Session Information
Date: Monday, October 27, 2025
Title: (1147–1190) Miscellaneous Rheumatic & Inflammatory Diseases Poster II
Session Type: Poster Session B
Session Time: 10:30AM-12:30PM
Background/Purpose: Treatment of IgG4-related disease (IgG4-RD) is recommended for patients with severe organ involvement or for patients with reduced quality of life even in the absence of severe organ involvement. On the other hand, some patients with no severe lesions and acceptable quality of life, especially those with asymptomatic single organ disease, can be followed up without treatment. Therefore, we aimed to investigate the clinical characteristics and outcomes of patients without therapeutic intervention at the time of IgG4-RD diagnosis in single center.
Methods: Patients with IgG4-RD diagnosed from 2005 to 2024 according to the comprehensive diagnostic criteria for IgG4-RD revised in 2020 at our institution were included in our study. Clinical characteristics including IgG4-RD Responder Index (IgG4-RD RI) and immunological laboratory findings were retrospectively collected from medical records. In the cases observed without treatment after IgG4-RD diagnosis, we investigated whether the subsequent therapeutic intervention became necessary or not. We then analyzed the predictors of the need for treatment.
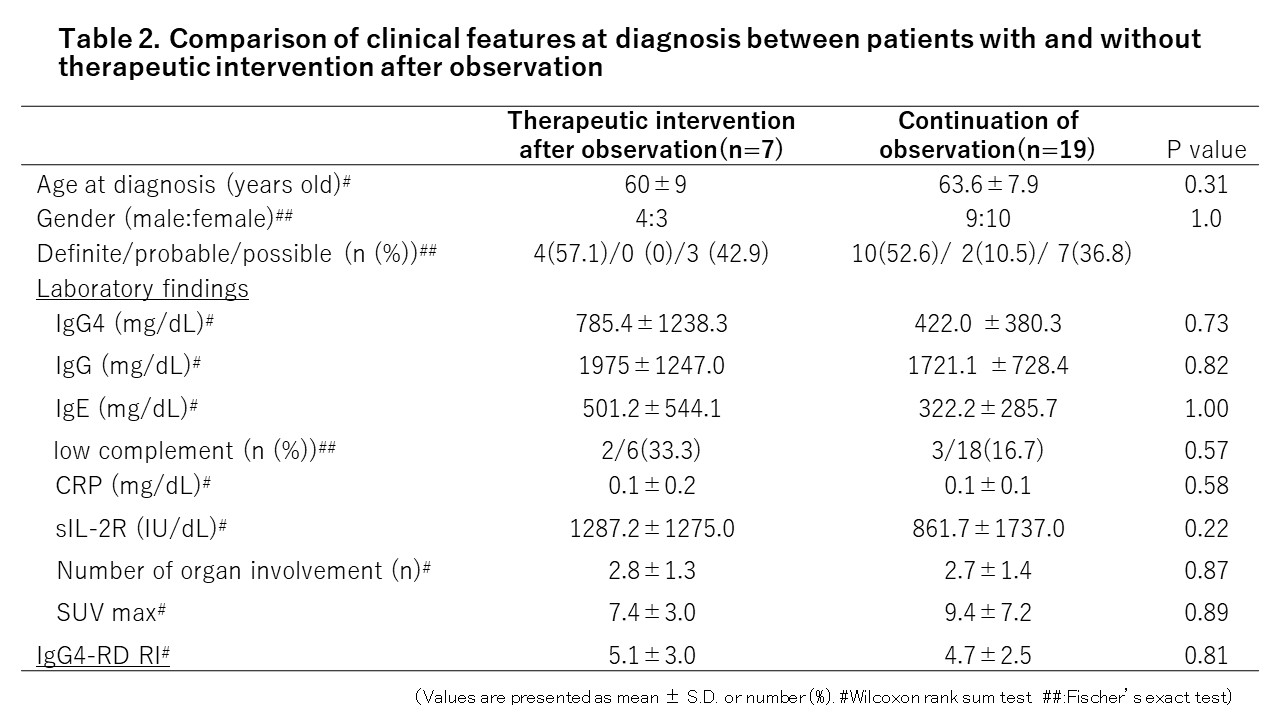
Results: Of all 80 cases diagnosed with IgG4-RD, 54 cases (67.5%) were started to treat at diagnosis (treatment group), while 26 cases (32.5%) were observed without therapeutic intervention (observation group).In the observation group, age at diagnosis was significantly younger and the levels of CRP, IgG, sIL-2R and IgG4-RD RI were lower. Serum IgG4 levels also tended to be lower compared to the treatment group (Table 1). Cases with only glandular and lymph node involvement were more common in the observation group. In contrast, patients with severe organ involvement such as retroperitoneal, renal, pancreatic, pulmonary and orbital lesions were more likely to have started treatment at the time of diagnosis (Figure 1).Of the 26 cases in the observation group, 7 required therapeutic intervention during the observation period. New organ involvement, including the pancreas, was observed in 5 cases. There were no significant differences in clinical characteristics at the time of diagnosis between the patients with (n=7) and without (n=19) treatment intervention (Table 2). The mean duration from diagnosis to the initiation of therapeutic intervention was 30 ± 25 months. Among the 19 cases without treatment intervention, 13 cases (68.4%) had multiple organ involvement, such as glandular, lymph node, and pulmonary involvement.
Conclusion: In our study, some cases of IgG4-RD could be observed without treatment, even with multiple lesions. It is important to have an appropriate monitoring strategy to determine the need for therapeutic intervention in IgG4-RD.
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Chujo K, Shimada H, Nakashima S, Miyagi T, Sugihara K, Ushio Y, Mizusaki M, Manabe N, Wada M, Wakiya R, Ozaki H, Dobashi H. Clinical Characteristics and Outcomes of IgG4-Related Disease Patients Who Chose Watchful Observation without Treatment Intervention: A Single-Center Study [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2025; 77 (suppl 9). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/clinical-characteristics-and-outcomes-of-igg4-related-disease-patients-who-chose-watchful-observation-without-treatment-intervention-a-single-center-study/. Accessed .« Back to ACR Convergence 2025
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/clinical-characteristics-and-outcomes-of-igg4-related-disease-patients-who-chose-watchful-observation-without-treatment-intervention-a-single-center-study/

.jpg)
.jpg)