Session Information
Date: Tuesday, November 9, 2021
Title: RA – Treatments Poster III: RA Treatments & Their Safety (1674–1710)
Session Type: Poster Session D
Session Time: 8:30AM-10:30AM
Background/Purpose: The preferential Janus kinase (JAK)-1 inhibitor filgotinib (FIL) is approved for treatment of moderately to severely active RA in Europe and Japan. In this post hoc, exploratory analysis, we assessed efficacy and safety of long-term treatment with FIL (with or without MTX) in MTX-naïve patients (pts) treated with FIL or MTX in the Phase 3 parent study (PS; NCT02886728).1
Methods: Pts received FIL 200 mg (FIL200)+MTX, FIL 100 mg (FIL100)+MTX, FIL200 alone, or MTX alone up to 52 weeks (w) in the PS.1 Those who completed the PS on study drug could enter the long-term extension (LTE; NCT03025308). MTX completers were rerandomized, blinded, to FIL200 or FIL100; pts who took FIL in the PS remained on the same dose in LTE. MTX was washed out for 4 w at LTE baseline (BL); pts could (re)start MTX and/or other csDMARDs ≥4 w after LTE first dosing.1 We report proportions of pts who achieved ACR 20%, 50%, and 70% response (ACR20/50/70), DAS in 28 joints with CRP (DAS28[CRP]) ≤3.2 and < 2.6, and Clinical Disease Activity Index (CDAI) ≤10 and ≤2.8. Exposure-adjusted incidence rates (EAIR)/100 pt-years of exposure of treatment-emergent adverse events (TEAEs) and AEs of special interest (AESIs) are summarized, with data cutoff of June 1, 2020.
Results: As of June 1, 2020, 439 of 492 (89%) pts who entered LTE from the PS FIL200 groups and 144/169 (85%) from the PS FIL100 group were still on LTE study treatment; of those rerandomized from MTX, 131/148 (89%) FIL200 and 133/151 (88%) FIL100 pts were still on study treatment. LTE BL characteristics were similar between FIL200 and FIL100 groups: mean RA duration was 3.1 and 3.3 years; mean DAS28(CRP) was 2.5 and 2.7. After MTX washout, only 17% of FIL200 and 23% of FIL100 pts (re)started MTX (at clinical judgment). ACR20/50/70 response rates among pts from PS FIL arms decreased modestly from LTE BL to W12 then stabilized. Among pts who switched from PS MTX to LTE FIL, response rates remained stable or improved to approach those of PS FIL pts by W48 (Table 1). Similar trends were seen in proportions of pts attaining DAS28(CRP) ≤3.2, DAS28(CRP) < 2.6, CDAI ≤10, and CDAI ≤2.8 (Table 2). TEAEs, Grade ≥3 AEs, serious AEs, and infections were largely comparable across groups and did not appear to increase after MTX to FIL switch (Table 3). There were 6 deaths, all among PS FIL200 pts. There were 5 major cardiovascular events, 3 in PS FIL200+MTX and 2 in PS FIL200 monotherapy pts and 2 venous thromboembolisms, 1 each in PS FIL200+MTX and PS FIL200 monotherapy pts. EAIRs of herpes zoster were comparable across groups regardless of PS treatment. EAIRs for other AESIs were low.
Conclusion: Overall, response rates improved from LTE BL to W48 for pts switched from PS MTX to FIL and decreased modestly for PS FIL pts. In general, rates of AESIs were low and tended to be higher in pts maintained on FIL from PS. Safety findings in this subpopulation were comparable with the PS through W521 and with a 7-trial integrated safety analysis.2 Limitations: the LTE was not formally randomized at BL, the groups were of unequal size, and the switch from MTX to FIL for LTE was by design, rather than based on disease activity.
References
1. Westhovens R et al. Ann Rhem Dis. 2021;80:727–38. 2. Winthrop K et al. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2020;72(suppl 10):abstract 0229.
