Session Information
Date: Sunday, November 17, 2024
Title: Abstracts: Innate Immunity: Molecular Insights Into Immune Dysregulation
Session Type: Abstract Session
Session Time: 3:00PM-4:30PM
Background/Purpose: Polymyalgia Rheumatica (PMR) and Giant Cell Arteritis (GCA) are autoimmune/autoinflammatory disorders affecting patients over 50 years and are characterized by an acute inflammatory response. The majority of patients respond well to steroids even after a few hours of treatment. Changes in cell subpopulations, plasma cytokines and small effector molecules at the very early stages of glucocorticoid (GC) initiation, have never been studied. In this report, we aim to decipher the immune landscape in 4 distinct time points during disease course [0h (T1), 48h (T2), 96h (T3) and 24 weeks (T4)] after GC treatment in GCA and PMR patients.
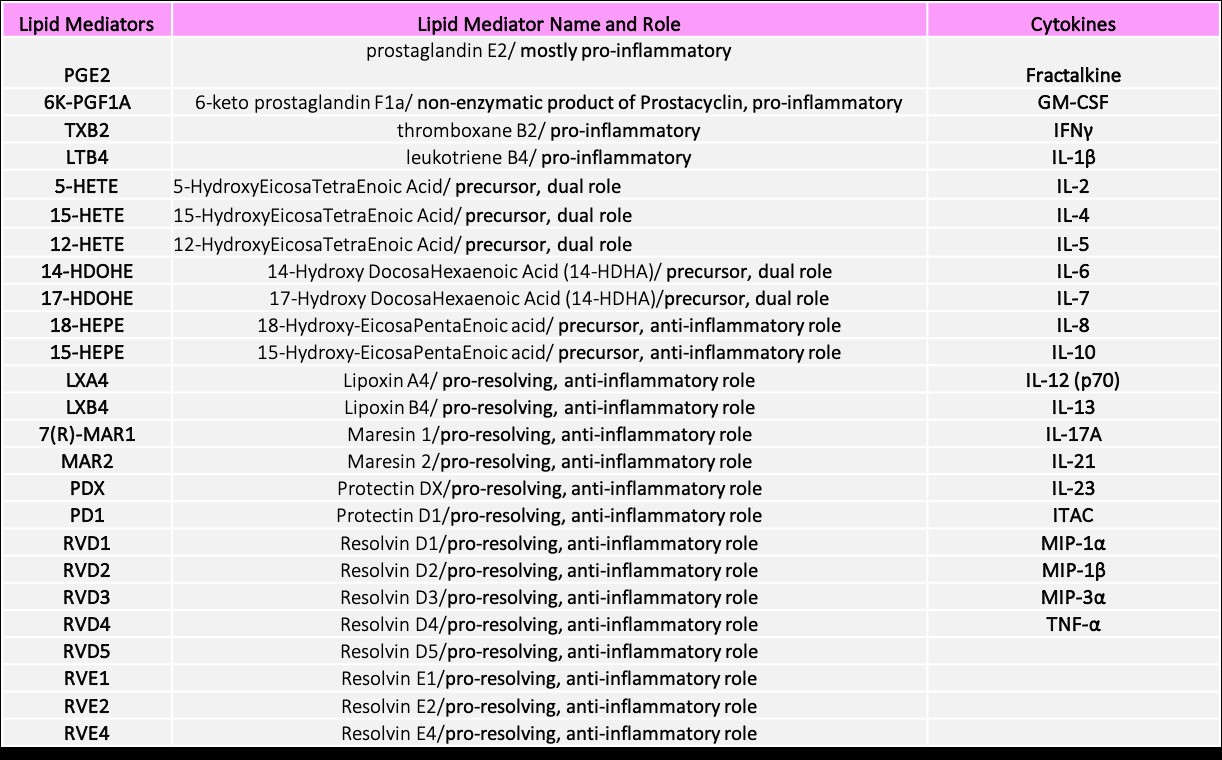
Methods: Serum, plasma and peripheral blood mononuclear cells (PBMCs) were collected prospectively from 8 GCA and 6 PMR newly diagnosed patients along with their demographic, clinical and serological data. Sixteen healthy individuals served as controls (HC). Deep immunophenotyping [Mass cytometry, (CyTOF)] was performed in PBMCs at T1-T3. Serum levels of 21 cytokines (Table 1) were measured at T1 and T3 with Luminex technology. Lipid mediators (LMs) levels including the most well characterized pro-inflammatory and pro-resolving LMs were measured at T1,T3 and T4 with the LC-MS/MS method (Table 1).
