Session Information
Date: Saturday, November 7, 2020
Title: RA – Treatments Poster II: Comparative Effectiveness, Biosimilars, Adherence & the Real World
Session Type: Poster Session B
Session Time: 9:00AM-11:00AM
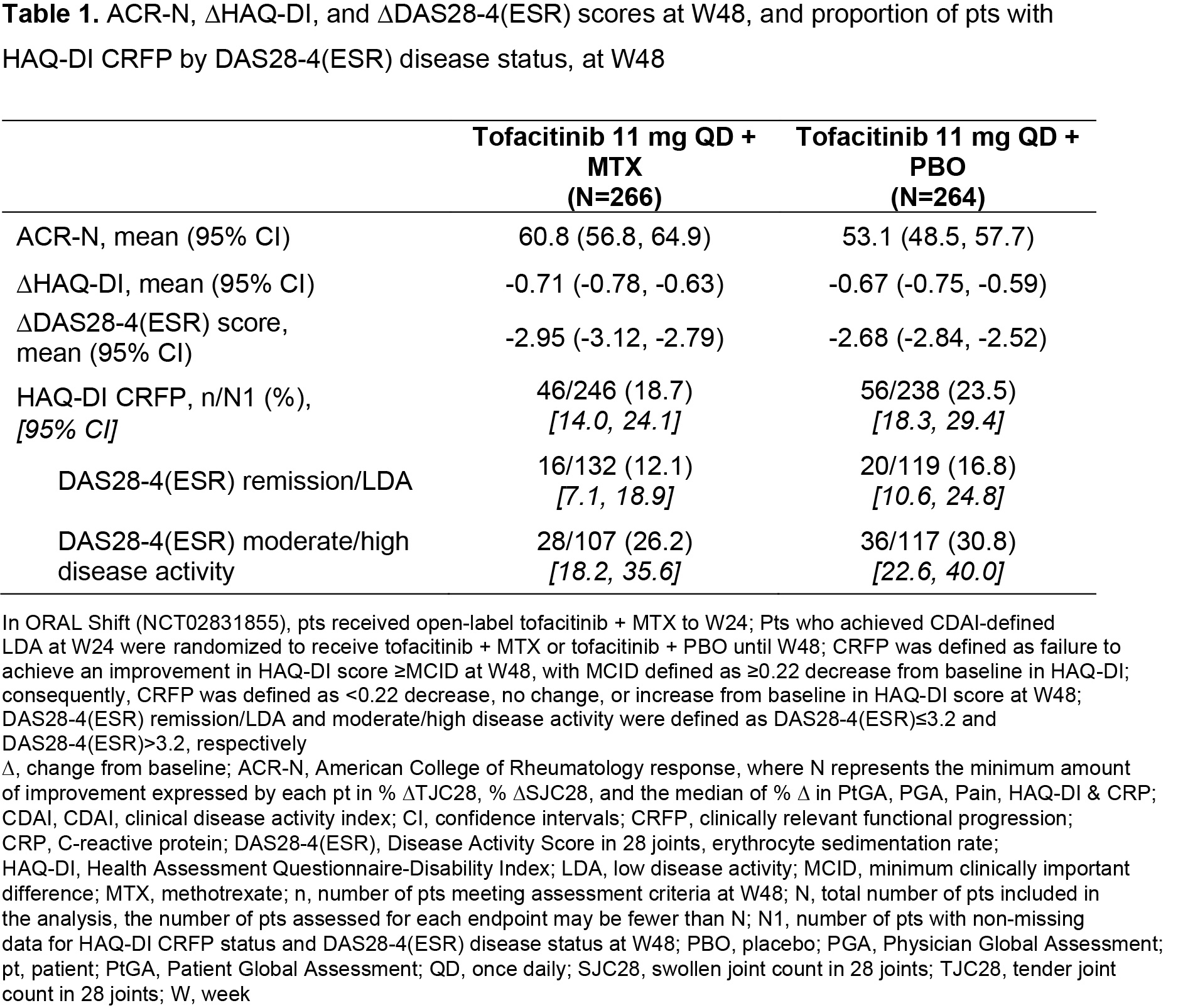
Background/Purpose: ORAL Shift (NCT02831855) was a 48-week Phase 3b/4 study, which demonstrated sustained efficacy/safety of tofacitinib modified release 11 mg once daily (QD) following MTX withdrawal, that was non-inferior to continued use of tofacitinib + MTX, in patients (pts) with moderate to severe RA who achieved low disease activity (LDA) with tofacitinib + MTX at Week (W)24.1 This post hoc analysis of data from ORAL Shift assessed the differences and similarities in clinical/functional responses in pts receiving tofacitinib ± MTX.
