Session Information
Session Type: Poster Session C
Session Time: 10:30AM-12:30PM
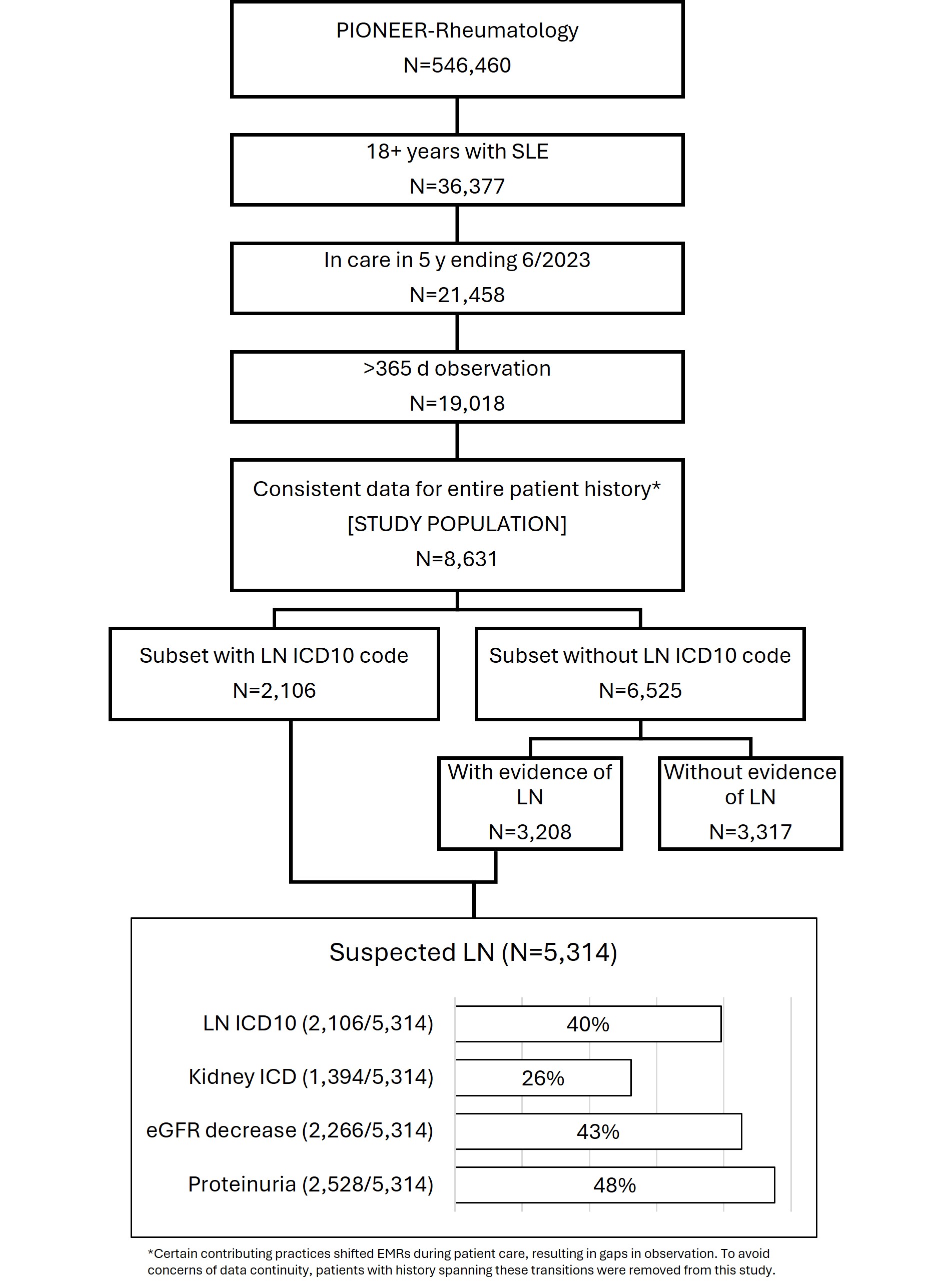
Background/Purpose: Lupus nephritis (LN) has been estimated to develop in up to 40% of all patients with systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE), with higher rates in subsets based upon demographic or other factors. In this study of patients with SLE in care of community rheumatologists, we identified a population with suspected LN based upon ICD codes and indicators of kidney impairment.
Methods: A retrospective analysis of the American Rheumatology Network (ARN) electronic medical records database included patients with ≥2 diagnosis codes for SLE and an observation window of at least 365 days between July 2018 and June 2023. Individual patient observation windows were calculated from the first date of observation by ARN i.e. the index date. Suspected LN criteria included a qualifying events of (1) ICD 10 codes for lupus nephritis, (2) ICD codes indicative of kidney conditions such as nephrotic/nephritic syndrome, hematuria, proteinuria, chronic kidney disease, and end-staged kidney disease, (3) eGFR decrease ≥20% occurring >30 days past initial measure and ≤72 ml/min/1.73m2, and/or (4) evidence of proteinuria by a) protein test strip 3+ or higher, b) protein in urine >14 mg/dL (or >150mg/day), and/or c) UPCR >0.5 mg/mg.