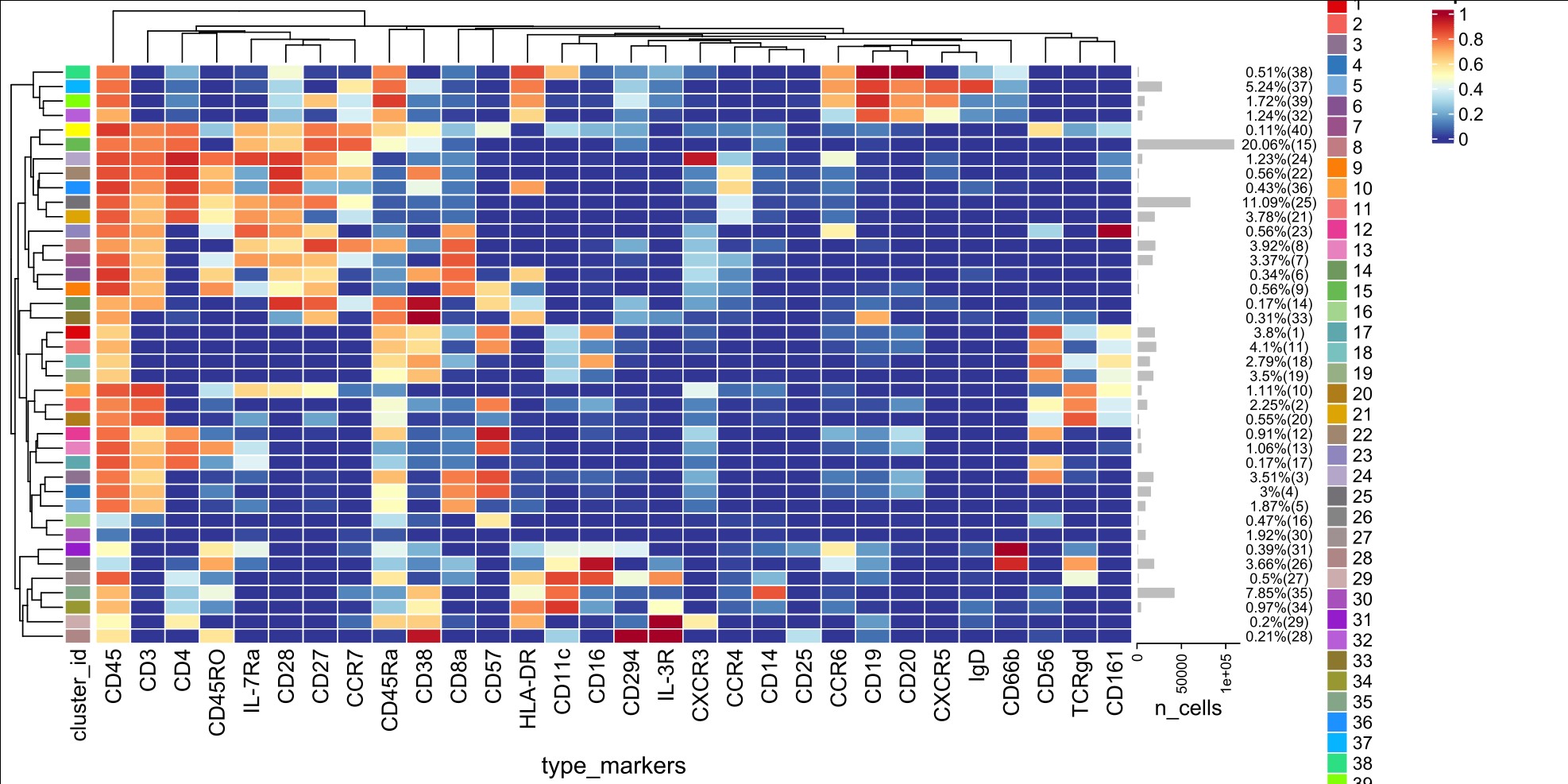
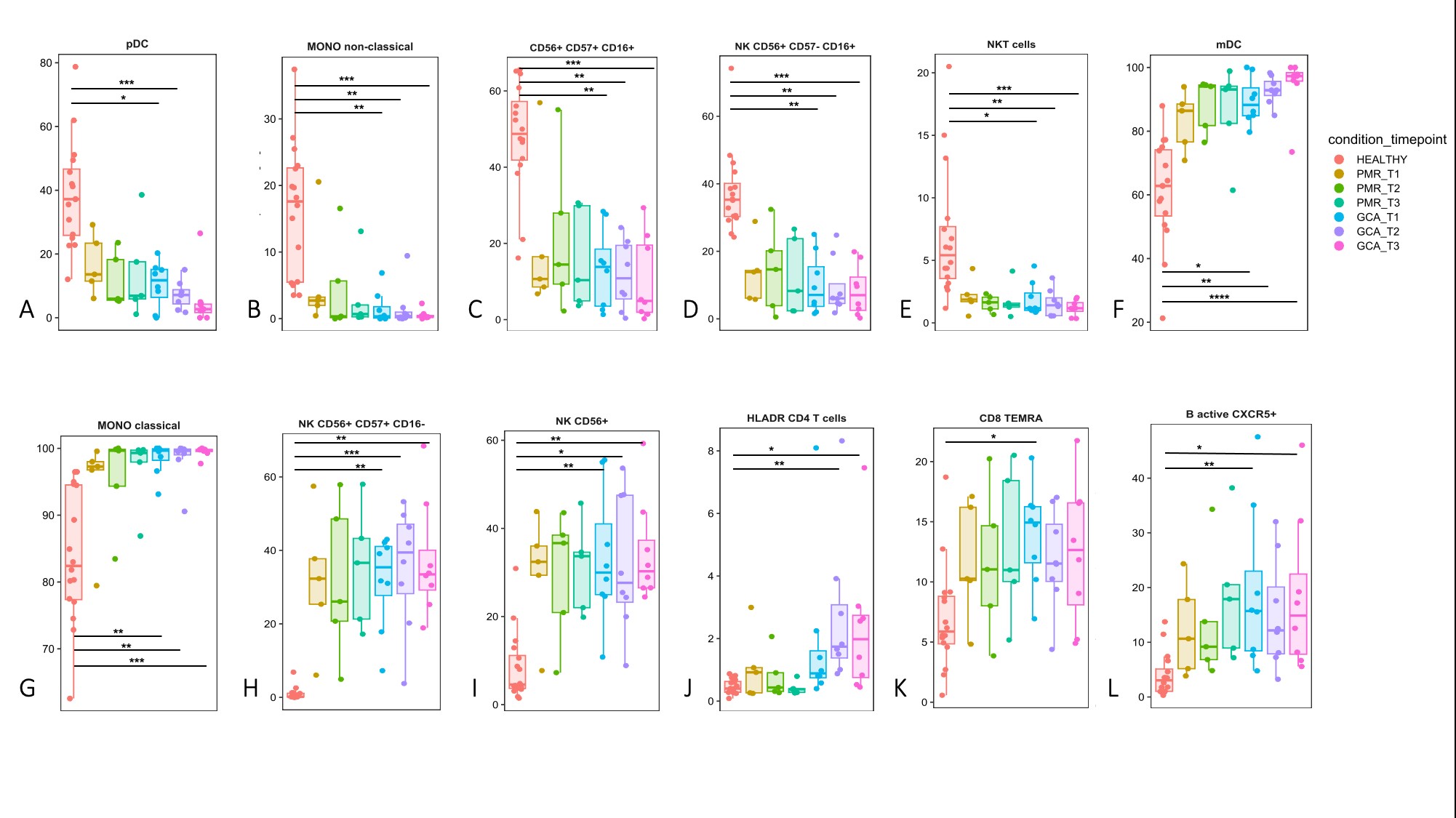
Results: Unsupervised clustering of CyTOF results identified 40 clusters corresponding to different immune cell subsets/phenotypes (Fig.1). For the main individual immune cell types identified [CD4, CD8, TCRγδ cells, NK cells, B cells, Monocytes and Dendritic Cells (DCs)] there was no significant intra and inter group alterations in cell numbers among HC, GCA and PMR at the 3 time points tested (0, 48, 96h). No changes were also observed in serum cytokine levels between GCA and PMR patients at the same time points. However, in depth cell cluster analysis disclosed significant changes in certain cell phenotypes between GCA patients and HC (Fig.2). Indeed, a significant decrease in cell frequencies of pDCs (Fig.2A), non-classical monocytes (Fig.2B), NK CD56+CD57+CD16+ cells (Fig.2C), NK CD56+CD57-CD16+ cells (Fig.2D), and NKT cells (Fig.2E), with a concomitant increase in mDCs (Fig.2F), classical monocytes (Fig.2G), NK CD56+CD57+CD16- cells (Fig.2H), NK