Session Information
Date: Sunday, November 12, 2023
Title: (0609–0672) Systemic Sclerosis & Related Disorders – Clinical Poster I: Research
Session Type: Poster Session A
Session Time: 9:00AM-11:00AM
Background/Purpose: Systemic sclerosis (SSc) patients with clinical features of another connective tissue disease (CTD) may have different clinical characteristics from patients with SSc alone. Our aim was to compare the clinical characteristics and survival of patients with SSc, SSc-overlap and SSc-mixed connective tissue disease (MCTD).
Methods: This retrospective cohort study included SSc, SSc-overlap and SSc-MCTD patients from Australia, Hong Kong, Malaysia, Singapore, and Thailand. SSc patients fulfilled the 2013 ACR-EULAR SSc classification criteria; SSc-overlap patients also fulfilled the criteria for another CTD which included rheumatoid arthritis, systemic lupus erythematosus, or inflammatory myositis; SSc-MCTD patients had anti-RNP antibody positivity and at least 3 of the following features (per Alargon-Sergovia criteria): swollen hands, synovitis, myositis, Raynaud phenomenon (RP) and acrosclerosis/sclerodactyly. Univariate comparison of clinical characteristics among groups was performed by analysis of variance or chi-square testing. Survival analysis was performed using Kaplan-Meier curves.
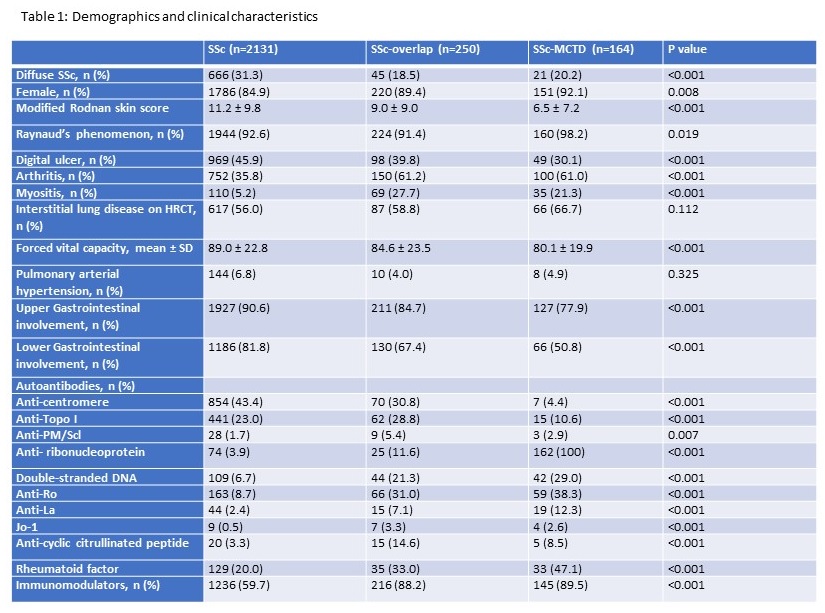
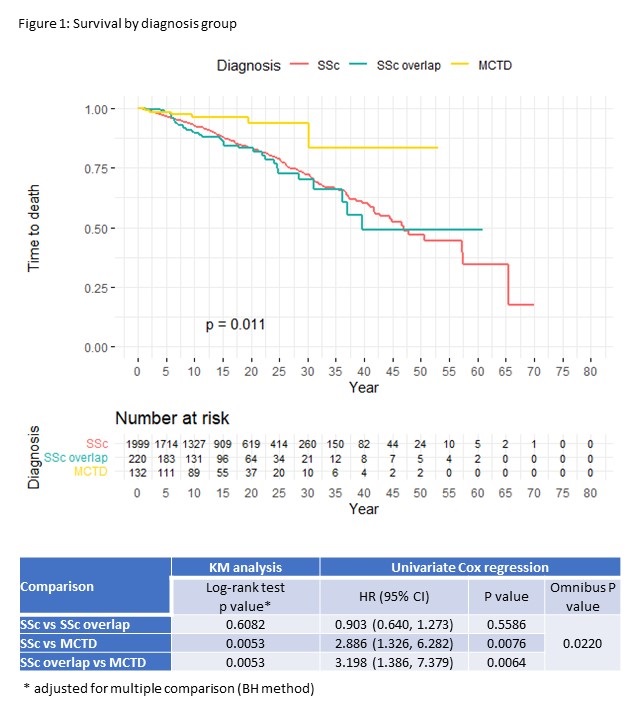
Results: Among 2545 patients (11.3% from Singapore, 5.3% from Malaysia, 3.8% from Thailand, 3.3% from Hong Kong and 76.3% from Australia), 250 (9.8%) had SSc-overlap syndrome, 164 (6.4%) had SSc-MCTD and 2131 (83.7%) had SSc. SSc-overlap and SSc-MCTD, respectively, occurred more frequently in the Asian (SSc-overlap: 13.2%-17.9%; MCTD: 8.3%-31.8%) vs Australian (SSc-overlap: 8.2%; MCTD: 3.7%) cohorts. SSc patients were more likely to have diffuse cutaneous SSc, significantly higher modified Rodnan skin score (11.2 ± 9.8 in SSc vs 9.0 ± 9.0 in SSc-overlap vs 6.5 ± 7.2 in SSc-MCTD, p< 0.001), gastrointestinal involvement, higher % predicted forced vital capacity (89.0 ± 22.8 in SSc vs 84.6 ± 23.5 in SSc-overlap vs 80.1 ± 19.9 in SSc-MCTD, p< 0.001) and digital