Session Information
Session Type: ACR Poster Session B
Session Time: 9:00AM-11:00AM
Background/Purpose: Focal lymphocytic sialadenitis (FLS) on minor salivary gland biopsy (MSGB) is one of the classification criteria for Sjögren’s syndrome (SS). As no diagnostic criteria exist, there is a need for timely diagnosis of seronegative patients (SSA and SSB antibody negative), to allow earlier intervention and prevent end-organ damage. There are only a few studies on how seronegative patients with FLS on MSGB differ clinically from seropositive patients (SSA and/or SSB antibody positive). Therefore, the objective of our study was to compare the clinical and laboratory features of patients with and without autoantibodies (anti-SSA and/or anti-SSB) among those with FLS on MSGB. As a secondary objective, we compared the clinical and laboratory features of those with and without FLS on MSGB among the seronegative patients only.
Methods: Cases > 18 years old with a MSGB performed at the University of Iowa Hospital and Clinics between 1/1/2000-12/31/2016 were identified, excluded patients with incomplete clinical and laboratory data. Then data was extracted by retrospective chart review. Fisher’s exact test or chi-square test was used to compare categorical variables between the groups; student’s t-test was used for comparison of continuous variables.
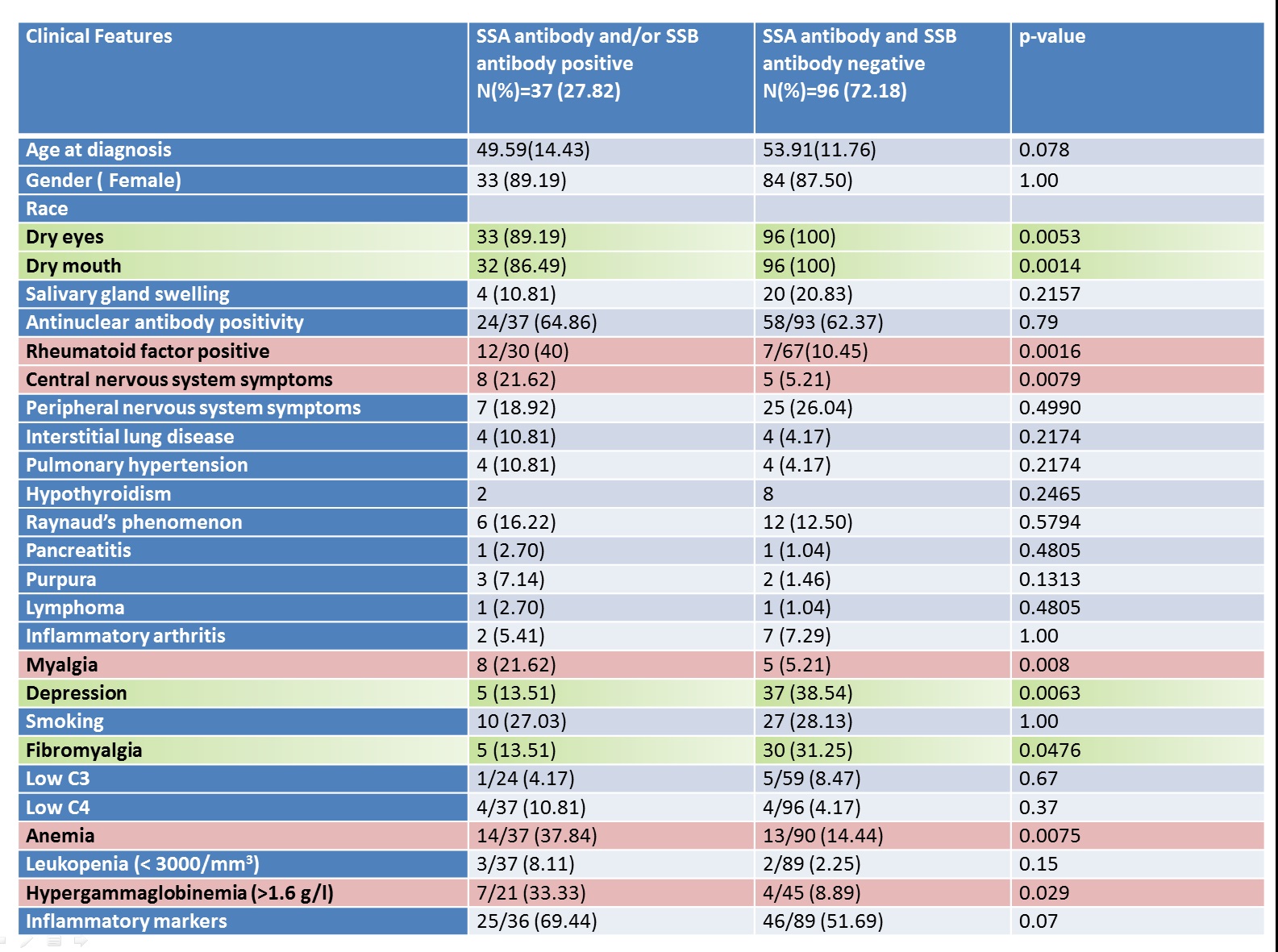
Results: During the study period 230 patients had MSGB done for sicca symptoms, 51 patients were excluded due to incomplete clinical data. FLS on MSGB was found in 133 patients, 27% (37/133) were seropositive and 72% (96/133) were seronegative. Dry eyes, dry mouth, fibromyalgia and depression, predominated as statistically significant clinical features in the seronegative group compared to the seropositive group (Table1– Among all MSGB positive patients, comparison of the clinical and laboratory features of those with and without SSA antibody and/or SSB antibody). Symptomatic seronegative patients who underwent MSGB were 137, and no FLS on MSGB was found in 41 patients. Smoking predominated as a statistically significant variable (p=0.0003) in the seronegative patients with no FLS on biopsy, whereas seronegative patients with a positive biopsy tended to be older and have more sicca symptoms.
Conclusion: Identifying the subset of symptomatic SS patients, who are seronegative is challenging. When patients have sicca symptoms, associated with other clinical features like fatigue, inflammatory arthritis, peripheral nervous system clinical symptoms; with no serological markers, these patients should be considered for a further evaluation by MSGB. Smoking can also cause sicca symptoms with no FLS on MSGB, this should be considered while evaluating the patients with sicca symptoms.
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Ayesha B, Fernandez-Ruiz R, Shrock D, Tuetken R, Lieberman S, Field E, Singh N. Clinical and Laboratory Features of Patients with Focal Lymphocytic Sialadenitis on Minor Salivary Gland Biopsy for Sicca Symptoms: A 16 Year Experience [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2017; 69 (suppl 10). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/clinical-and-laboratory-features-of-patients-with-focal-lymphocytic-sialadenitis-on-minor-salivary-gland-biopsy-for-sicca-symptoms-a-16-year-experience/. Accessed .« Back to 2017 ACR/ARHP Annual Meeting
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/clinical-and-laboratory-features-of-patients-with-focal-lymphocytic-sialadenitis-on-minor-salivary-gland-biopsy-for-sicca-symptoms-a-16-year-experience/