Session Information
Date: Monday, November 14, 2022
Title: Systemic Sclerosis and Related Disorders – Clinical Poster III
Session Type: Poster Session D
Session Time: 1:00PM-3:00PM
Background/Purpose: Systemic sclerosis (SSc) is a chronic autoimmune disorder with microangiopathy and fibrosis affecting the skin and visceral organs. Interstitial lung disease (ILD) is a frequent complication of SSc and related to mortality. Although lung transplantation (LT) is a potential therapeutic option for advanced SSc-associated ILD (SSc-ILD), there is still little evidence of its long-term effect on SSc-ILD. We here aimed to assess clinical benefits and outcomes of LT on patients with advanced SSc-ILD.
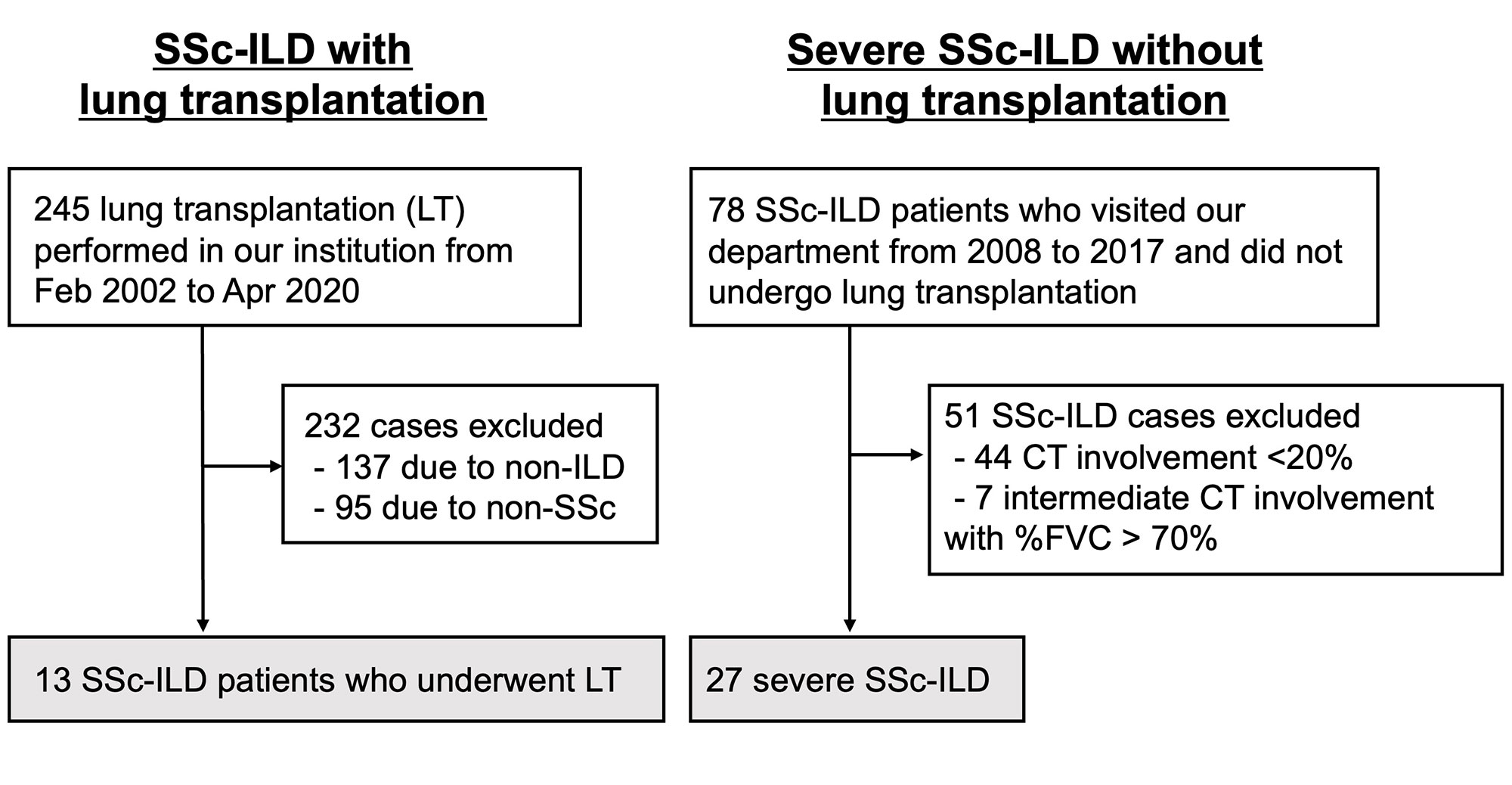
Methods: We conducted a single-center retrospective study. The cohort inclusion diagram is shown in Figure 1. Post-transplant outcomes of patients with SSc-ILD undergoing LT between February 2002 and April 2020 were analyzed. Overall survival of patients experiencing LT for SSc-ILD from the time of LT registration was compared to that of patients with extensive SSc-ILD who did not undergo LT.