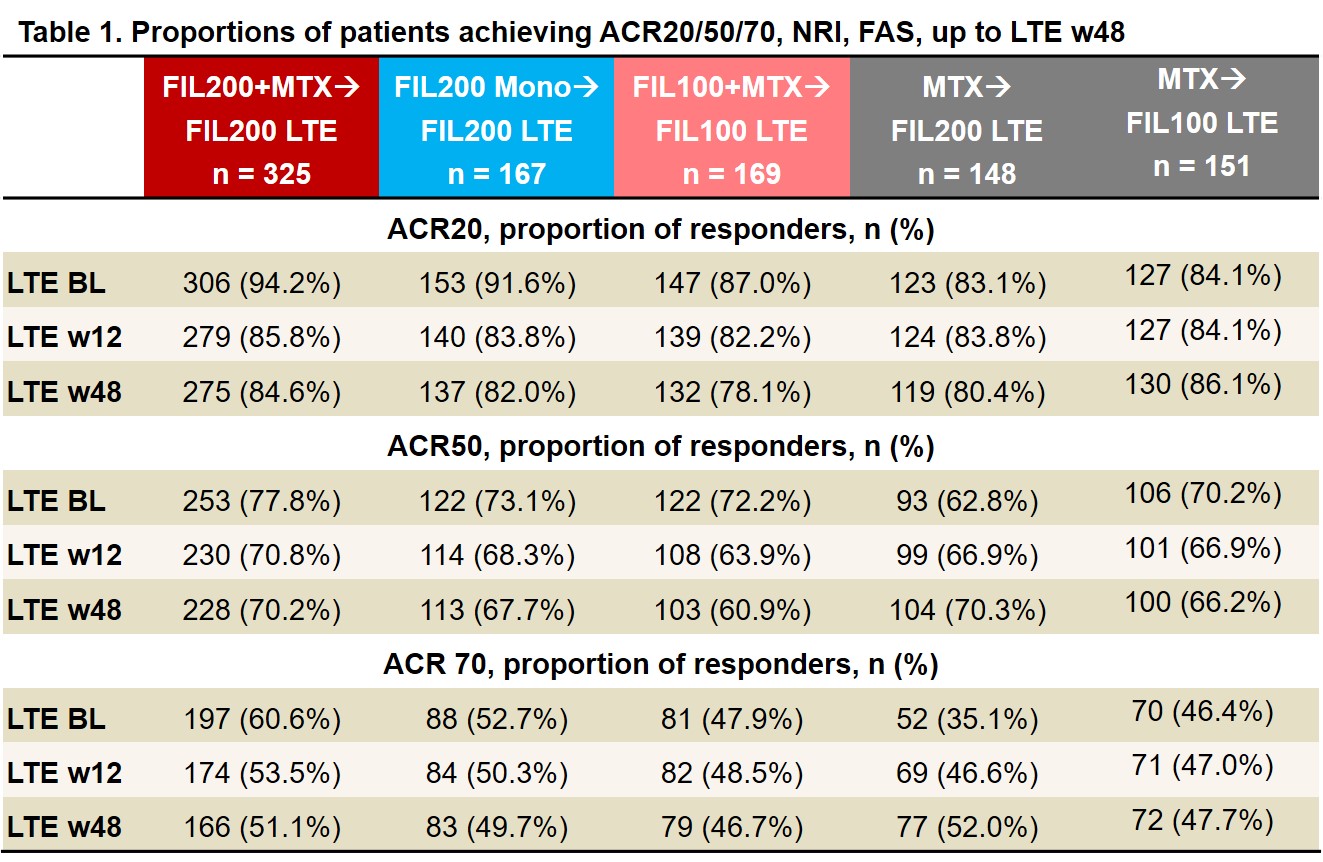 LTE FIL represents FIL dose with and without MTX. ACR20/50/70 is calculated based on PS BL. Data are presented as n (%). Analysis by logistic regression model, including treatment group and stratification factors. NRI: patients with missing values were considered nonresponders. BL, baseline; FAS, full analysis set; FIL, filgotinib; LTE, long-term extension; NRI, nonresponder imputation; w, week.
LTE FIL represents FIL dose with and without MTX. ACR20/50/70 is calculated based on PS BL. Data are presented as n (%). Analysis by logistic regression model, including treatment group and stratification factors. NRI: patients with missing values were considered nonresponders. BL, baseline; FAS, full analysis set; FIL, filgotinib; LTE, long-term extension; NRI, nonresponder imputation; w, week.
