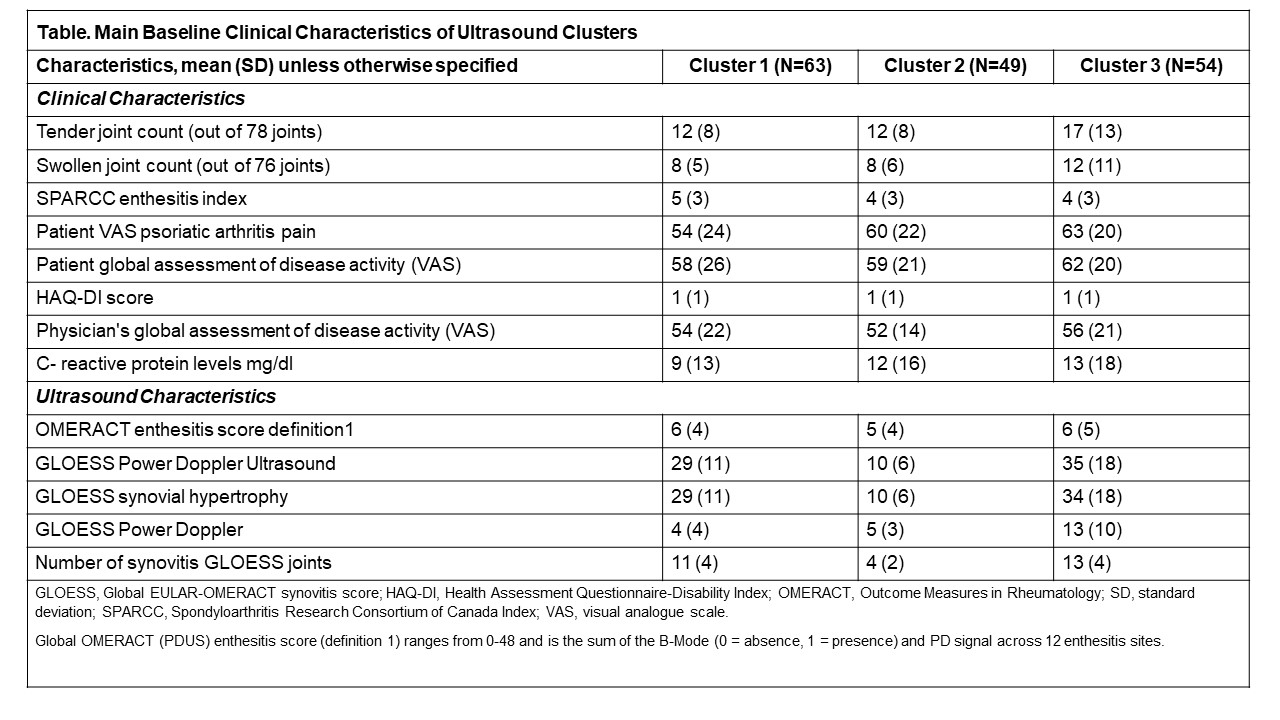 Table. Main Baseline Clinical Characteristics of Ultrasound Clusters
Table. Main Baseline Clinical Characteristics of Ultrasound Clusters
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
D'Agostino M, Schett G, Gaillez C, Conaghan P, Naredo E, Carron P, Burgos-Vargas R, Mandl P, Rosa J, Boers M, Goyanka P, Bao W, Demanse D. Clusters of Psoriatic Arthritis Patients at Baseline Based on Different Ultrasound Detected Synovitis: Exploratory Analysis from a Phase III Study [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2021; 73 (suppl 9). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/clusters-of-psoriatic-arthritis-patients-at-baseline-based-on-different-ultrasound-detected-synovitis-exploratory-analysis-from-a-phase-iii-study/. Accessed .« Back to ACR Convergence 2021
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/clusters-of-psoriatic-arthritis-patients-at-baseline-based-on-different-ultrasound-detected-synovitis-exploratory-analysis-from-a-phase-iii-study/