ulcerations as compared to SSc-overlap and SSc-MCTD patients. Arthritis and myositis were significantly more prevalent in SSc-overlap and SSc–MCTD than in SSc patients. RP was more frequent in SSc-MCTD than in SSc and SSc-overlap patients. At baseline, more patients with SSc (27.7%) and SSc-overlap (21.2%) were in NYHA III/IV than MCTD (15.3%; p< 0.001). There was no significant difference in the frequency of interstitial lung disease and pulmonary arterial hypertension in the 3 groups. Anti-centromere antibody was more frequently seen in SSc patients, and anti-topoisomerase I antibody in SSc-overlap and SSc patients; other antibodies including anti-PM/Scl, double-stranded DNA, rheumatoid factor, anti-Ro, anti-La and Jo-1 were significantly less frequent in the SSc group compared to the SSc-overlap and SSc-MCTD groups. SSc-MCTD and SSc-overlap patients were also more likely to receive immunomodulators than SSc patients (Table 1). Overall survival was better in SSc-MCTD than SSc or SSc-overlap (p=0.011) (Figure 1).
Conclusion: Our study showed significant differences in the clinical characteristics and survival outcomes in patients with SSc, SSc-overlap and SSc-MCTD.
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Ng S, Saffari S, Stevens W, RAJA J, Wangkaew S, Ho G, Teng G, Proudman S, Nikpour M, Low A. Clinical Characteristics of Systemic Sclerosis, Systemic Sclerosis Overlap Syndromes and Systemic Sclerosis-mixed Connective Tissue Disease in an Asia-Pacific Cohort- an APLAR Scleroderma Special Interest Group Study [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2023; 75 (suppl 9). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/clinical-characteristics-of-systemic-sclerosis-systemic-sclerosis-overlap-syndromes-and-systemic-sclerosis-mixed-connective-tissue-disease-in-an-asia-pacific-cohort-an-aplar-scleroderma-special-inte/. Accessed .« Back to ACR Convergence 2023
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/clinical-characteristics-of-systemic-sclerosis-systemic-sclerosis-overlap-syndromes-and-systemic-sclerosis-mixed-connective-tissue-disease-in-an-asia-pacific-cohort-an-aplar-scleroderma-special-inte/