Session Information
Date: Tuesday, November 14, 2023
Title: (1913–1944) Miscellaneous Rheumatic & Inflammatory Diseases Poster III
Session Type: Poster Session C
Session Time: 9:00AM-11:00AM
Background/Purpose: Interstitial lung disease (ILD) comprises a wide range of disorders categorized by clinical, radiographic and pathologic findings that is closely associated with autoimmune connective tissue diseases (CTD), requiring an investigation into a potential unknown CTD when diagnosing ILD. A significant number of patients can exhibit nonspecific signs of autoimmunity, either clinical and/or serologic, without meeting the criteria for a distinct CTD, which has led to the classification of this disease as Interstitial Pneumonia with Autoimmune Features (IPAF). In our study, we aim to characterize a cohort of patients with ILD who satisfy the IPAF criteria.
Methods: We collected data of patients assessed in a multidisciplinary clinic of Pneumology and Rheumatology at the Marqués de Valdecilla University Hospital (Santander, Spain). Included patients had a confirmed diagnosis of ILD, determined either through a chest high-resolution computed tomography (HRCT) or lung biopsy. Medical records were examined to assess clinical and/or serologic IPAF criteria, as well as HRCT and lung biopsy reports. Exclusion from the study took place if patients met classification criteria for a distinct CTD or if there was incomplete data to asses their case.
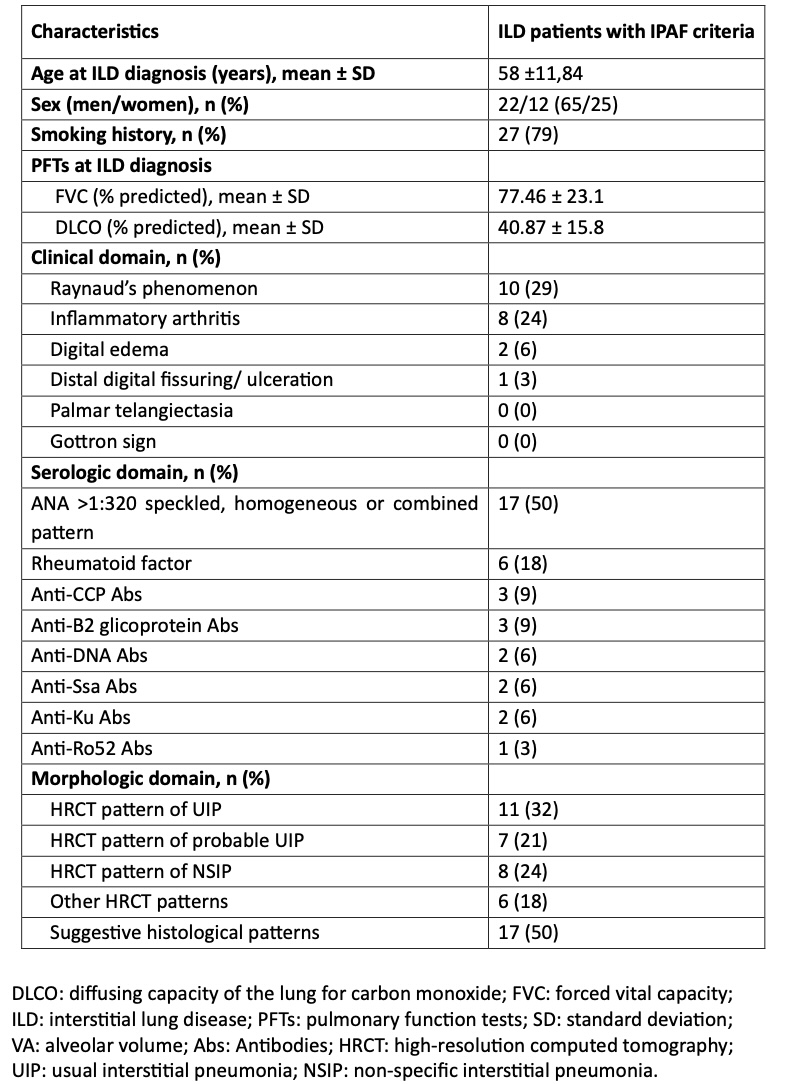
Results: From a cohort of 689 patients with ILD, we included a total of 34 individuals who fulfilled the criteria for IPAF. Among them, mean age at diagnosis was 58 ±11,84. 22 (65%) were male and 12 (35%) female. 27 (79%) had smoking history. 15 out of the 34 patients (44%) met the clinical criteria for IPAF, being Raynaud’s phenomenon the most frequent (n=10), followed by inflammatory arthritis (n=8), digital edema (n=2) and digital ulceration (n=1). Serologic criteria for IPAF were fulfilled by 28 out of 34 patients (84%). The most prevalent serologic criterion was the presence of an ANA higher than 1:320 (patterns: speckled, homogeneous or combined. n=17) followed by positive rheumatoid factor (n=6), anti-CCP (n=3), anti-ß2 glicoprotein (n=3), anti-DNA (n=2), anti-Ssa (n=2), anti-Ku (n=2) and anti-Ro52 (n=1). As for radiologic and morphologic criteria, 30 patients (88%) met the requirements for IPAF, being usual interstitial pneumonia (UIP) (n=11) the most frequently observed, followed by probable UIP pattern (n=7) and non-specific interstitial pneumonia (NSIP) (n=8). Table 1 shows the demographic, clinical, serologic and morphologic features of our patients.
Conclusion: This is a single-center, retrospective study focused on patients who fulfilled IPAF criteria. Among this cohort, a majority of men was reported (65%), and a high proportion of patients presented smoking history (79%). Regarding clinical, serologic or morphologic features, even with less than half of the patients (44%) showing clinical features of CTD, serologic (84%) and radiologic-morphologic (88%) criteria were met by a majority of patients. Given the benefits of early immunosuppressive treatment in this disease, a thorough identification of findings in either clinical, serologic and/or morphologic domains must be prioritized when approaching patients when suspecting a IPAF diagnosis.
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Llobell A, Atienza-Mateo B, Iturbe-Fernández D, Mora-Cuesta V, Lopez-Hoyos M, Cifrian J, Blanco R. Characterization of Interstitial Pneumonia with Autoimmune Features (IPAF) in a National Referral Centre [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2023; 75 (suppl 9). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/characterization-of-interstitial-pneumonia-with-autoimmune-features-ipaf-in-a-national-referral-centre/. Accessed .« Back to ACR Convergence 2023
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/characterization-of-interstitial-pneumonia-with-autoimmune-features-ipaf-in-a-national-referral-centre/