Session Information
Date: Monday, November 18, 2024
Title: Vasculitis – Non-ANCA-Associated & Related Disorders Poster III
Session Type: Poster Session C
Session Time: 10:30AM-12:30PM
Background/Purpose: IgG4-related disease (IgG4-RD) is a systemic fibroinflammatory condition characterized by tissue infiltration with IgG4+ plasma cells. Fibrosis in the target organs is one of the main features of the disease. Diverse fibroblast subsets have been implicated in fibrotic diseases. The repertoire of tissue fibroblasts in IgG4-RD has not been explored, so the study’s objective focuses on determining them in IgG4-related ophthalmic disease (IgG4-ROD).
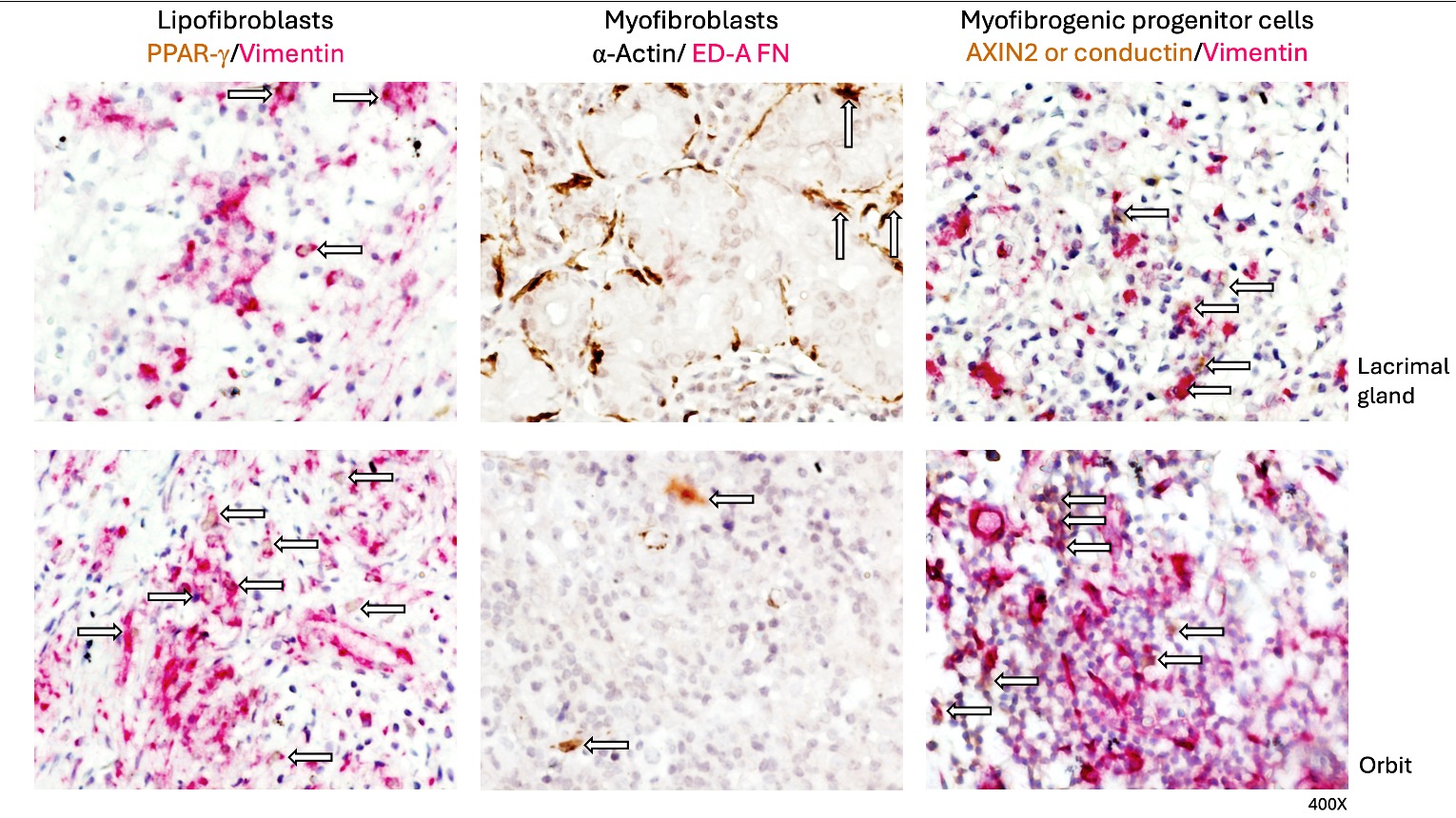
Methods: This was a cross-sectional study including patients fulfilling the 2019 ACR/EULAR classification criteria for IgG4-RD with an available tissue specimen from the orbital region. Patients were categorized into clinical phenotypes: pancreatobiliary, retroperitoneal/aortic, head and neck limited, Mikulicz/systemic, proliferative, and fibrotic. Lipofibroblasts (PPAR-g+/vimentin+), myofibroblasts (α-Actin+/ED-A FN+), and myofibrogenic progenitor cells (AXIN2 or conductin+/vimentin+) subsets were determined by immunohistochemistry. At least two sections of orbital tissue or lacrimal gland and three fields (×400) were examined for each biopsy. Double immunostained cells were reported as the percentage of immunoreactive cells. Results are expressed as the median (IQR) of cells quantified (Figure 1).
