Session Information
Session Type: Poster Session (Monday)
Session Time: 9:00AM-11:00AM
Background/Purpose: Behcet´s disease (BD) is a systemic autoimmune disease that affects multiple organ systems with recurrent oral ulcers, genital ulcers and skin lesions, which might be accompanied by psychological abnormalities such as anxiety or depression. Behcet´s Disease Current Activity Form (BDCAF) and Electronic Medical Record-based Activity Index (EMRAI) are commonly used internationally to evaluate the disease activity of BD; Hospital Anxiety & Depression Scale (HADS) is commonly used to evaluate patients’ mental health.
This study aimed to analyze the clinical characteristics, the level of disease activity, and the incidence of anxiety and depression for Chinese BD patients. Patients can perform self-management of disease with Smart System of Disease Management (SSDM).
Methods: SSDM is a series of doctor-patient interactive applications for self-management of patients with chronic diseases. Patients can perform BDCAF, EMRAI and HADS self-assessment with SSDM and upload the self-assessment data to their authorized doctors. The SSDM patients’ application system integrates the BDCAF and EMRAI into one scoring system. Patients could obtain scores of BDCAF and EMRAI by responding to one questionnaire through SSDM. Patients with a score ≥4, will be diagnosed as BD. HADS is divided into two sub-tables of HADS-Anxiety (HADS-A) and HADS- Depression (HADS-D). A patient’s HADS score >10, will be diagnosed with anxiety or depression.
Results: From April 2017 to May 2019, 1,072 BD patients from 225 hospitals used SSDM, with a mean age of 38.78±12.23 (14~78) years old, and median disease duration of 21.77 months. 513 patients performed BDCAF and EMRAI self-assessment 873 times, 130 patients repeat assessments for 360 times. The mean score of BDCAF and EMRAI are 3.69±2.25 and 3.60±2.03, respectively. The matching degree of the two score was 0.8818.
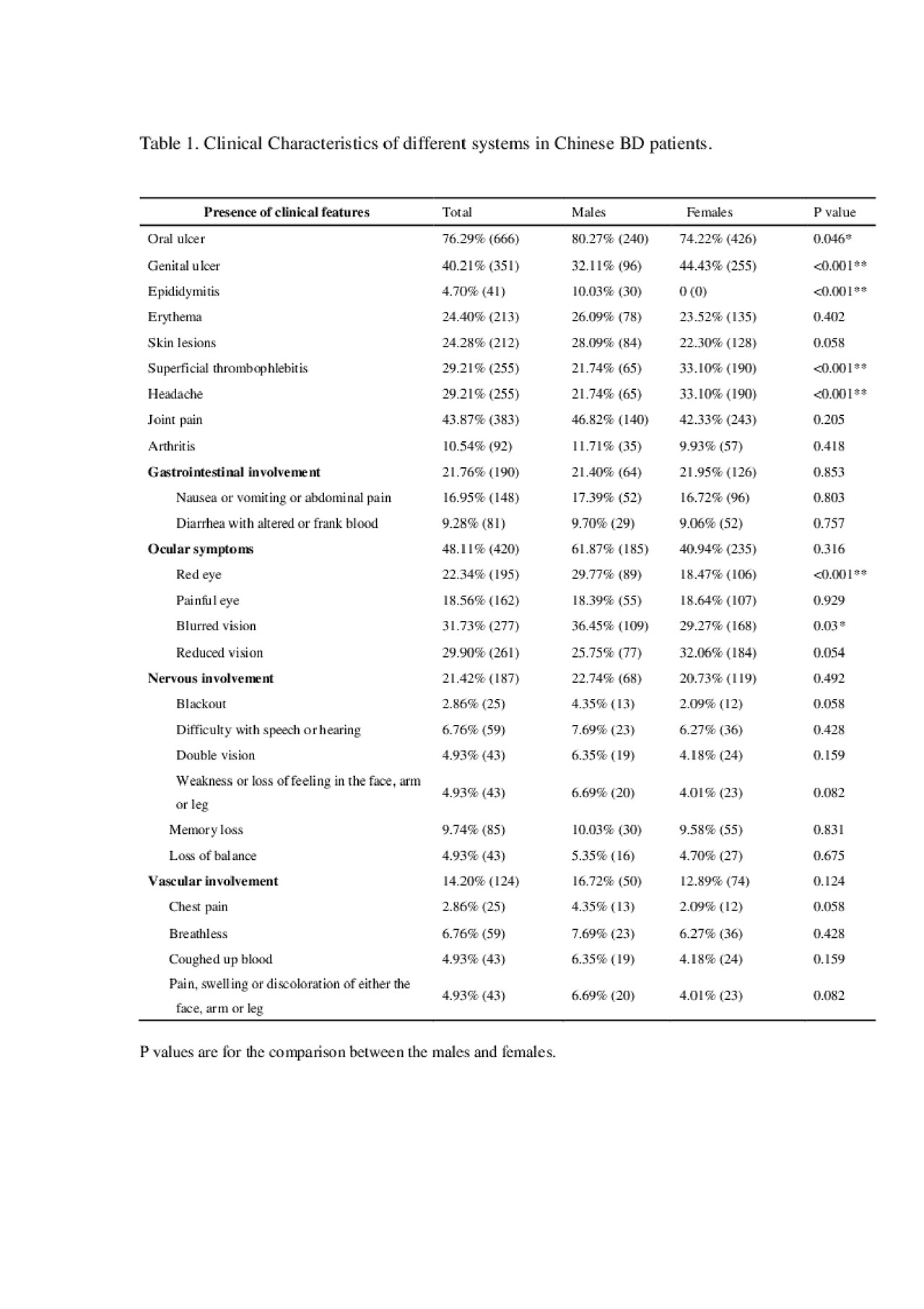
The most common clinical characteristics were oral ulcers (76.9%), joint pain (43.87%) and genital ulcer (40.21%). The comparative study between males and females revealed significant difference in the aspects of epididymitis (10.03% vs 0, p< 0.001), genital ulcer (32.11% vs 44.43%, p< 0.001), headache (21.74% vs 33.10%, p< 0.001), superficial thrombophlebitis (21.74% vs 33.10%, p< 0.001) and red eye (29.77% vs 18.47%, p< 0.001). Please see details in Table 1.
The incidence of anxiety and depression was 15% and 16%, among 134 patients assessed for HADS.
Conclusion: Chinese BD patients can effectively perform BDCAF and EMRAI self-assessment with SSDM. The results of the assessment conducted by the two scoring systems are similar. The clinical characteristics of Chinese BD were different depending on gender.
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Dong L, Li S, Wang F, Wu Z, Zhang S, Li Q, Wu H, Wang Z, Guo H, Yu Y, Shen L, Li Y, Liu Y, Wang T, Ji P, Shuai Z, Li H, Luo L, Xiao H, Jia Y, Wu B, Jia S, Xiao F, Wu L. Clinical Characteristics and the Level Disease Activity of Behcet´s Disease in China: A Study Based on Smart System of Disease Management (SSDM) [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2019; 71 (suppl 10). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/clinical-characteristics-and-the-level-disease-activity-of-behcets-disease-in-china-a-study-based-on-smart-system-of-disease-management-ssdm/. Accessed .« Back to 2019 ACR/ARP Annual Meeting
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/clinical-characteristics-and-the-level-disease-activity-of-behcets-disease-in-china-a-study-based-on-smart-system-of-disease-management-ssdm/