Methods: Clinical efficacy endpoints included ACR-N (minimum percentage change from baseline [∆] at W48 achieved by each pt in three efficacy measures), ∆Disease Activity Score in 28 joints, erythrocyte sedimentation rate (DAS28-4[ESR]), and DAS28‑4(ESR)-defined clinical remission/LDA and moderate/high disease activity (defined as DAS28‑4[ESR] ≤ 3.2 and > 3.2, respectively). Functional efficacy endpoints included ΔHAQ-Disability Index (HAQ-DI) score and clinically relevant functional progression (CRFP) status at W48, defined as failure to achieve an improvement in HAQ-DI score ≥ minimum clinically important difference (MCID; defined as ≥ 0.22 decrease from baseline in HAQ-DI). Consequently, CRFP was defined as < 0.22 decrease, no change, or increase from baseline in HAQ-DI at W48. Cumulative probability plots of ACR-N and HAQ-DI at W48 were used to evaluate tofacitinib ± MTX efficacy. Descriptive statistics were produced for all efficacy endpoints; median of mean CRP values from > baseline–W24 and > W24–W48 were assessed by response subgroups.
Results: The analysis included 266 and 264 pts receiving tofacitinib + MTX and tofacitinib + placebo (PBO), respectively, from W24–W48. Cumulative probability plots and descriptive statistics suggested that overall ACR-N responses and mean ACR-N at W48 were numerically greater in pts receiving tofacitinib + MTX vs tofacitinib + PBO (Figure 1a, Table 1); ΔHAQ‑DI at W48 was generally similar between groups (Figure 1b; Table 1). ∆DAS28‑4(ESR) was numerically greater in pts receiving tofacitinib + MTX vs tofacitinib + PBO (Table 1). A lower proportion of pts receiving tofacitinib + MTX vs tofacitinib + PBO had CRFP; CRFP rates were numerically lower in pts with remission/LDA vs moderate/high disease activity (Table 1). Median of mean CRP over time was generally numerically lower in pts with CRFP vs non‑CRFP in pts with DAS28-4(ESR)-defined remission/LDA vs moderate/high disease activity, and in pts receiving tofacitinib + PBO vs tofacitinib + MTX, irrespective of CRFP or DAS28‑4(ESR) disease status (Table 2).
Conclusion: Although clinical and functional responses were generally similar between treatment groups overall, numerical improvements were observed in some efficacy endpoints with tofacitinib + MTX, compared with tofacitinib + PBO. A numerically higher rate of CRFP may be associated with higher DAS28‑4(ESR) disease activity. Changes in CRP up to W48 may not trend with CRFP status.
- Cohen SB et al. Lancet Rheumatol 2019; 1: e23-e34.
Acknowledgments: Study sponsored by Pfizer Inc. Medical writing support was provided by Anthony G McCluskey, CMC Connect, and funded by Pfizer Inc.
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Cohen S, Chen Y, Sugiyama N, Rivas J, Diehl A, Lukic T, Paulissen J, Fan H, Hirose T, Keystone E. Clinical and Functional Response to Tofacitinib in Patients with Rheumatoid Arthritis: Probability Plot Analysis of Results from a Phase 3b/4 Methotrexate Withdrawal Study [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2020; 72 (suppl 10). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/clinical-and-functional-response-to-tofacitinib-in-patients-with-rheumatoid-arthritis-probability-plot-analysis-of-results-from-a-phase-3b-4-methotrexate-withdrawal-study/. Accessed .« Back to ACR Convergence 2020
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/clinical-and-functional-response-to-tofacitinib-in-patients-with-rheumatoid-arthritis-probability-plot-analysis-of-results-from-a-phase-3b-4-methotrexate-withdrawal-study/