Session Information
Date: Sunday, October 21, 2018
Title: Rheumatoid Arthritis – Treatments Poster I: Strategy and Epidemiology
Session Type: ACR Poster Session A
Session Time: 9:00AM-11:00AM
Background/Purpose: Tofacitinib is an oral Janus kinase inhibitor for the treatment of RA, originally approved at 5 mg twice daily (BID). In 2016, an extended-release (XR) dose of tofacitinib 11 mg once daily (QD) was approved. Limited clinical or real-world data exist comparing efficacy outcomes between 11 mg QD and 5 mg BID doses. We aimed to compare the efficacy of these formulations.
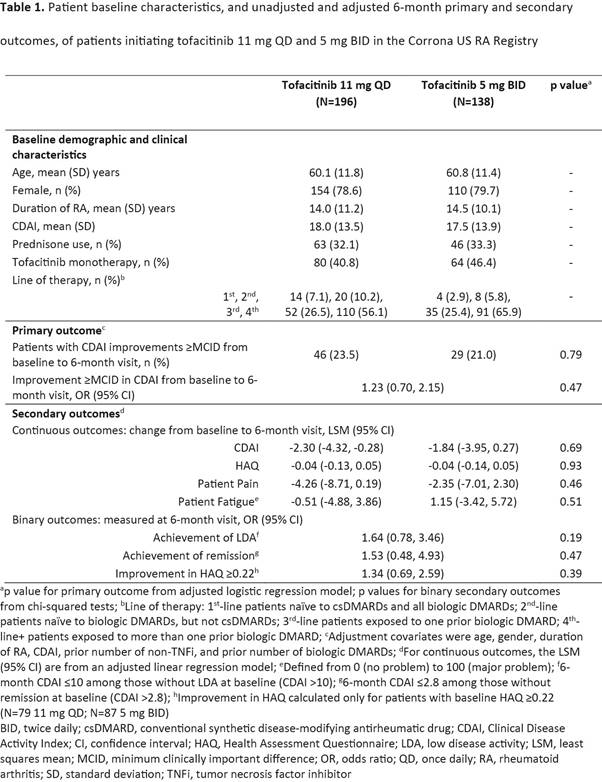
Methods: Treatment effectiveness at 6 (±3) months (mos) after initiation (baseline) was evaluated in an observational cohort of patients (pts) initiating tofacitinib 5 mg BID or 11 mg QD between February 2016 and March 2018, identified from the Corrona US RA Registry. The primary outcome was achievement of a minimum clinically important difference (MCID) in Clinical Disease Activity Index (CDAI) improvement at approximately the 6-mo visit following initiation. The MCID was dependent on baseline disease activity (≥2 if low baseline CDAI [≤10], ≥6 if moderate baseline CDAI [10<CDAI≤22], and ≥11 if high baseline CDAI [>22]). Secondary outcomes included: CDAI change from baseline to 6-mo visit, Pt Pain, and Pt Fatigue; achievement of low disease activity (LDA; CDAI ≤10) in pts without baseline LDA, or remission (CDAI ≤2.8) in pts without baseline remission, at 6 mos; and improvement ≥MCID in HAQ (≥0.22) at 6 mos. Outcomes were compared between groups in unadjusted analyses and adjusted linear and logistic regression models (covariates: age, sex, baseline CDAI, duration of RA [a priori decision], and additional covariates with standardized differences >0.2). An exploratory analysis (limited sample size) was conducted to examine 6-mo outcomes in pts who switched to 11 mg QD after 5 mg BID initiation.
Results: 791 pts initiated tofacitinib (11 mg QD: n=460; 5 mg BID: n=234), of whom 334 pts (11 mg QD: n=196; 5 mg BID: n=138) had a registry visit and thus CDAI data at 6 mos after initiation. Baseline characteristics are shown in the Table. There were no significant differences in the proportion of pts with CDAI improvements ≥MCID between formulations with and without adjustment (23.5% vs 21.0%; odds ratio 1.23; 95% confidence interval 0.70, 2.15; covariates added in the model were prior number of non-TNF inhibitors and biologic DMARDs). There were no significant differences in the odds of achieving LDA, remission or improvement in HAQ ≥0.22 between formulations with adjustment (Table). Similar proportions of pts initiating 11 mg QD and 5 mg BID remained on tofacitinib at 6 mos (61.2% vs 67.4%; p=0.43). There were 135 switchers (5 mg BID to 11 mg QD); their post-6-mo outcomes were similar to those at the time of switch.
Conclusion: Results suggest that pts with RA who initiated treatment with tofacitinib 11 mg QD achieved comparable efficacy outcomes with pts who initiated with 5 mg BID. Although currently available person years of exposure is limited, data do not suggest the emergence of any new or unexpected safety risks for the XR formulation.
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Cohen S, Litman HJ, Chen C, Lukic T, Madsen A, Takiya L, Dandreo KJ, Blachley T, Greenberg J. Clinical Effectiveness of Tofacitinib 11mg Once Daily (QD) Versus Tofacitinib 5mg Twice Daily (BID) in the Corrona US RA Registry [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2018; 70 (suppl 9). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/clinical-effectiveness-of-tofacitinib-11mg-once-daily-qd-versus-tofacitinib-5mg-twice-daily-bid-in-the-corrona-us-ra-registry/. Accessed .« Back to 2018 ACR/ARHP Annual Meeting
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/clinical-effectiveness-of-tofacitinib-11mg-once-daily-qd-versus-tofacitinib-5mg-twice-daily-bid-in-the-corrona-us-ra-registry/