Session Information
Date: Tuesday, November 9, 2021
Title: RA – Treatments Poster III: RA Treatments & Their Safety (1674–1710)
Session Type: Poster Session D
Session Time: 8:30AM-10:30AM
Background/Purpose: The preferential Janus kinase-1 inhibitor filgotinib (FIL) is approved to treat RA in Europe and Japan. We assessed FIL efficacy and safety in patients (pts) with inadequate response (IR) to biologic DMARDs (bDMARDs) in a long-term extension trial (LTE; NCT03025308) enrolled from a Phase 3 parent study (PS; NCT02873936).1
Methods: bDMARD-IR pts received FIL 200 mg (FIL200), FIL 100 mg (FIL100), or placebo (PBO) all with stable conventional synthetic (cs)DMARDs up to 24 weeks (W). At W14 of the PS, pts with IR to FIL or PBO (< 20% improvement in swollen [66] and tender [68] joint counts) switched to standard of care (SOC; investigator’s choice of appropriate treatment). Pts completing the PS on FIL, PBO, or SOC could enter the LTE. PS FIL pts were maintained, blinded, on their FIL dose; PS PBO and PS SOC pts were rerandomized, blinded, to FIL200 or FIL100. We report efficacy up to LTE W48 for ACR 20%, 50%, and 70% improvement (ACR20/50/70), DAS in 28 joints with CRP (DAS28[CRP]) ≤3.2 and < 2.6, and Clinical Disease Activity Index (CDAI) ≤10 and ≤2.8. Exposure-adjusted incidence rates (EAIR)/100 pt-years of exposure of treatment-emergent adverse events (TEAEs) and AEs of special interest (AESIs) are summarized up to data cutoff of June 1, 2020.
Results: The PS included 147, 153, and 148 pts on FIL200, FIL100, and PBO. Of the 121 pts who entered LTE from PS on FIL200, 80 (66%) continued study drug at June 1, 2020, as did 76/110 (69%) FIL100 pts. Pts still on LTE FIL from PBO were 35/47 (75%) FIL200 and 32/46 (70%) FIL100 pts; from SOC: 13/23 (57%) FIL200 and 13/22 (59%) FIL100 pts. LTE baseline (BL) characteristics were similar in FIL200 and FIL100 pts (mean RA duration: 13.2 and 12.8 years, DAS28[CRP]: 3.5 and 3.7). During LTE, PS FIL ACR20/50/70 response rates decreased modestly by W48 (Table 1). Among PS PBO pts, response rates were lower at LTE BL but reached similar levels as PS FIL pts by W48; rates increased up to W48 in PS SOC pts on either FIL dose but not to levels of other groups. Percentages of pts attaining DAS28(CRP) ≤3.2, DAS28(CRP) < 2.6, CDAI ≤10, and CDAI ≤2.8 were maintained up to W48 for FIL/FIL pts, while PBO/FIL and SOC/FIL pts showed similar patterns as for ACR responses (Table 2). At W48, DAS28 ≤3.2 and < 2.6 response rates were highest among PBO/FIL200 pts. By W12, more SOC/FIL200 pts attained DAS28 and CDAI activity scores versus SOC/FIL100, but rates were similar by W48 (except for CDAI ≤10). TEAE, serious AE, and serious infection EAIRs were higher in SOC/FIL pts vs FIL/FIL or PBO/FIL pts, with 2 nonmelanoma skin cancers on SOC/FIL200, but samples were small, and confidence intervals overlapped (Table 3). 5 pts died: FIL200/FIL200, n=3; PBO/FIL200, n=1; FIL100/FIL100, n=1. There were no opportunistic infections. EAIRs of major cardiovascular events were low, absent in PS SOC pts. Deep vein thrombosis and pulmonary embolism occurred in 2 FIL200/FIL200, 1 FIL100/FIL100, and 1 SOC/FIL200 pts.
Conclusion: Efficacy was mostly maintained in PS FIL pts up to W48. Response among PS PBO and SOC pts increased from BL to W48, but response in PS SOC pts continued to be lower than in other groups; these pts may represent a refractory population. FIL safety was largely consistent between PS and LTE.
