Session Information
Date: Sunday, November 5, 2017
Title: Systemic Sclerosis, Fibrosing Syndromes and Raynaud's – Clinical Aspects and Therapeutics Poster I
Session Type: ACR Poster Session A
Session Time: 9:00AM-11:00AM
Background/Purpose: The Prospective Registry of Early Systemic Sclerosis (PRESS), an 11 center US cohort study of early diffuse cutaneous systemic sclerosis (dcSSc) patients, was designed to study dcSSc pathogenesis and patient response to treatments. Modified Rodnan skin score (mRSS), used to quantify skin severity, correlates with mortality. The study purpose was to identify a serum signature associated with dcSSc and correlated with mRSS.
Methods: Baseline serum samples and clinical data were collected from PRESS subjects at enrollment and healthy matched controls. Subjects met SSc ACR criteria, had early dcSSc (defined as < 2 years duration since first non-Raynaud symptom attributed to SSc; swollen hands or sclerodactyly; PLUS 1 or more of the following: present anti-topoisomerase I or anti-RNA polymerase III serum autoantibodies; proximal skin involvement; tendon friction rubs). Samples were subjected to a custom Multi-Analyte Profiles (MAP) that uses multiplexed ELISA for serum protein quantification. Analytes with >40% missing values were excluded. The fold-change in protein expression between early dcSSc versus control samples was calculated. A t-test was used to test for statistical significance with correction for multiple hypothesis testing using the Benjamini-Hochberg method. mRSS was fitted to a linear model to assess for correlation with protein expression.
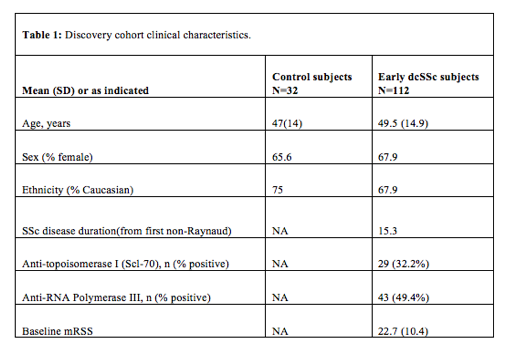
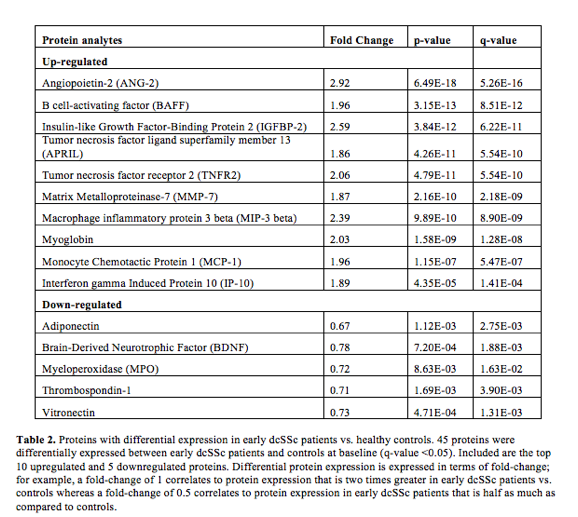
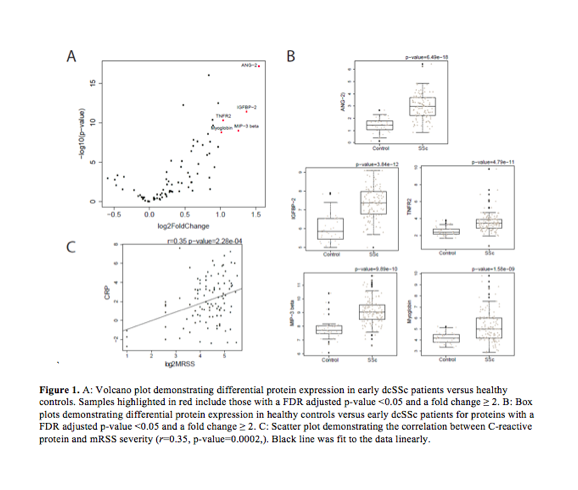
Results: Characteristics of dcSSc patients and controls were summarized (Table 1). Of 109 analytes, 28 analytes with missing values were excluded, leaving 81 analytes for analysis. 45 proteins were differentially expressed between early dcSSc patients and controls at baseline (q-value <0.05, Table 2). ANG-2, IGFBP-2, MIP-3 beta, TNFR2 and myoglobin had >2 fold-change in dcSSc patients vs. controls (Fig 1). 106 out of 112 (95%) dcSSc patients had baseline mRSS values. C-reactive protein correlated with mRSS (Fig 1).
Conclusion: We identified 45 proteins with variable expression between early dcSSc patients and healthy controls. Further, we identified that C-reactive protein expression correlates with mRSS severity, which has also been shown to be associated with lung disease progression. Future work includes developing a mRSS-predictive model by studying changes in protein expression in patients with longitudinal mRSS.
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Cai G, Flood KS, Assassi S, Bernstein EJ, Domsic RT, Gordon JK, Hant F, Schiopu E, Steen VD, Frech TM, Khanna D, Shah AA, Shanmugam VK, Castelino FV, Hinchcliff M. Clinically Relevant Serum Proteins in Patients with Early Diffuse Cutaneous Systemic Sclerosis [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2017; 69 (suppl 10). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/clinically-relevant-serum-proteins-in-patients-with-early-diffuse-cutaneous-systemic-sclerosis/. Accessed .« Back to 2017 ACR/ARHP Annual Meeting
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/clinically-relevant-serum-proteins-in-patients-with-early-diffuse-cutaneous-systemic-sclerosis/