Session Information
Session Type: Poster Session (Sunday)
Session Time: 9:00AM-11:00AM
Background/Purpose: Across all phase 3 studies, treatment with upadacitinib (UPA), a JAK1-selective inhibitor, was associated with significantly higher remission (REM) rates, compared to placebo (PBO) or active comparators in RA patients (pts) who were methotrexate (MTX)-naive, had inadequate response to conventional synthetic (csDMARD-IR) or had inadequate response or intolerance to biologic DMARDs (bDMARD-IR).
REM definitions are based on composite scores of various individual assessments of disease activity. To determine the response to UPA on REM and component assessments, we assessed the proportions of pts achieving REM using multiple REM definitions, and the improvement in their respective individual components, compared to PBO or active comparators, in 3 different RA pt populations spanning a range of RA pt populations.
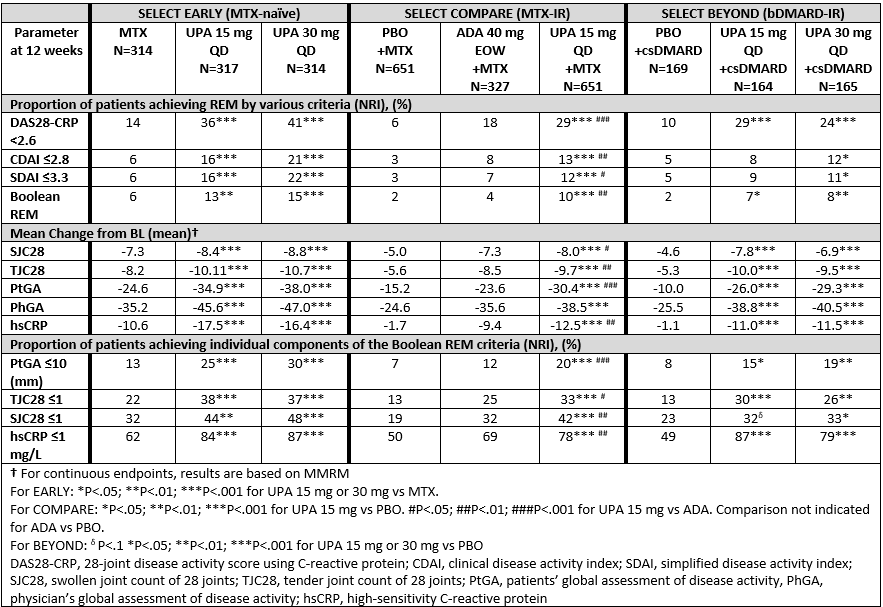
Methods: Three phase 3 studies included pts who were MTX naïve (SELECT EARLY, n=945), MTX-IR (SELECT COMPARE, n=1629) and bDMARD-IR (SELECT BEYOND, n=498). The proportion of pts achieving REM at Week (Wk) 12 by 4 definitions (DAS28-CRP< 2.6; CDAI ≤2.8; SDAI ≤3.3 and Boolean, defined as ≤1 for TJC, SJC, patient’s global assessment of disease activity [PtGA], and CRP ≤1 mg/L) were determined. For each definition of REM, the mean change in each of the respective component scores was also assessed. Binary endpoints are based on Non-responder imputation (NRI), and continuous endpoints on mixed-effect model repeat measurement (MMRM). Comparisons were made between UPA-treated groups vs respective control arms (MTX, adalimumab [ADA] or PBO).
Results: Pt demographics and disease characteristics have been previously reported. 1-3 At 12 wks, in EARLY and COMPARE, a significantly greater proportion of pts receiving UPA 15 mg or 30 mg QD achieved REM by all 4 definitions vs MTX, PBO or ADA (Table). In BEYOND, (a refractory population many of whom had inadequate response to multiple bDMARDs), a significantly greater proportion of pts receiving UPA 30mg achieved all REM definitions vs PBO within the first 12 wks, with significantly greater proportions receiving UPA 15mg achieving DAS28-CRP< 2.6 and Boolean REM (Table). Rates of REM in BEYOND further increased through Wk 24 for both dose groups.1 Compared to respective control groups, pts receiving UPA 15 or 30 mg QD had significantly greater improvements in each REM disease component (except for PhGA vs ADA in COMPARE). Significantly more pts receiving UPA also achieved the required cutoffs on the individual components of Boolean REM compared to respective controls.
Conclusion: Significantly greater proportions of pts receiving UPA 15 or 30mg achieved REM by multiple definitions at 12 wks compared to PBO, MTX or ADA. All disease activity components of each REM definition were significantly improved in pts receiving UPA compared to MTX or PBO, and all Boolean components were significantly improved in pts receiving UPA 15mg compared to ADA.
1. Genovese et al 2018;Lancet.18;31116-4
2. van Vollenhoven R et al. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2018;70 -supp10-
3. Fleischmann et al. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2018;70 -supp10-
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Hall S, Takeuchi T, Thomson G, Emery P, Combe B, Everding A, Pavelka K, Song Y, Shaw T, Friedman A, Song I, Mysler E. Characterization of Remission in Patients with Rheumatoid Arthritis Treated with Upadacitinib or Comparators [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2019; 71 (suppl 10). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/characterization-of-remission-in-patients-with-rheumatoid-arthritis-treated-with-upadacitinib-or-comparators/. Accessed .« Back to 2019 ACR/ARP Annual Meeting
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/characterization-of-remission-in-patients-with-rheumatoid-arthritis-treated-with-upadacitinib-or-comparators/