Session Information
Date: Tuesday, November 9, 2021
Title: RA – Treatments Poster III: RA Treatments & Their Safety (1674–1710)
Session Type: Poster Session D
Session Time: 8:30AM-10:30AM
Background/Purpose: The preferential Janus kinase (JAK)-1 inhibitor filgotinib (FIL) is approved for treatment of moderately to severely active RA in Europe and Japan. We assessed efficacy and safety of FIL in patients (pts) with inadequate response to MTX (MTX-IR) who completed a Phase 3 trial (NCT02889796)1 and went on to enroll in a long-term extension (LTE; NCT03025308).
Methods: Pts who completed the parent study1 (PS) on study drug were eligible to enter the LTE. LTE data cutoff was June 1, 2020, and safety data are reported to that date, with median exposure 2.2 years. Efficacy data to W48 are reported for 4 treatment groups (all with background MTX): pts who received FIL 200 mg (FIL200) or FIL 100 mg (FIL100) in the PS and continued their dose in LTE (FIL200/FIL200, FIL100/FIL100) and ADA pts who were rerandomized, double blind, to FIL200 or FIL100 for LTE (ADA/FIL200, ADA/FIL100). ACR 20%, 50%, and 70% response rates (ACR20/50/70), DAS in 28 joints with CRP (DAS28[CRP]) ≤3.2 and < 2.6, and Clinical Disease Activity Index (CDAI) ≤10 and ≤2.8 are reported. Exposure-adjusted incidence rates (EAIR)/100 pt-years of exposure of treatment-emergent adverse events (TEAEs) and AEs of special interest (AESIs) are summarized.
Results: As of June 1, 2020, 522/571 (91%) FIL200/FIL200, 502/570 (88%) FIL100/FIL100, 118/128 (92%) ADA/FIL200, and 115/130 (89%) ADA/FIL100 pts were still on study drug. LTE baseline (BL) disease characteristics were similar between groups: mean duration of RA was approximately 8.7 years; DAS28(CRP) was 2.55, and mean concurrent MTX dosage was 15.0 mg/week. In general, proportions of pts achieving ACR20/50/70, DAS28(CRP) ≤3.2, < 2.6, and CDAI ≤10, ≤2.8 were maintained in all 4 LTE groups through W48 (Tables 1, 2). Numerically greater proportions of pts met response criteria at W48 in the FIL200 groups vs FIL100, regardless of PS treatment. TEAEs, serious AEs, and AEs Grade ≥3 were largely comparable between groups and lowest in ADA/FIL100 pts (Table 3). There were 3 deaths in each PS FIL group and 2 in each PS ADA group; EAIRs for deaths were lower for FIL/FIL groups compared with ADA/FIL groups. Opportunistic infections occurred only in FIL/FIL pts (2 in each group). Nonmelanoma skin cancer (NMSC; n=5) occurred only in FIL/FIL groups, and malignancies excluding NMSC occurred in all groups except ADA/FIL100.
Conclusion: During the LTE through W48, response rates generally were maintained for FIL/FIL and ADA/FIL pts. Though there were differences between LTE groups, safety was largely comparable and consistent with that observed in the PS1 and in previously reported results of safety data from 7 trials2: rates of AESIs were low, and all confidence intervals were overlapping. Limitation: the LTE was not formally randomized for comparison between FIL/FIL and ADA/FIL treatment groups, the groups were of unequal size, and the switch from ADA to FIL for LTE was by design, rather than based on disease activity.