CD56+ cells (Fig.2I), HLADR+ CD4 T cells (Fig.2J), and CD8+ TEMRA cells (Fig.2K), were observed. Lipidomic analysis revealed that both PMR and GCA at T1 had a low ratio of pro-inflammatory as opposed to pro-resolving LMs. In T3, GCA patients exhibited a two-fold increase in the prevalence of pro-inflammatory LMs. In T4, the ratio of pro-inflammatory/resolving LMs in GCA patients remained (x1.5) increased compared to PMR ratio.
Conclusion: Rapid clinical improvement of GCA and PMR patients, following steroid treatment is associated with cellular alterations, involving mainly DCs, non-classical macrophages and NK cells, that are not associated with changes in plasma cytokine levels. Pro-resolving lipid mediators can differentiate GCA and PMR patients, remaining increased in GCA patients after 24 weeks of GC treatment, suggesting a possible underlying residual inflammation or active tissue remodeling. Further studies with a larger number of patients are required to validate these findings and define, new next generation biomarkers.
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Palamidas D, Papadaki M, Paschalidis N, Pavlos E, chatzis L, Argyropoulou O, Palla P, Galani I, Goules A, Andreakos E, Tzioufas A. Cluster Analysis of Peripheral Blood Mononuclear Cell Subpopulations Using Deep Immunophenotyping, Multiplex Serum Cytokines and Small Lipid Mediators at the Very Early Stages of Steroid Treatment in Polymyalgia Rheumatica and Giant Cell Arteritis [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2024; 76 (suppl 9). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/cluster-analysis-of-peripheral-blood-mononuclear-cell-subpopulations-using-deep-immunophenotyping-multiplex-serum-cytokines-and-small-lipid-mediators-at-the-very-early-stages-of-steroid-treatment-in/. Accessed .« Back to ACR Convergence 2024
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/cluster-analysis-of-peripheral-blood-mononuclear-cell-subpopulations-using-deep-immunophenotyping-multiplex-serum-cytokines-and-small-lipid-mediators-at-the-very-early-stages-of-steroid-treatment-in/