Session Information
Session Type: Poster Session D
Session Time: 8:30AM-10:30AM
Background/Purpose: Since the beginning of the COVID-19 pandemic, some studies have addressed risk factors for severe forms of the disease in patients with rheumatic diseases. Higher prednisolone doses and rituximab (RTX) have been associated with an increased risk of severe COVID-19, although not consistently. Our main goal was to assess the clinical features and to identify risk factors for severe COVID-19 in patients with rheumatic diseases.
Methods: Multicenter observational nationwide study of adult patients with rheumatic diseases and confirmed or suspected infection by SARS-CoV-2 prospectively-followed in the Rheumatic Diseases Portuguese Register – Reuma.pt – between march and september 2020. Mild COVID-19 was defined as symptomatic disease without pneumonia; moderate disease if clinical signs of pneumonia without hypoxemia; severe disease as hypoxemic pneumonia and/or need for hospitalization; and critical disease as requiring admission to intensive care unit or death. Clinical features and treatment of patients with mild/moderate vs. severe/critical COVID19 were compared using Pearson Chi-Square, exact Fisher and Mann-Whitney U tests, as adequate. Independent association between demographic, disease-related and treatment-related variables and COVID-19 severity was evaluated through multivariate logistic regression.
Results: We included 179 patients with confirmed (97.2%) or suspected (2.8%) COVID-19 (Table 1). Forty-five (25.1%) patients developed severe/critical disease, requiring hospitalization, and 10 (5.6%) patients died. In the same time frame, the national rate of hospitalization was 8.4% and mortality 2.6%. Most patients reported direct contact with a positive patient (65.9%). Major symptoms reported were cough, fever, malaise, fatigue, myalgia, headache and anosmia (Table 2). Lymphopenia and elevated CRP were the most frequent laboratory abnormalities. Patients with severe/critical disease were older (p< 0.001), had a higher prevalence of arterial hypertension (p=0.001), diabetes (p< 0.001), cardiovascular disease (p=0.007) and chronic kidney disease (p=0.036) (Table 3). Considering inflammatory arthritis as the reference category, patients with CTD/vasculitis (33.3% vs 26.9%, OR 1.69, 95CI 0.787-3.611) and non-inflammatory diseases (17.8% vs 6.7%, OR 3.60, 95CI 1.25-10.39) had a higher probability of severe/critical COVID-19. Regarding therapy, the proportion of patients under RTX was higher in severe/critical COVID-19 patients (11.1% vs 1.5%, OR 8.25, p=0.012). Treatment with TNF inhibitors was associated with less probability of severe/critical COVID-19 (2.2% vs 17%, OR 0.11, p=0.033). Treatment with other DMARDs was not associated with COVID-19 severity. Age (OR 1.09, 95CI 1.06-1.13, p< 0.001) and treatment with RTX (OR 13.77, 95CI 2.23-85.17, p=0.005) were independently associated with severe/critical COVID-19 (Table 3).
Conclusion: Hospitalization and mortality in rheumatic patients was higher than the reported in the general national population for the same time frame, although a reporting bias must be considered. Older age and treatment with RTX were independent risk factors for severe/critical COVID-19 in patients with rheumatic diseases.
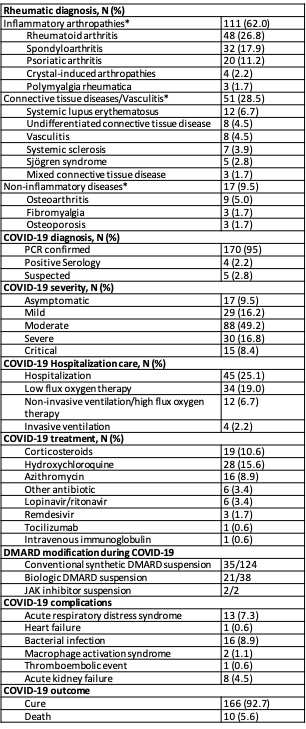 Table 1 – Characteristics of patients with COVID_19 *Diagnosis with n≥3 are specified
Table 1 – Characteristics of patients with COVID_19 *Diagnosis with n≥3 are specified
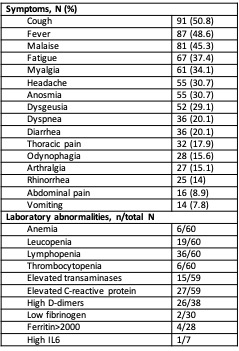 Table 2 – Symptoms and laboratory data in COVID_19 patients
Table 2 – Symptoms and laboratory data in COVID_19 patients
 Table 3 – Comparison of patients with severe/critical vs mild/moderate COVID_19 *At least 1 comorbidity among arterial hypertension, obesity, diabetes, cardiovascular disease, asthma, chronic obstructive pulmonary disease, chronic kidney disease.
Table 3 – Comparison of patients with severe/critical vs mild/moderate COVID_19 *At least 1 comorbidity among arterial hypertension, obesity, diabetes, cardiovascular disease, asthma, chronic obstructive pulmonary disease, chronic kidney disease.
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Carvalho Barreira S, Cruz-Machado A, Bandeira M, Duarte C, Rato M, Fernandes B, Garcia S, Pinheiro F, Bernardes M, Madeira N, Miguel C, Torres R, Bento Silva A, Pestana J, Almeida D, Mazeda C, Cunha Santos F, Pinto P, Sousa M, Parente H, Sequeira G, José Santos M, Fonseca J, Romão V. Clinical Course and Risk Factors for Severe/Critical COVID-19 in Patients with Rheumatic Diseases – a Multicenter, Nationwide Study [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2021; 73 (suppl 9). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/clinical-course-and-risk-factors-for-severe-critical-covid-19-in-patients-with-rheumatic-diseases-a-multicenter-nationwide-study/. Accessed .« Back to ACR Convergence 2021
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/clinical-course-and-risk-factors-for-severe-critical-covid-19-in-patients-with-rheumatic-diseases-a-multicenter-nationwide-study/