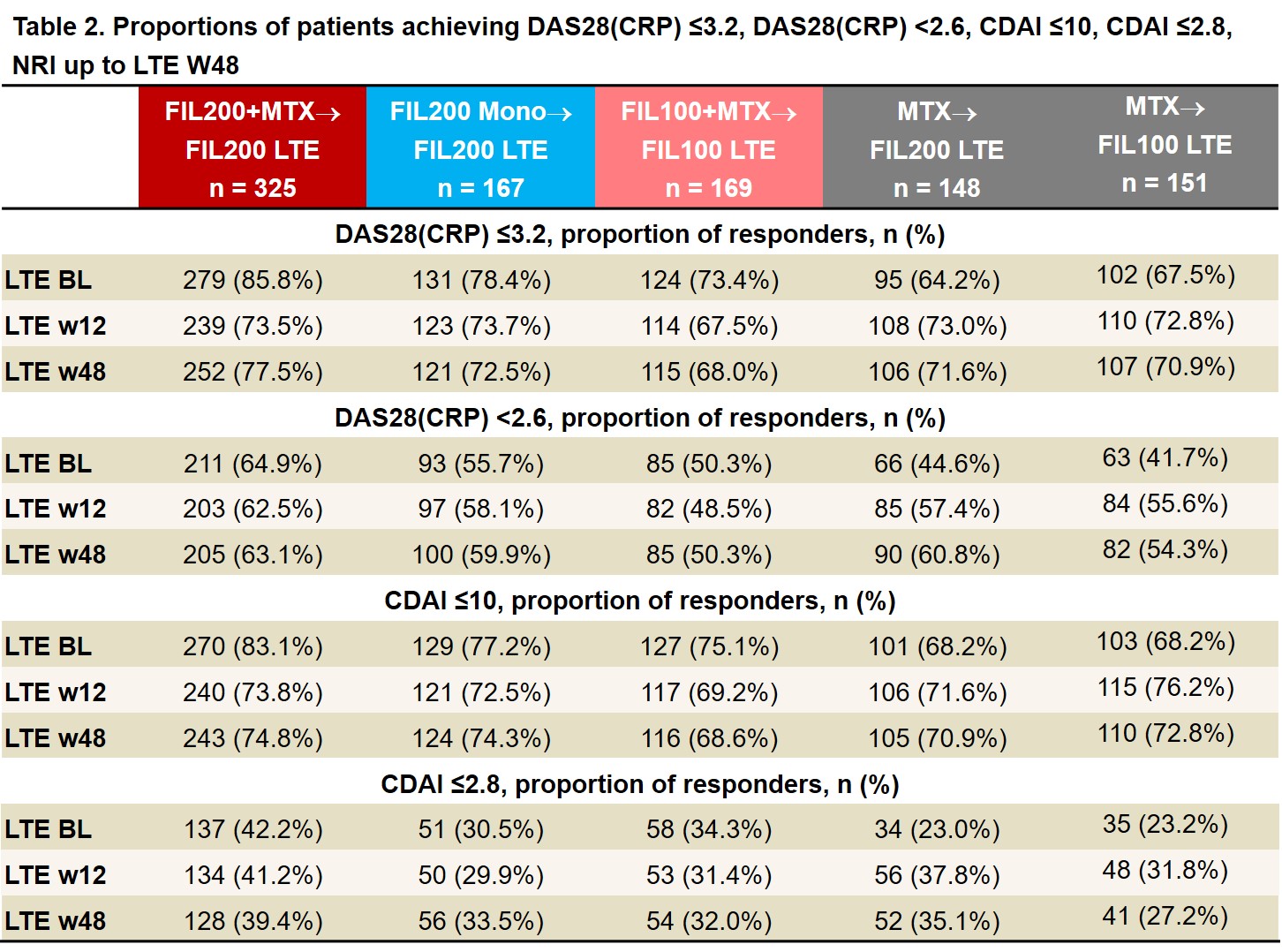 LTE FIL represents FIL dose with and without MTX. Data are presented as n (%). Analysis by logistic regression model, including treatment group and stratification factors. NRI: patients with missing values were considered nonresponders. BL, baseline; CDAI, clinical disease activity index; DAS28(CRP), disease activity score for 28 joint count using CRP; FIL, filgotinib; LTE, long-term extension; NRI, nonresponder imputation; w, week.
LTE FIL represents FIL dose with and without MTX. Data are presented as n (%). Analysis by logistic regression model, including treatment group and stratification factors. NRI: patients with missing values were considered nonresponders. BL, baseline; CDAI, clinical disease activity index; DAS28(CRP), disease activity score for 28 joint count using CRP; FIL, filgotinib; LTE, long-term extension; NRI, nonresponder imputation; w, week.
