Session Information
Date: Sunday, October 26, 2025
Title: (0731–0764) Vasculitis – Non-ANCA-Associated & Related Disorders Poster I
Session Type: Poster Session A
Session Time: 10:30AM-12:30PM
Background/Purpose: Giant cell arteritis (GCA) is a chronic granulomatous vasculitis affecting medium- and large-sized arteries (1). The classic symptoms are cranial symptoms, including headache, jaw claudication, scalp hyperalgesia and sometimes visual disturbances. Additionally, extracranial involvement may occur due to stenosis and aneurysms in different segments of the aorta, potentially leading to pulse loss and limb claudication. Polymyalgia rheumatica (PMR) is a disease characterized by pain and stiffness in the cervical region and/or the shoulder and/or pelvic girdles (2). Approximately, 50% of patients with GCA also present with PMR (3).The aim of this study was to define the clinical, analytical and imaging characteristics, as well as the factors associated with PMR in patients with GCA.
Methods: The ARTESER study (Arteritis of the Spanish Society of Rheumatology), promoted by the Spanish Society of Rheumatology, is a longitudinal observational study based on a review of clinical records of patients diagnosed with GCA between June 1, 2013, and March 29, 2019, in 26 hospitals of the Spanish National Health System. Sociodemographic, clinical, analytical, and imaging variables at diagnosis were collected. Additionally, treatment and outcome variables were recorded at the end of follow-up. Patients with and without PMR were compared through a bivariate analysis. To identify potential factors associated with PMR, a multivariate logistic regression model was performed. Statistical significance set at p< 0.05.
Results: A total of 1,527 patients with GCA were included in the analysis, of whom 43.6% presented with PMR at the time of diagnosis (Table 1). When comparing patients with and without PMR at diagnosis, it was observed that patients with PMR had a higher proportion of women, were younger, and had a longer duration of symptoms (p< 0.05). Regarding comorbidities, patients with PMR showed lower rates of smoking and a higher frequency of osteoporosis. They also more frequently presented scalp hypersensitivity, jaw claudication, and constitutional syndrome (p< 0.05). Regarding treatment, the initial dose of corticosteroids at diagnosis was lower in patients with PMR (p< 0.001). When evaluating outcomes, patients with PMR experienced more relapses, with minor relapses being particularly more frequent in this group (p=0.024). In the multivariate analysis, factors associated with PMR were longer symptom duration at diagnosis, the presence of jaw claudication, asthenia, and synovitis. Conversely, the initial dose of glucocorticoids was associated with a lower risk of PMR (Table 2).
Conclusion: Patients with GCA and PMR present a longer duration of symptoms at diagnosis, higher prevalence of osteoporosis, scalp hypersensitivity, jaw claudication, constitutional syndrome, cranial phenotype and a lower initial corticosteroid dose. Factors associated with PMR included longer symptom duration, jaw claudication, asthenia and synovitis, while the initial corticosteroid dose was associated with a lower risk of PMR.
