Session Information
Session Type: Abstract Submissions (ACR)
Background/Purpose
Golimumab is a TNF inhibiting biological drug that was approved in Sweden in 2010 for the treatment of RA, PsA and AS. Our previous analyses have demonstrated similar drug adherence as for other TNF-inhibitors and better adherence in bio-naïve patients (Saevarsdottir S et al, ACR 2013). Given that, the aim of the current study in an updated dataset with longer follow-up time, was to investigate the differences in clinical characteristics and drug survival probability between golimumab treated patients that were bio-naïve compared to those previously exposed to biologicals, separately for patients with RA, PsA, AS as well as other SpA.
Methods
Data were retrieved for all patients initiating golimumab treatment in 2010-2013 from the nationwide SRQ register. A survival analysis (Kaplan Meier) was performed over 24 months with right censoring and log-rank test of equality across strata.
Results
Of 2106 patients initiating golimumab treatment during the study period, 849 (40%) had RA, 454 (22%) PsA, 303 (14%) AS, 242 (12%) SpA and 258 (12%) had other diagnoses. The proportions of women in RA/PsA/AS/SpA patient groups were 78%/50%/29%/55%, respectively; and their median age at baseline was 54/48/42/40 years. In patients with RA/PsA/AS/SpA, the proportions receiving golimumab as the first biological treatment were 48%/46%/42%/40%; and the proportions receiving concurrent disease-modifying anti-rheumatic drugs (DMARDs) were 76%/64%/32%/47%.
Several baseline characteristics differed between bio-naïve patients (0) and those previously exposed to biological treatment (1-2 or 3+ biologic drugs, see Table 1, parameters showing significant difference in each disease are mentioned below). Bio-naïve patients were less likely to have concurrent treatment with DMARDs (PsA, AS), prednisolone (all) and NSAID (all); and they reported lower HAQ (RA, PsA, SpA), DAS28 (RA, PsA), inflammatory markers (CRP/ESR: RA, SpA), VAS-global health (RA, PsA, SpA) and VAS-pain (RA) at baseline. Furthermore, bio-naïve were more likely to be male (RA, PsA), older (RA, PsA, AS) and with short disease duration (RA, AS, SpA).
The drug survival probability over 24 months was also higher in bio-naïve patients (RA, AS, trend for PsA but less so for SpA).
Conclusion
In this real-life nationwide cohort, patients starting golimumab as their first biologic were treated with co-medication to a lesser extent, but had more favorable prognostic factors, and better drug survival over two years compared to those previously treated with other biologics. Patterns were similar for the various rheumatologic diseases treated with golimumab. It is of major importance to take previous biologic exposure into account when evaluating new biologics in observational studies.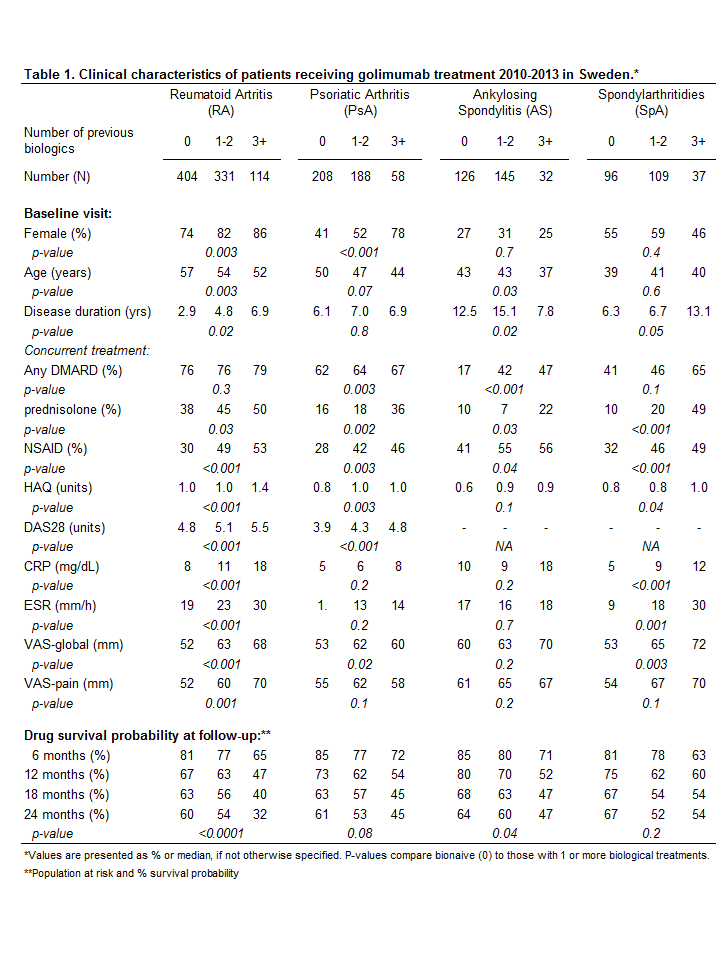
Disclosure:
S. Saevarsdottir,
None;
M. Santacatterina,
None;
C. Turesson,
Unrestricted research grants from Abbvie, Pfizer and Roche,
2,
Abvisory Boards: Bristol-Myers Squibb, MSD, Pfizer, Roche,
5;
H. Forsblad,
None;
L. Jacobsson,
None;
S. Lindblad,
None.
« Back to 2014 ACR/ARHP Annual Meeting
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/clinical-characteristics-and-outcome-of-golimumab-treatment-differs-between-bio-naive-and-patients-previously-exposed-to-biologicals-nationwide-results-on-rheumatoid-arthritis-ra-psoriatic-arthrit/