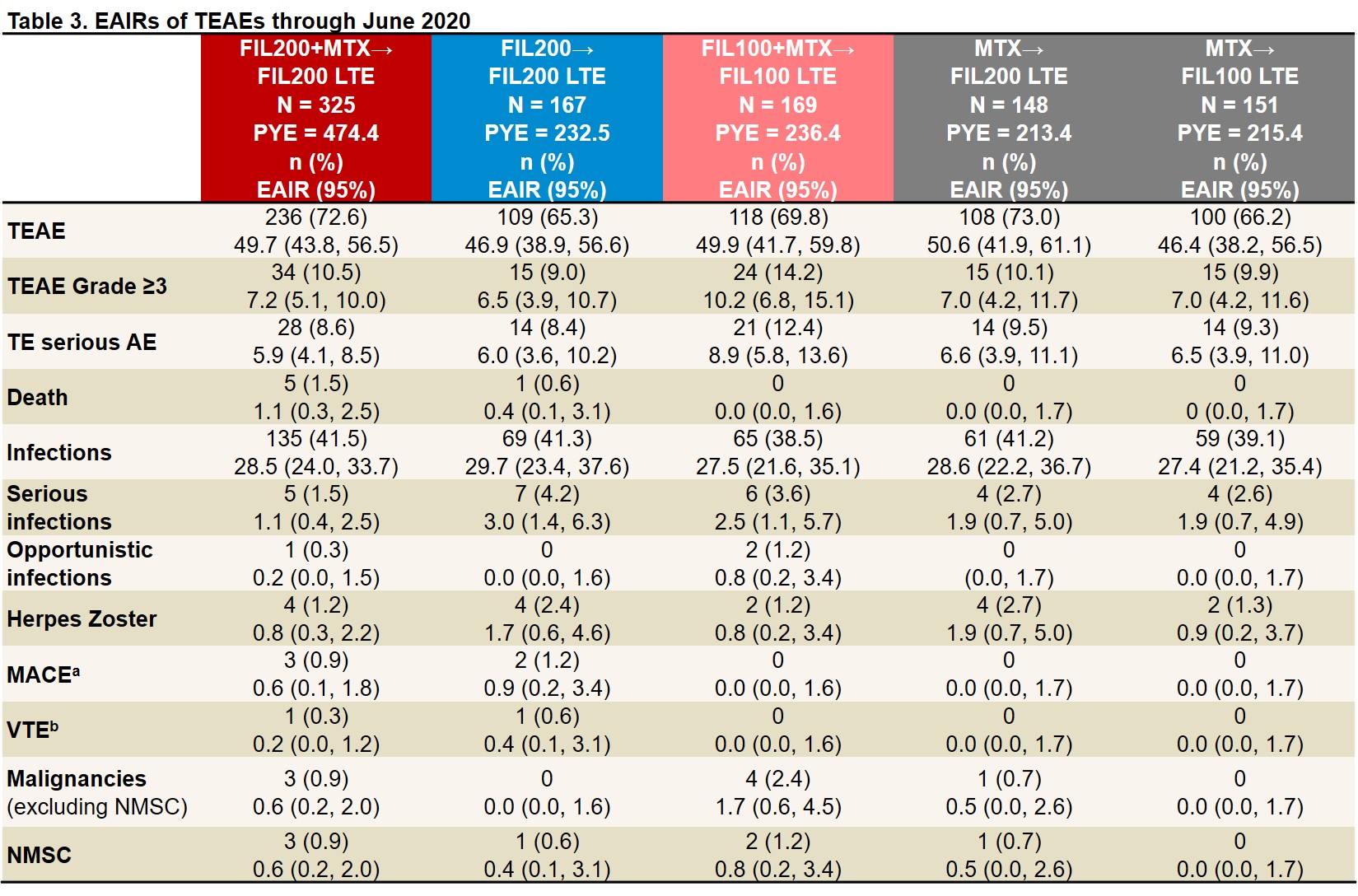 aPositively adjudicated. bVTE adjudicated for DVT and PE. LTE FIL represents FIL dose with and without MTX. EAIR and 95% CIs were estimated using Poisson regression model including treatment group with an offset of natural log of exposure time. AE, adverse event; CI, confidence interval; DVT, deep vein thrombosis; EAIR, exposure-adjusted incidence rate; FIL, filgotinib; LTE, long-term extension; MACE, major adverse cardiovascular event; NMSC, nonmelanoma skin cancer; PBO, placebo; PE, pulmonary embolism; PYE, patient-years of exposure; TE, treatment-emergent; VTE, venous thromboembolism.
aPositively adjudicated. bVTE adjudicated for DVT and PE. LTE FIL represents FIL dose with and without MTX. EAIR and 95% CIs were estimated using Poisson regression model including treatment group with an offset of natural log of exposure time. AE, adverse event; CI, confidence interval; DVT, deep vein thrombosis; EAIR, exposure-adjusted incidence rate; FIL, filgotinib; LTE, long-term extension; MACE, major adverse cardiovascular event; NMSC, nonmelanoma skin cancer; PBO, placebo; PE, pulmonary embolism; PYE, patient-years of exposure; TE, treatment-emergent; VTE, venous thromboembolism.
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Aletaha D, Westhovens R, Atsumi T, Tan Y, Pechonkina A, Gong Q, Rajendran V, Strengholt S, Burmester G. Clinical Outcomes of MTX-Naïve RA Patients on Filgotinib Long-term Extension Trial Initially on FIL or MTX During Phase 3 Parent Trial [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2021; 73 (suppl 9). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/clinical-outcomes-of-mtx-naive-ra-patients-on-filgotinib-long-term-extension-trial-initially-on-fil-or-mtx-during-phase-3-parent-trial/. Accessed .« Back to ACR Convergence 2021
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/clinical-outcomes-of-mtx-naive-ra-patients-on-filgotinib-long-term-extension-trial-initially-on-fil-or-mtx-during-phase-3-parent-trial/