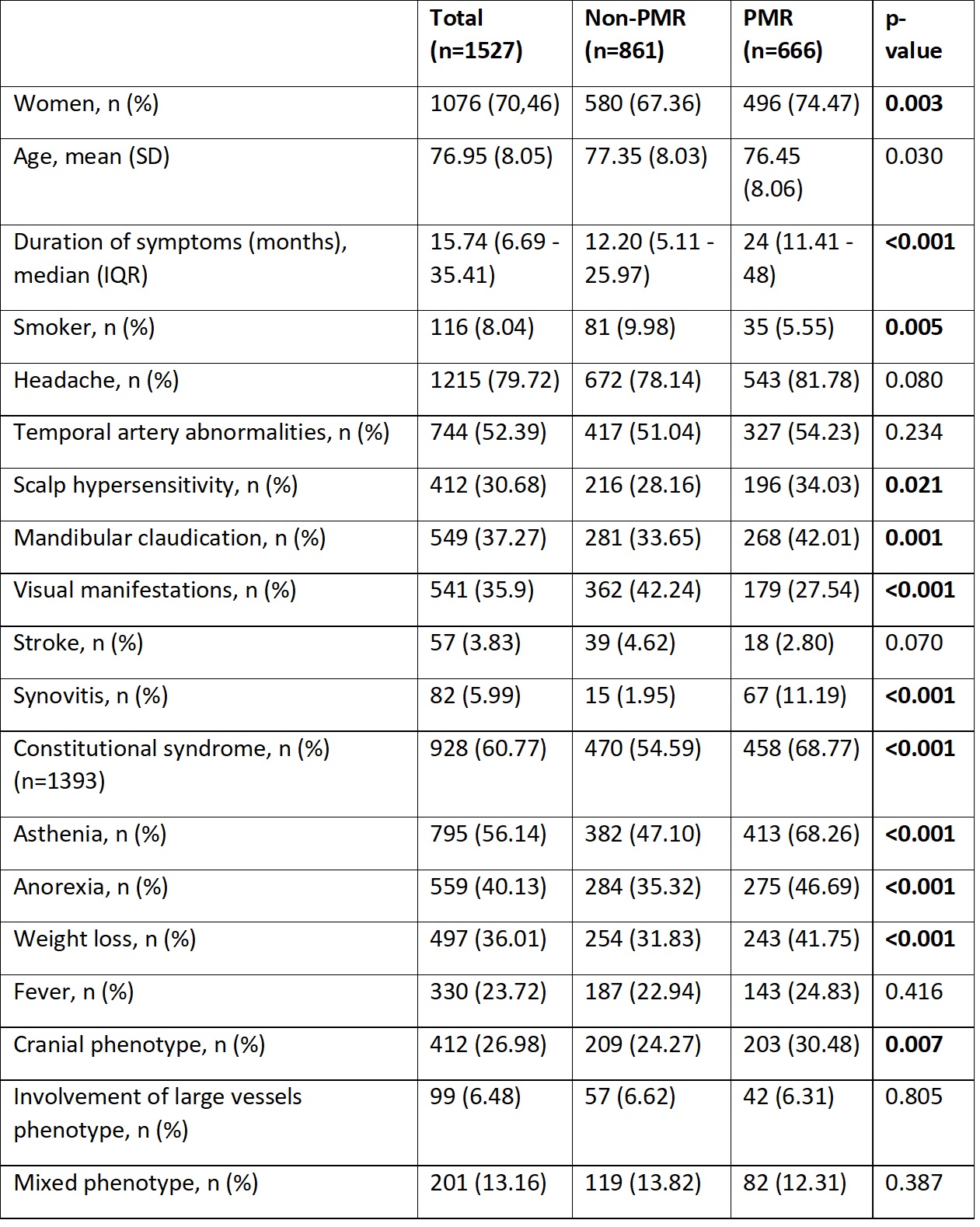 Table 1. Demographic characteristics, clinical variables and phenotypes of patients with GCA according to presence of PMR
Table 1. Demographic characteristics, clinical variables and phenotypes of patients with GCA according to presence of PMR
.jpg) Table 2. Multivariate analysis
Table 2. Multivariate analysis
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Silva-Diaz M, Domínguez-Álvaro M, Melero-González R, Fernández-Fernández E, Valero J, González I, Sánchez Martín J, Narváez J, Galíndez Agirregoikoa E, Aldasoro Cáceres V, Abasolo Alcazar l, Loricera J, Garrido N, Castañeda S, Iñiguez C, Garcia A, Molina Almela C, Alcalde Villar M, Mas A, Blanco R. Characterization of patients with polymyalgia rheumatica in the ARTESER giant cell arteritis cohort [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2025; 77 (suppl 9). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/characterization-of-patients-with-polymyalgia-rheumatica-in-the-arteser-giant-cell-arteritis-cohort/. Accessed .« Back to ACR Convergence 2025
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/characterization-of-patients-with-polymyalgia-rheumatica-in-the-arteser-giant-cell-arteritis-cohort/