Reference
1. Genovese MC et al. JAMA. 2019;322:315–25.
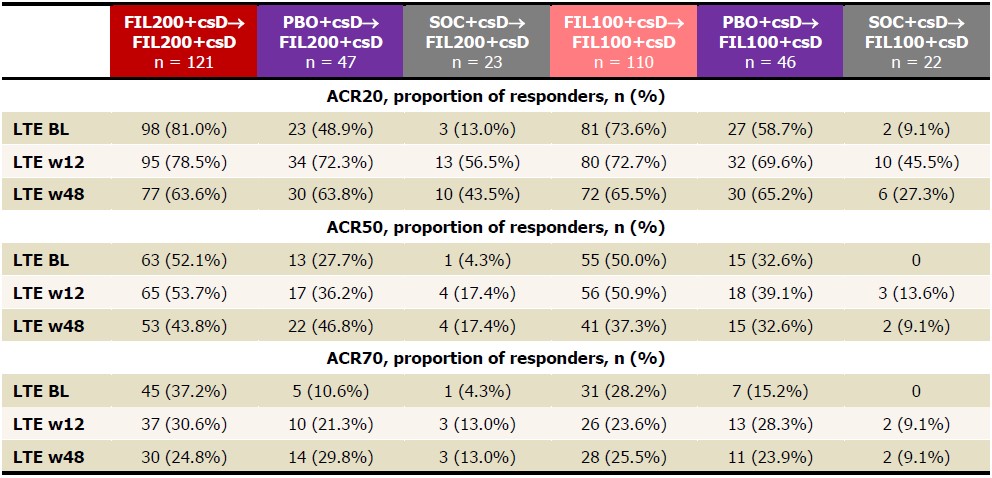 Table 1. Proportions of patients achieving ACR20/50/70, NRI, FAS, up to LTE w48. ACR20/50/70 is calculated based on PS BL. Analysis used the logistic regression model, including treatment group and stratification factors. NRI: patients with missing values were considered nonresponders. BL, baseline; csD, conventional synthetic DMARDs; FAS, full analysis set; FIL, filgotinib; LTE, long-term extension; NRI, nonresponder imputation; PBO, placebo; PS, parent study; w, week.
Table 1. Proportions of patients achieving ACR20/50/70, NRI, FAS, up to LTE w48. ACR20/50/70 is calculated based on PS BL. Analysis used the logistic regression model, including treatment group and stratification factors. NRI: patients with missing values were considered nonresponders. BL, baseline; csD, conventional synthetic DMARDs; FAS, full analysis set; FIL, filgotinib; LTE, long-term extension; NRI, nonresponder imputation; PBO, placebo; PS, parent study; w, week.
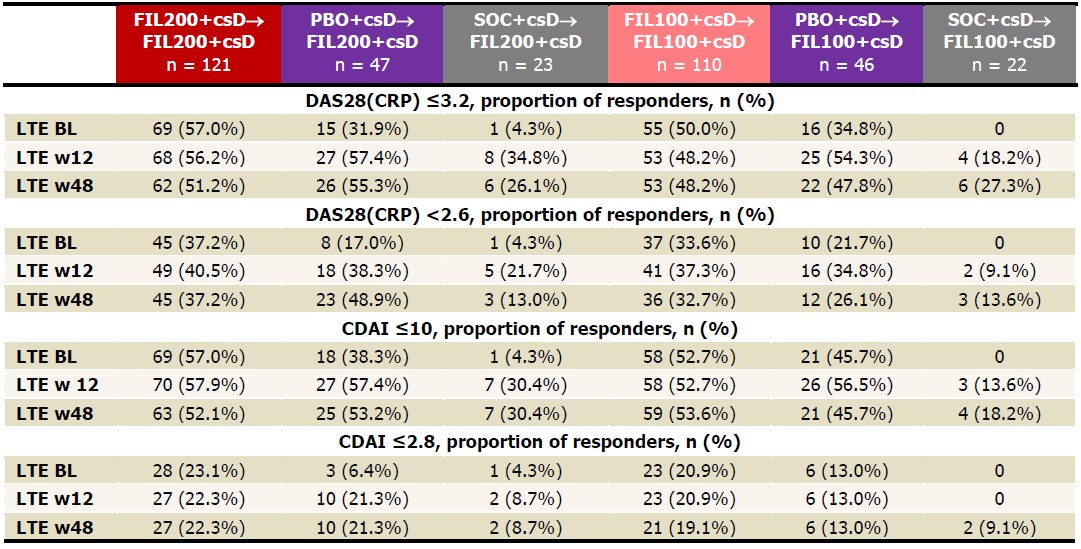 Table 2. Proportions of patients achieving DAS28(CRP) ≤3.2, DAS28(CRP) < 2.6, CDAI ≤10, CDAI ≤2.8, NRI up to LTE w48. Analysis used the logistic regression model, including treatment group and stratification factors. NRI: patients with missing values were considered nonresponders. BL, baseline; CDAI, clinical disease activity index; csD, conventional synthetic DMARDs; DAS28(CRP), disease activity score for 28 joint count using CRP; FIL, filgotinib; LTE, long-term extension; NRI, nonresponder imputation; PS, parent study; w, week.