References
1. Combe B et al. Ann Rheum Dis. Epub ahead of print: Jan 27, 2021. doi:10.1136/annrheumdis-2020-219214.
2. Winthrop K et al. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2020;72(suppl 10).
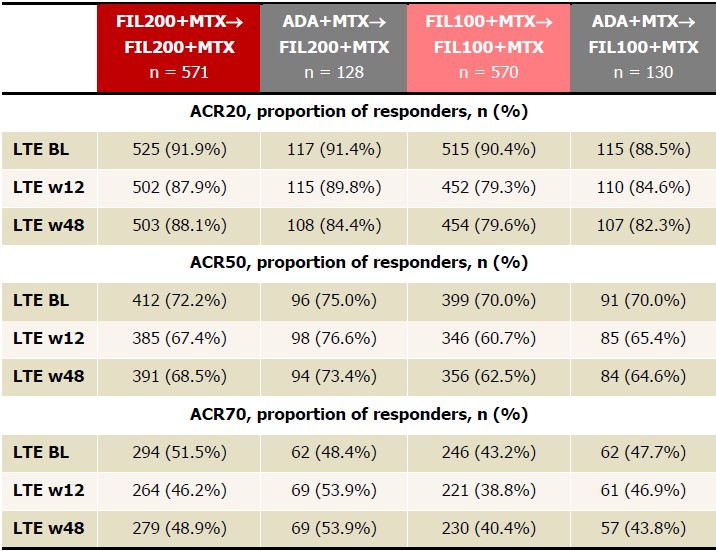 Table 1. Proportions of patients achieving ACR20/50/70, NRI, FAS, up to LTE w48. FIL200+MTX and FIL100+MTX groups include patients who were initially on PBO but later were rerandomized at W24 to FIL200+MTX or FIL100+MTX to W52. ACR20 is calculated based on parent study baseline. Analyzed using the logistic regression model including treatment group and stratification factors; no formal comparison of efficacy outcomes was performed. ADA, adalimumab; BL, baseline; FAS, full analysis set; FIL, filgotinib; LTE, long-term extension; MTX, methotrexate; NRI, nonresponder imputation; PBO, placebo; W, week.
Table 1. Proportions of patients achieving ACR20/50/70, NRI, FAS, up to LTE w48. FIL200+MTX and FIL100+MTX groups include patients who were initially on PBO but later were rerandomized at W24 to FIL200+MTX or FIL100+MTX to W52. ACR20 is calculated based on parent study baseline. Analyzed using the logistic regression model including treatment group and stratification factors; no formal comparison of efficacy outcomes was performed. ADA, adalimumab; BL, baseline; FAS, full analysis set; FIL, filgotinib; LTE, long-term extension; MTX, methotrexate; NRI, nonresponder imputation; PBO, placebo; W, week.
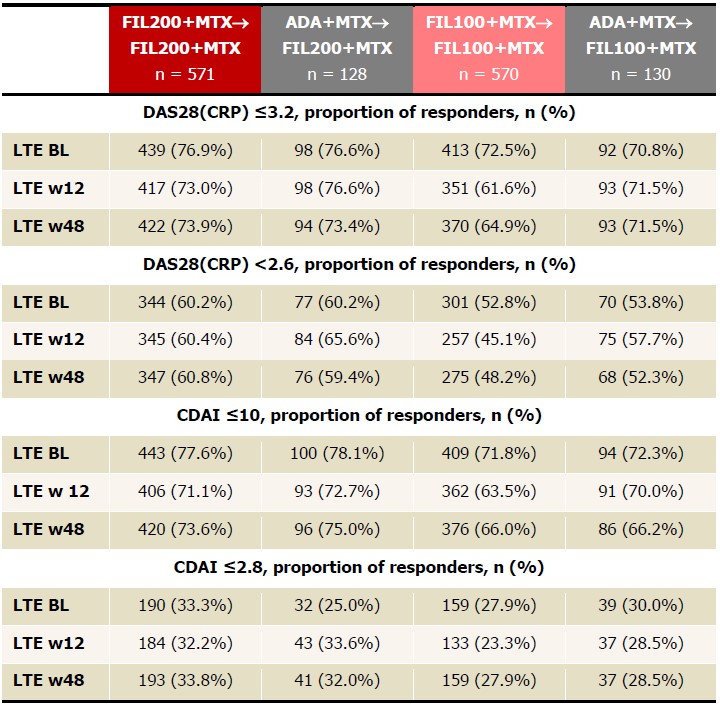 Table 2. Proportions of patients achieving DAS28(CRP) ≤3.2, DAS28(CRP) < 2.6, CDAI ≤10, CDAI ≤2.8, NRI up to LTE w48. FIL200+MTX and FIL100+MTX groups include patients who were initially on PBO but later were rerandomized at W24 to FIL200+MTX or FIL100+MTX to W52. Analyzed using the logistic regression model including treatment group and stratification factors; no formal comparison of efficacy outcomes was performed. ADA, adalimumab; BL, baseline; CDAI, Clinical Disease Activity Index; FAS, full analysis set; FIL, filgotinib; LTE, long-term extension; MTX, methotrexate; NRI, nonresponder imputation; PBO, placebo; W, week.
Table 2. Proportions of patients achieving DAS28(CRP) ≤3.2, DAS28(CRP) < 2.6, CDAI ≤10, CDAI ≤2.8, NRI up to LTE w48. FIL200+MTX and FIL100+MTX groups include patients who were initially on PBO but later were rerandomized at W24 to FIL200+MTX or FIL100+MTX to W52. Analyzed using the logistic regression model including treatment group and stratification factors; no formal comparison of efficacy outcomes was performed. ADA, adalimumab; BL, baseline; CDAI, Clinical Disease Activity Index; FAS, full analysis set; FIL, filgotinib; LTE, long-term extension; MTX, methotrexate; NRI, nonresponder imputation; PBO, placebo; W, week.