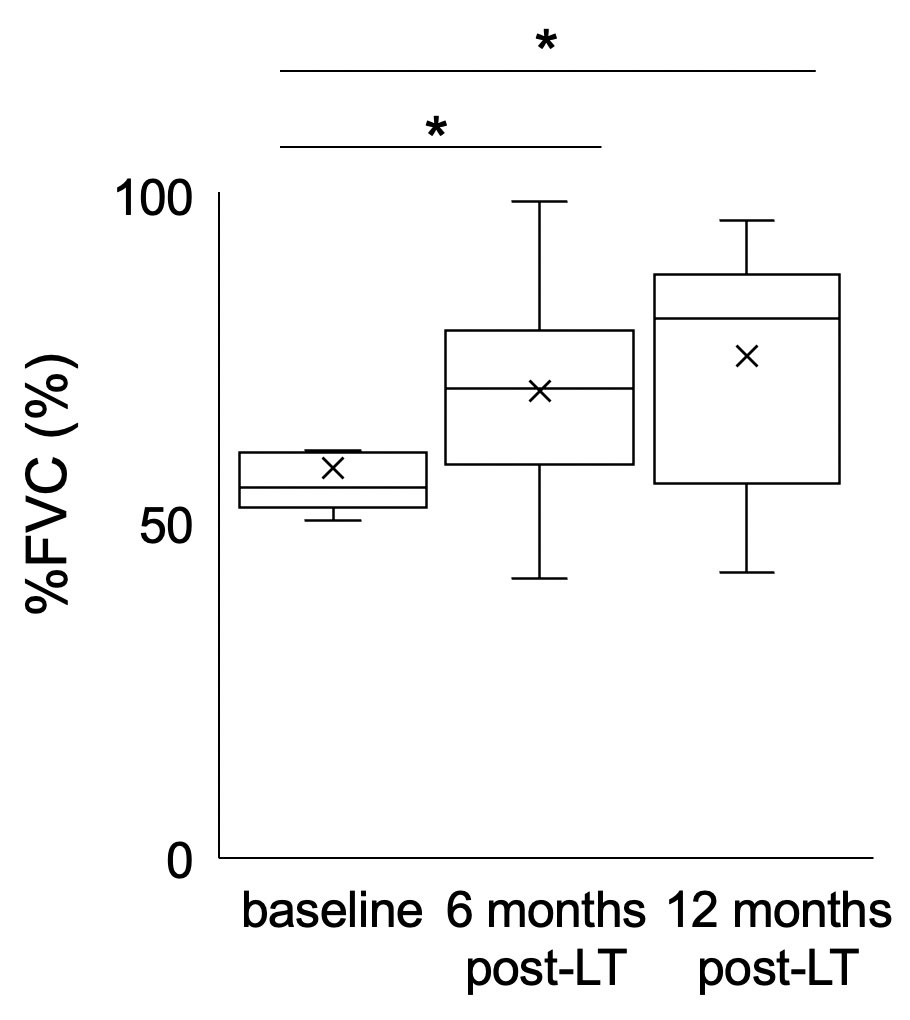
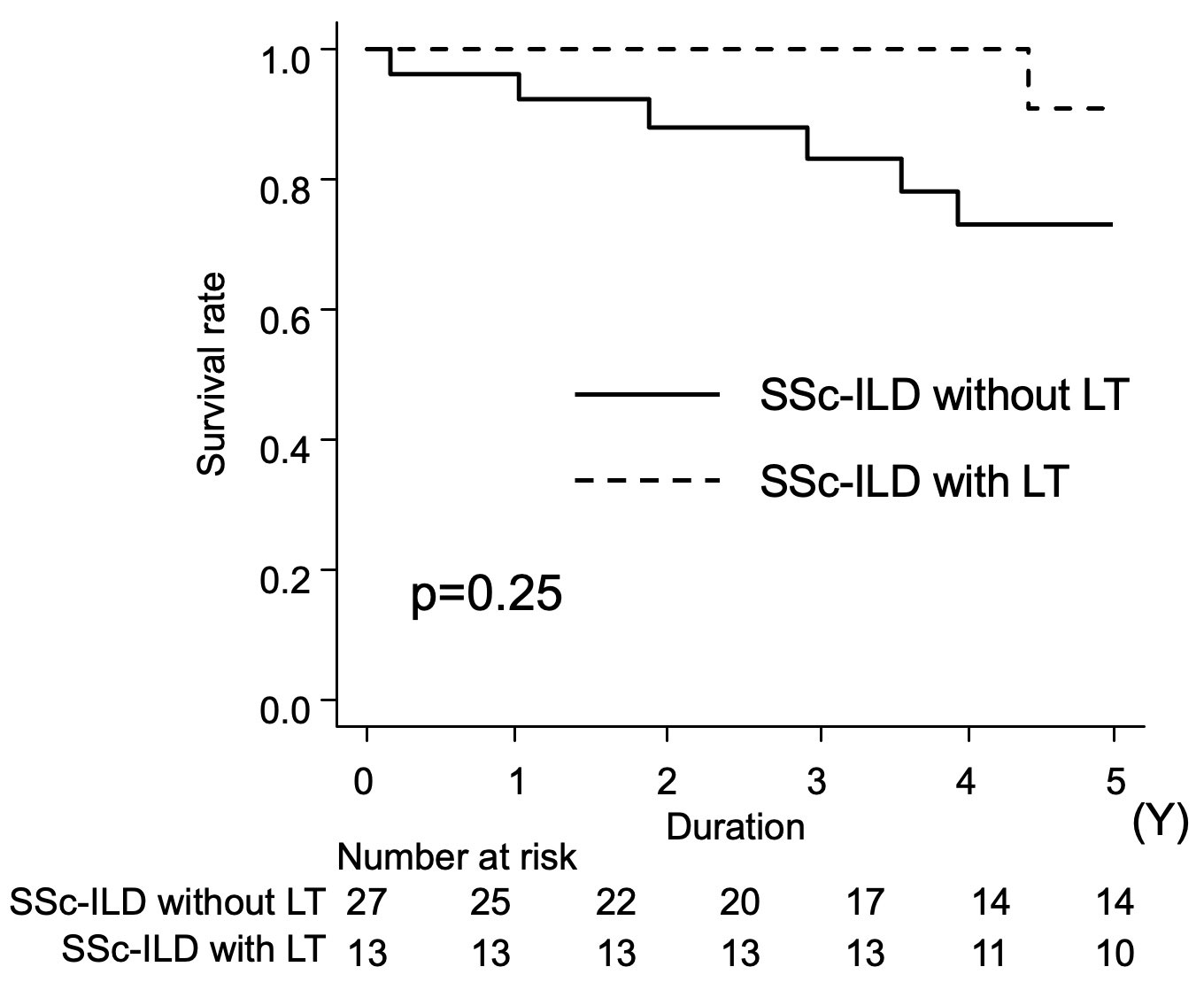
Results: Thirteen patients with SSc-ILD underwent LT and 27 patients did not undergo LT were extracted from the database. Regarding baseline characteristics, patients in the LT group were younger, had lower frequency of smoking history, higher frequency of gastrointestinal involvement and corticosteroid therapy. LT significantly improved the percentage to the predicted forced vital capacity significantly (Figure 2): the median of 56.1% at baseline; 70.8% at 6 months (P=0.002); and 81.2% at 12 months (P=0.003). There was no ILD relapse in transplanted lungs during the follow-up period (median, 59 months). No renal crisis was noted. Disease progression in the native lung was observed in two of the six single LT recipients. Eight out of twelve patients withdrew long-term oxygen therapy (LTOT) after LT. The estimated 5-year overall survival rates of SSc-ILD with LT and without LT were 90.9% and 72.9%, respectively (log-rank P = 0.25) (Figure 3).
Conclusion: LT for advanced SSc-ILD can be beneficial in terms of improving lung function, relief from LTOT and a favorable long-term survival, although survival benefit over medical therapy was not shown. Disease-specific indications for LT and the appropriate time of referral to LT centers in SSc-ILD should be sought in accordance with recent advances in medical therapy.
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Nakayama Y, Nakashima R, Handa T, Tanizawa K, Ohsumi A, Shirakashi M, Hiwa R, Tsuji H, Kitagori K, Akizuki S, Yoshifuji H, date H, Morinobu A. Clinical Benefits of Lung Transplantation in Systemic Sclerosis-related Interstitial Lung Disease; A Single-Center Retrospective Study [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2022; 74 (suppl 9). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/clinical-benefits-of-lung-transplantation-in-systemic-sclerosis-related-interstitial-lung-disease-a-single-center-retrospective-study/. Accessed .« Back to ACR Convergence 2022
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/clinical-benefits-of-lung-transplantation-in-systemic-sclerosis-related-interstitial-lung-disease-a-single-center-retrospective-study/