Table 2. Proportions of patients achieving DAS28(CRP) ≤3.2, DAS28(CRP) < 2.6, CDAI ≤10, CDAI ≤2.8, NRI up to LTE w48. Analysis used the logistic regression model, including treatment group and stratification factors. NRI: patients with missing values were considered nonresponders. BL, baseline; CDAI, clinical disease activity index; csD, conventional synthetic DMARDs; DAS28(CRP), disease activity score for 28 joint count using CRP; FIL, filgotinib; LTE, long-term extension; NRI, nonresponder imputation; PS, parent study; w, week.
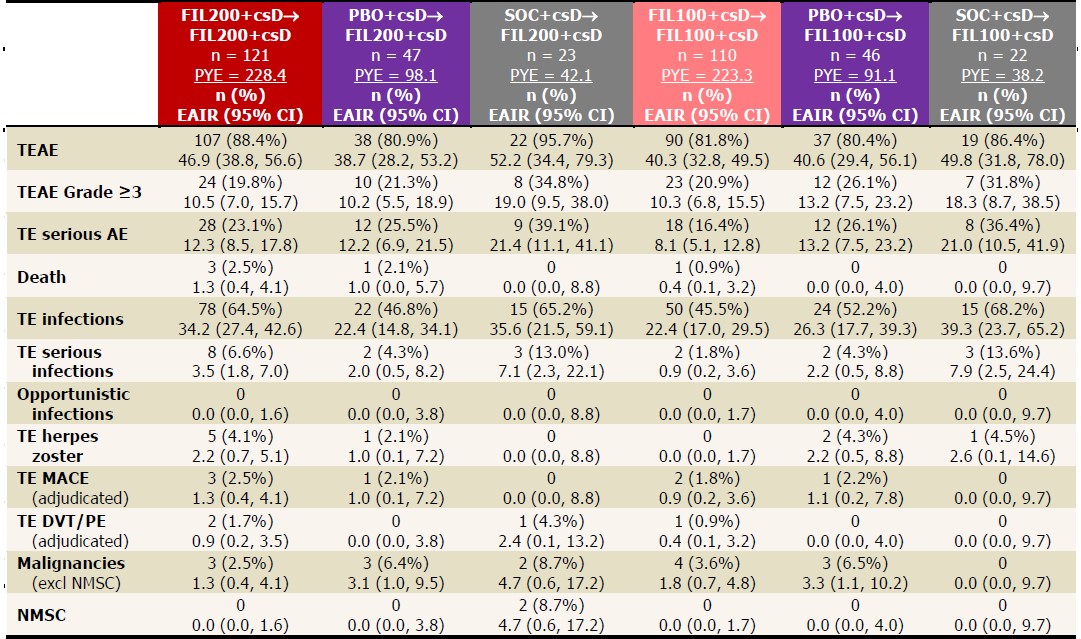 Table 3. EAIRs of TEAEs in LTE, as of June 1, 2020. Data presented as EAIR (95% CI)/100 PYE. EAIR and 95% CI were estimated using Poisson regression model including treatment group with an offset of natural log of exposure time. If any treatment had 0 event, exact Poisson method was applied. csD, conventional synthetic DMARD; DVT, deep-vein thrombosis; EAIR, exposure-adjusted incidence rate; FIL, filgotinib; MACE, major adverse cardiovascular event; PBO, placebo; PE, pulmonary embolism; PYE, patient-years of exposure; SOC, standard of care; TE, treatment-emergent; TEAE, TE adverse event.
Table 3. EAIRs of TEAEs in LTE, as of June 1, 2020. Data presented as EAIR (95% CI)/100 PYE. EAIR and 95% CI were estimated using Poisson regression model including treatment group with an offset of natural log of exposure time. If any treatment had 0 event, exact Poisson method was applied. csD, conventional synthetic DMARD; DVT, deep-vein thrombosis; EAIR, exposure-adjusted incidence rate; FIL, filgotinib; MACE, major adverse cardiovascular event; PBO, placebo; PE, pulmonary embolism; PYE, patient-years of exposure; SOC, standard of care; TE, treatment-emergent; TEAE, TE adverse event.
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Buch M, Takeuchi T, Rajendran V, Gottenberg J, Pechonkina A, Tan Y, Gong Q, Van Beneden K, Caporali R. Clinical Outcomes up to Week 48 of Ongoing Filgotinib RA Long-term Extension Trial of Biologic DMARD Inadequate Responders Initially on Filgotinib or Placebo in a Phase 3 Trial [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2021; 73 (suppl 9). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/clinical-outcomes-up-to-week-48-of-ongoing-filgotinib-ra-long-term-extension-trial-of-biologic-dmard-inadequate-responders-initially-on-filgotinib-or-placebo-in-a-phase-3-trial/. Accessed .« Back to ACR Convergence 2021
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/clinical-outcomes-up-to-week-48-of-ongoing-filgotinib-ra-long-term-extension-trial-of-biologic-dmard-inadequate-responders-initially-on-filgotinib-or-placebo-in-a-phase-3-trial/
