Session Information
Date: Monday, October 22, 2018
Title: Rheumatoid Arthritis – Diagnosis, Manifestations, and Outcomes Poster II: Diagnosis and Prognosis
Session Type: ACR Poster Session B
Session Time: 9:00AM-11:00AM
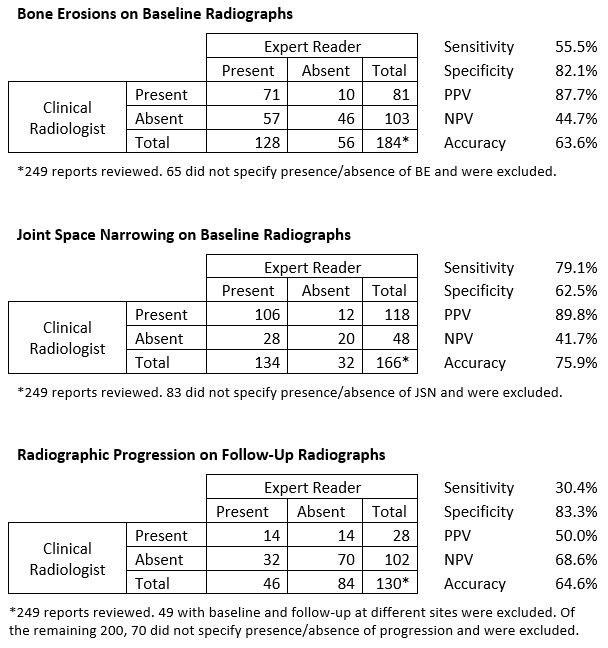
Background/Purpose: Rheumatologists rely on hand radiograph findings including bone erosions (BE) and joint space narrowing (JSN) to make treatment decisions for patients with rheumatoid arthritis (RA). Radiographic progression (RP) on serial hand radiographs may prompt changes in therapy. We assessed whether radiology reports reliably identify BE, JSN, and RP in a cohort of Veterans Affairs (VA) patients initiating tumor necrosis factor inhibitor (TNFi) therapy.
Methods: Subjects were US veterans with RA initiating TNFi therapy who had two sets of bilateral hand radiographs: baseline obtained between 6 months prior to and 1 month after TNFi initiation and follow-up obtained 10-18 months after TNFi initiation. An expert reader, blinded to radiograph sequence, quantified BE, JSN, and RP at baseline and follow-up by modified Sharp Score (mSS). An independent chart abstractor reviewed the corresponding radiology reports in the electronic medical record. BE and JSN were coded “present” or “absent” if the report specifically stated they were present or absent and were coded “not specified” if the report did not comment on their presence. RP was coded “present” or “absent” if the follow-up report specifically stated it was present or absent and was coded “not compared” if it did not include comparison to baseline. BE, JSN, and RP from radiology reports were then compared to BE, JSN, and RP as quantified by the expert reader. Sensitivity, specificity, positive predictive value (PPV), negative predictive value (NPV), and accuracy (true positive + true negative ÷ total cases) were calculated for baseline reports that reported BE and JSN, and for follow-up reports that reported RP.
Results: 249 patients from 84 VA sites were included. Baseline demographics: age 58 ±11 years, 81% male, 68% positive rheumatoid factor, 65% positive anti-cyclic citrullinated peptide antibody. Baseline mSS: 19.5±33.2 (median 8, range 0-214). Mean change in mSS: 0.5±4.6 (median 0, range -19-45). BE or JSN not reported in 65 (26%) and 83 (33%) baseline cases respectively. In 70 (35%) of cases with comparison radiographs at the same site, the follow-up radiology report did not include comparison of baseline and follow-up radiographs.
Conclusion: Many clinical radiology reports may be of limited value and reliability for assessing RP in patients with RA during TNFi therapy because reports often fail to include important data, do not include comparisons, and disagree with findings reported by an expert reader. Reports of radiologist assessments of BE and JSN are also of limited utility—while a report positive for BE or JSN appears to be accurate, a negative report does not reliably exclude these findings. Rheumatologists should be aware of the limitations of radiology reports when using these assessments to make changes in RA management. Standardization of radiologist reporting and terminology may be of clinical utility.
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Lammert KR, Erickson AR, Sauer BC, Cannon GW. Clinical Radiology Reports Are Unreliable for Assessment of Radiographic Structural Progression in US Veterans with Rheumatoid Arthritis Initiating Tumor Necrosis Factor Inhibitor Therapy [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2018; 70 (suppl 9). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/clinical-radiology-reports-are-unreliable-for-assessment-of-radiographic-structural-progression-in-us-veterans-with-rheumatoid-arthritis-initiating-tumor-necrosis-factor-inhibitor-therapy/. Accessed .« Back to 2018 ACR/ARHP Annual Meeting
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/clinical-radiology-reports-are-unreliable-for-assessment-of-radiographic-structural-progression-in-us-veterans-with-rheumatoid-arthritis-initiating-tumor-necrosis-factor-inhibitor-therapy/