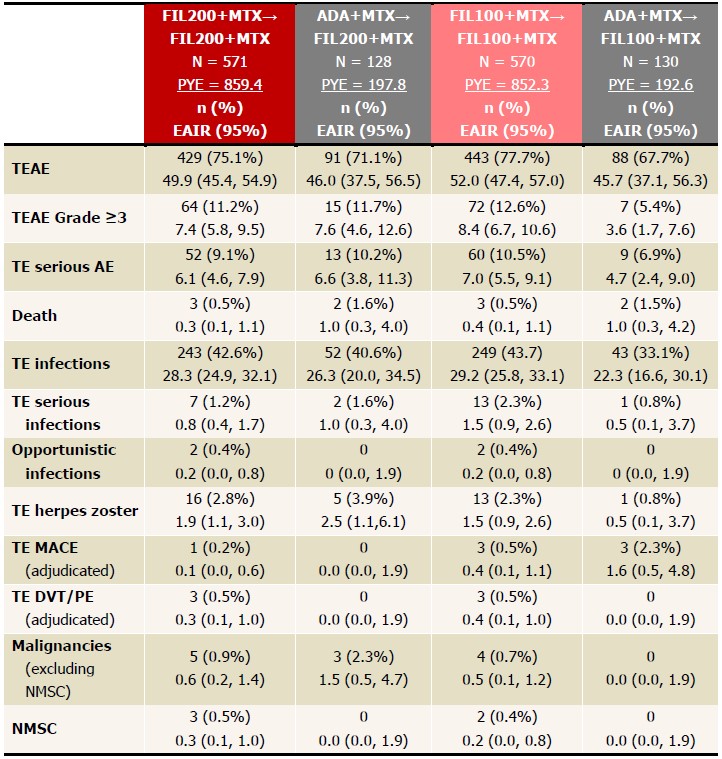 Table 3. EAIRs of TEAEs in LTE, as of June 1, 2020. Data presented as EAIR (95% CI)/100 patient-years. FIL200+MTX and FIL100+MTX groups include patients who were initially on placebo but were later rerandomized to FIL200+MTX or FIL100+MTX in FINCH 1. EAIR and 95% CI were estimated using Poisson regression model including treatment group with an offset of natural log of exposure time. If any treatment had 0 event, exact Poisson method was applied. ADA, adalimumab; AE, adverse event; DVT, deep vein thrombosis; EAIR, exposure-adjusted incidence rate; FIL, filgotinib; LTE, long-term extension; MACE, major cardiovascular event; MTX, methotrexate; NMSC, nonmelanoma skin cancer; PE, pulmonary embolism; PYE, patient years of exposure; TE, treatment emergent.
Table 3. EAIRs of TEAEs in LTE, as of June 1, 2020. Data presented as EAIR (95% CI)/100 patient-years. FIL200+MTX and FIL100+MTX groups include patients who were initially on placebo but were later rerandomized to FIL200+MTX or FIL100+MTX in FINCH 1. EAIR and 95% CI were estimated using Poisson regression model including treatment group with an offset of natural log of exposure time. If any treatment had 0 event, exact Poisson method was applied. ADA, adalimumab; AE, adverse event; DVT, deep vein thrombosis; EAIR, exposure-adjusted incidence rate; FIL, filgotinib; LTE, long-term extension; MACE, major cardiovascular event; MTX, methotrexate; NMSC, nonmelanoma skin cancer; PE, pulmonary embolism; PYE, patient years of exposure; TE, treatment emergent.
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Combe B, Tanaka Y, Emery P, Pechonkina A, Kuo A, Gong Q, Van Beneden K, Rajendran V, Schulze-Koops H. Clinical Outcomes up to Week 48 of Filgotinib Treatment in an Ongoing Long-term Extension Trial of RA Patients with Inadequate Response to MTX Initially Treated with Filgotinib or Adalimumab During the Phase 3 Parent Trial [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2021; 73 (suppl 9). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/clinical-outcomes-up-to-week-48-of-filgotinib-treatment-in-an-ongoing-long-term-extension-trial-of-ra-patients-with-inadequate-response-to-mtx-initially-treated-with-filgotinib-or-adalimumab-during-th/. Accessed .« Back to ACR Convergence 2021
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/clinical-outcomes-up-to-week-48-of-filgotinib-treatment-in-an-ongoing-long-term-extension-trial-of-ra-patients-with-inadequate-response-to-mtx-initially-treated-with-filgotinib-or-adalimumab-during-th/