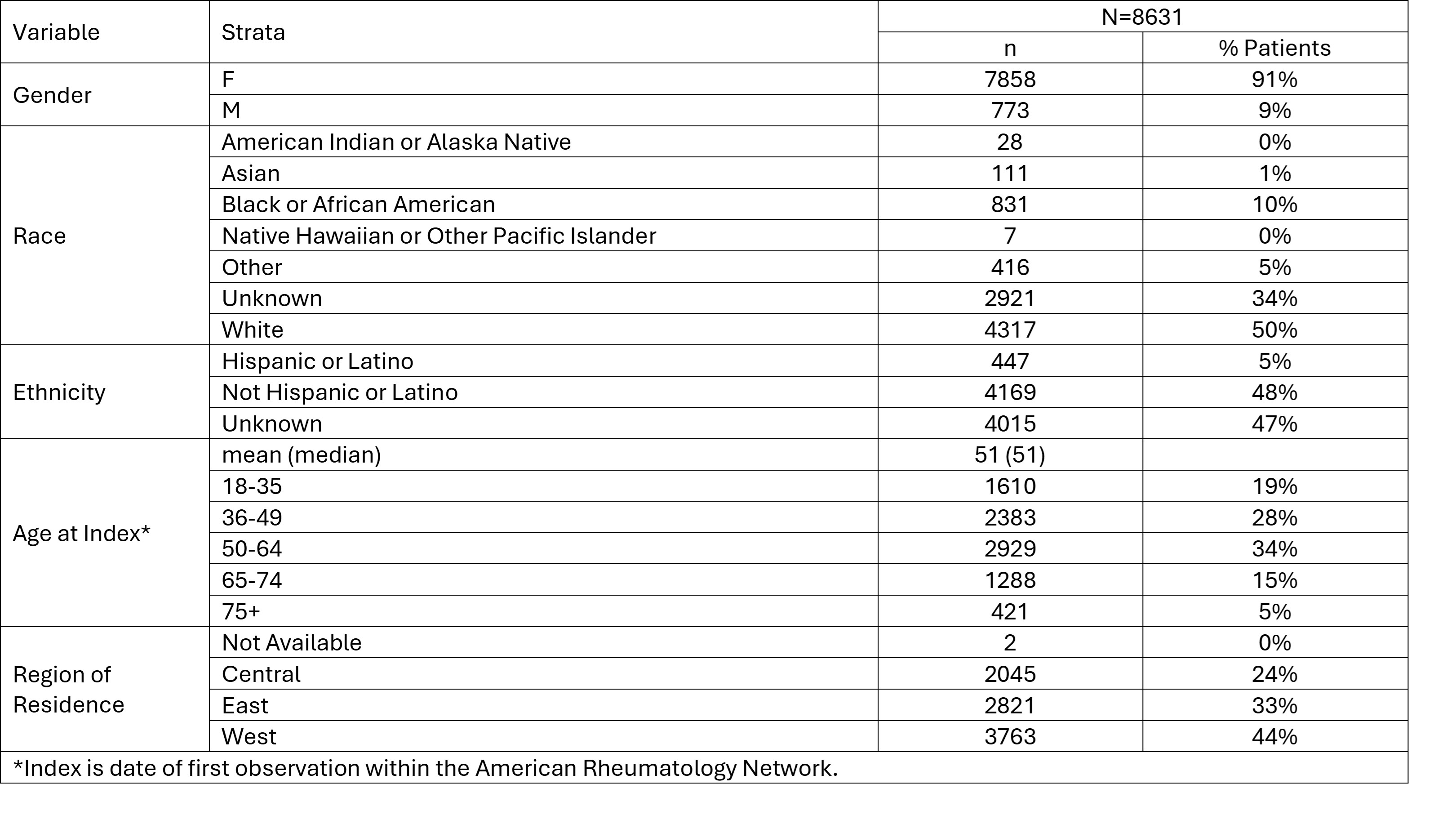
Results: A total of 8631 patients were included in the study. [FIGURE] Overall, 62% (5314/8631) of patients were identified as having suspected LN; 40% (2106/5314) with ICD 10 LN code; 26% (1394/5314) had an ICD 10 code associated with kidney conditions; 43% (2266/5314) had eGFR decrease events; 48% (2528/5314) had proteinuria. The study population was 91% female and 50% White race; 50% of patients were at least 50 years of age at the index date. Demographics of the study population and cohorts are provided in the TABLE.
Conclusion: This study provides real world descriptive demographic information characterizing patients with lupus receiving treatment in a community setting. Nearly two-thirds of patients had ICD 10 coding or clinical laboratory measures suggestive of renal involvement. Regular screening for proteinuria and hematuria via urinalysis may result in earlier detection and intervention to minimize long term renal organ damage.
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Soloman N, Bilal J, Cabacungan R, Milligan S, Sharobeem A, Tesser J, Leher H. Characterizing the Population with Suspected Lupus Nephritis in Care of a Community Rheumatology Network [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2024; 76 (suppl 9). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/characterizing-the-population-with-suspected-lupus-nephritis-in-care-of-a-community-rheumatology-network/. Accessed .« Back to ACR Convergence 2024
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/characterizing-the-population-with-suspected-lupus-nephritis-in-care-of-a-community-rheumatology-network/