Results: We included 9 patients with a mean age at diagnosis of 41.1 ± 15.4 years; 7 (77.7%) were female. Five (55.6%) belonged to the head and neck-limited and 4 (44.4%) to the Mikulicz/systemic phenotypes, while 6 (66.7%) belonged to the proliferative and 3 (33.3%) to the fibrotic phenotypes.
We evaluated 9 tissue specimens, all corresponding to excisional biopsies of orbital structures, including 5 from lacrimal glands and four from other orbital tissues (i.e. extraocular muscle, orbital fat, and conjunctiva). All the biopsies had dense lymphoplasmacytic infiltrates and fibrosis, arranged in a storiform pattern only in 3 (33.3%), and obliterative phlebitis in 2 (22.2%). The median IgG4+ plasma cell count was 30 (IQR 30-100), and the median IgG4+/IgG+ ratio was 60% (IQR 34-100).
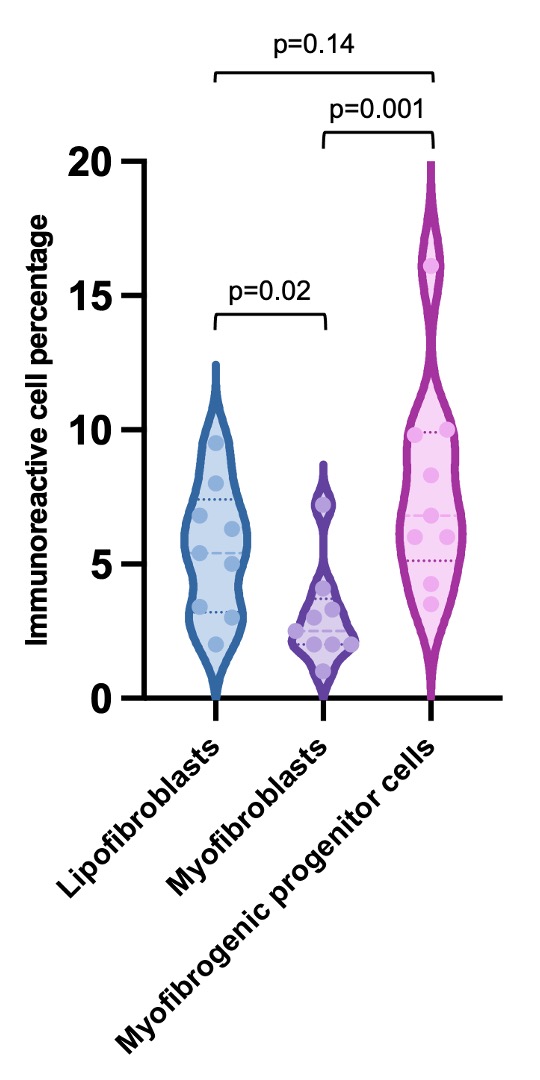
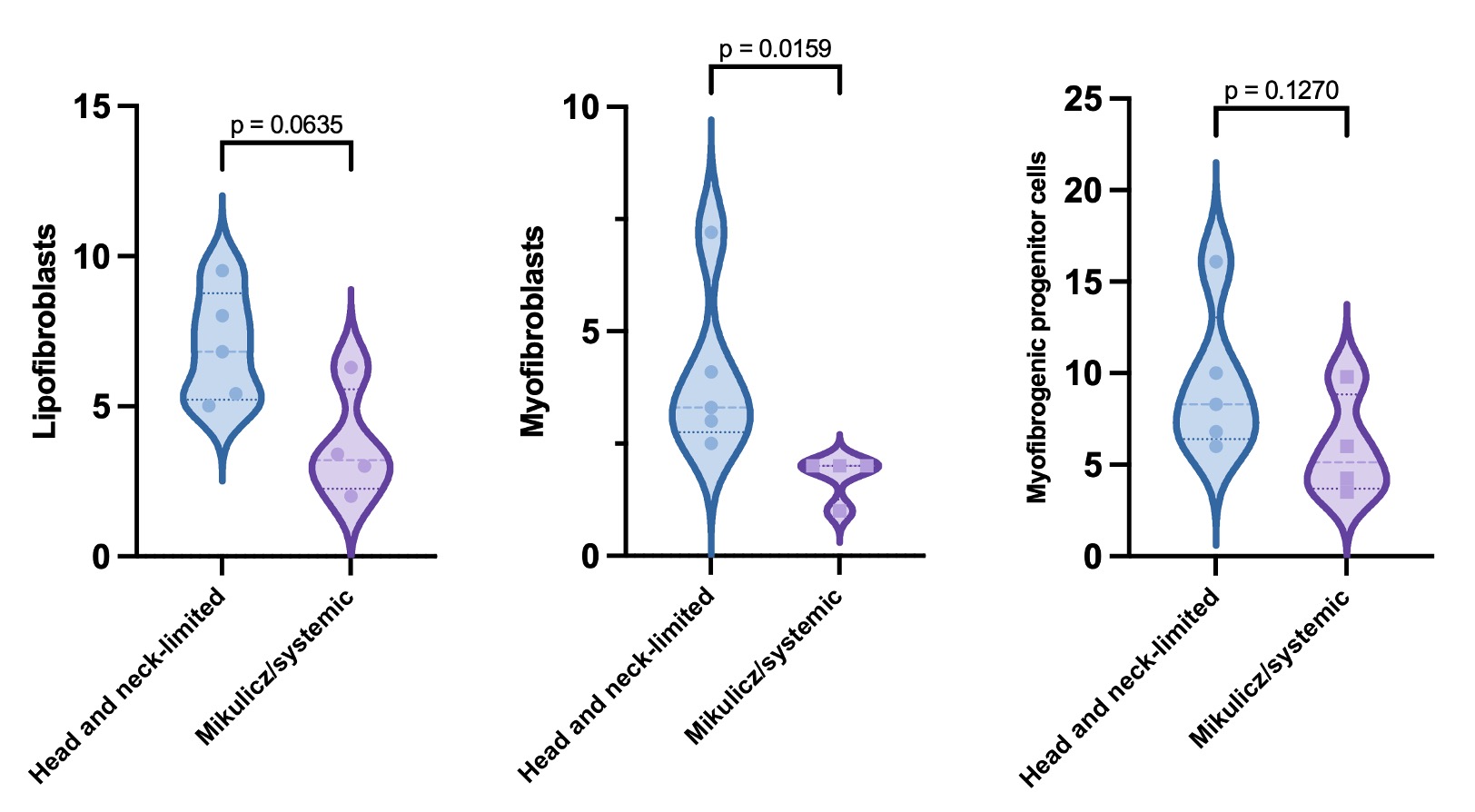
The percentages of lipofibroblasts (5.4 [IQR 3.2-7.4]) and myofibrogenic progenitor cells (6.8 [IQR 5.1-9.9]) were higher compared to myofibroblasts (2.5 [IQR 2-3.7]) (p=0.004) (Figure 2). The percentages of myofibroblasts were higher in biopsies from patients with the head and neck-limited compared to those with the Mikulicz/systemic phenotype (3.3 [IQR 2.8-5.6] vs. 2 [IQR 1.2-2], p=0.01) (Figure 3). Lipofibroblasts showed a tendency towards higher numbers (6.8 [IQR 5.2-8.7] vs. 3.2 [IQR 2.3-5.6], p=0.06), while the percentages of myofibrogenic progenitor cells did not differ (8.3 [IQR 6.4-13.1] vs. 5.1 [IQR 3.7-8.8], p=0.12). There was no difference in the presence of the three fibroblast subsets between the proliferative and fibrotic phenotypes or between the lacrimal gland and other orbital tissues.
Conclusion: Our findings show the presence of a heterogeneous fibroblast repertoire in IgG4-ROD. Higher percentages of lipofibroblasts and myofibrogenic progenitor cells were observed compared to myofibroblasts in IgG4-ROD, with a significant difference in the myofibroblast percentages between head and neck-limited and Mikulicz/systemic phenotypes.
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Martin Nares E, Hernández-Molina G, Aguilar-León D, Uribe-Uribe N, Furuzawa-Carballeda J. Characterization of the Tissue Fibroblast Repertoire in IgG4-Related Ophthalmic Disease [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2024; 76 (suppl 9). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/characterization-of-the-tissue-fibroblast-repertoire-in-igg4-related-ophthalmic-disease/. Accessed .« Back to ACR Convergence 2024
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/characterization-of-the-tissue-fibroblast-repertoire-in-igg4-related-ophthalmic-disease/