Session Information
Session Type: Poster Session B
Session Time: 10:30AM-12:30PM
Background/Purpose: The prevalence of ANCA positivity at diagnosis of interstitial lung disease (ILD) ranges between 4-36% for anti-MPO and 2-4% for anti-PR3. ILD is more frequently found in microscopic polyangiitis (MPA), and in most cases, ILD precedes the diagnosis of ANCA-associated vasculitis (AAV). However, to date, ANCAs are not included in the IPAF definition criteria. Our aim was to analyze the main characteristics of patients with ILD and ANCA.
Methods: Observational, retrospective, monocentric study. ANCA assessments were reviewed from January 2011 to March 2024 at our center. Patients diagnosed with ILD with at least 2 positive determinations for ANCA were selected. Demographic, clinical laboratory, pulmonary function tests (PFTs) and therapeutic variables were collected from electronic medical records. Data analysis using STATA 14 included descriptive statistics and between-group comparisons, according to the characteristics of the variables. A multivariate model was used to predict the factors associated with death.
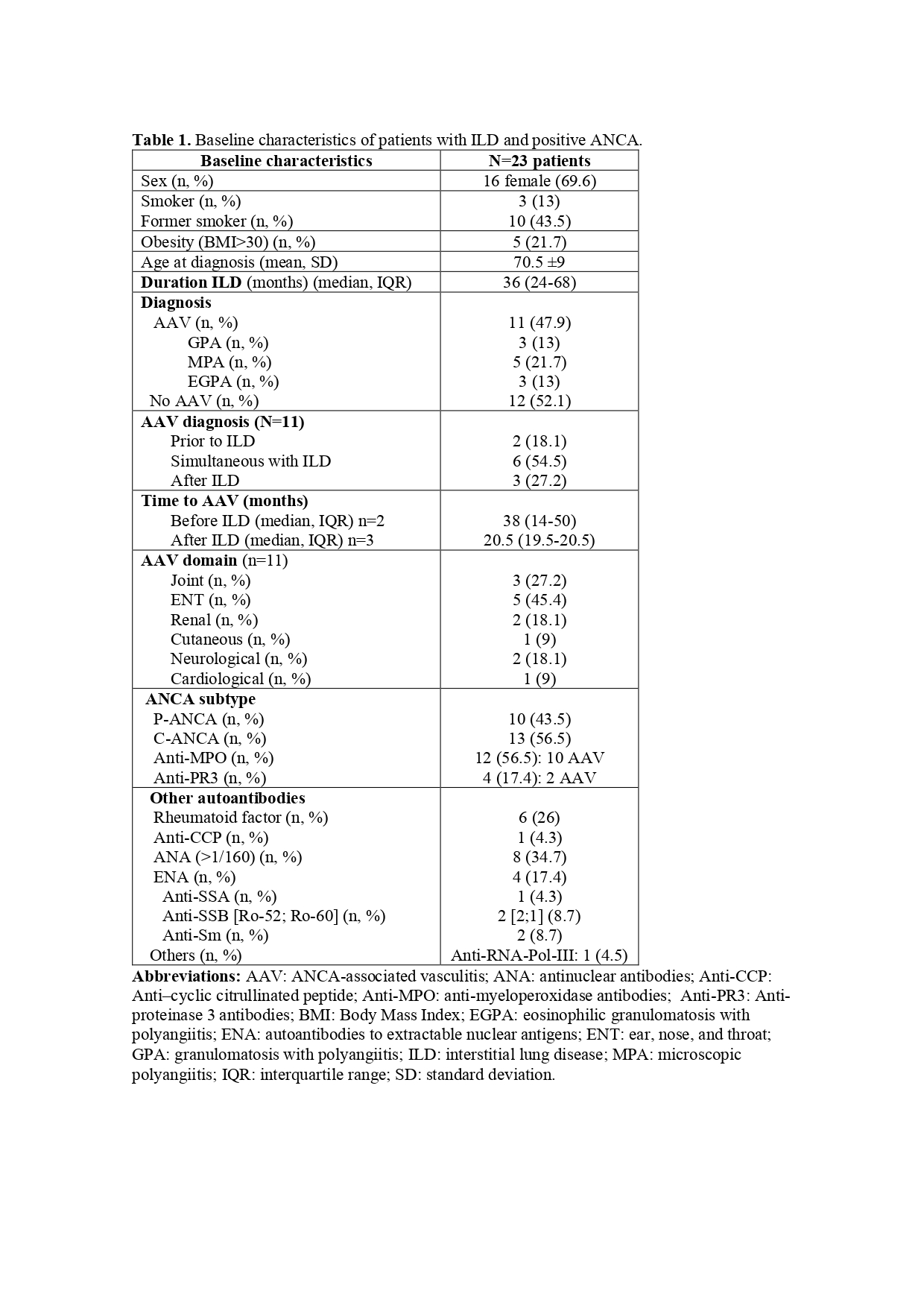
Results: 23 patients with ILD and ANCA were included (Table 1). Most patients were women, with a median 3 years of ILD duration .and the predominant ANCA pattern was anti-MPO (56.5%). Nearly half of the patients had AAV, mostly MPA (n=5/11; 45.4%), with a simultaneous diagnosis of ILD in 54.5%. The likelihood of AAV occurrence was higher in women (p=0.05) and in anti-MPO-positive patients (p=0.05). Most common AAV manifestations was otorhinolaryngological.
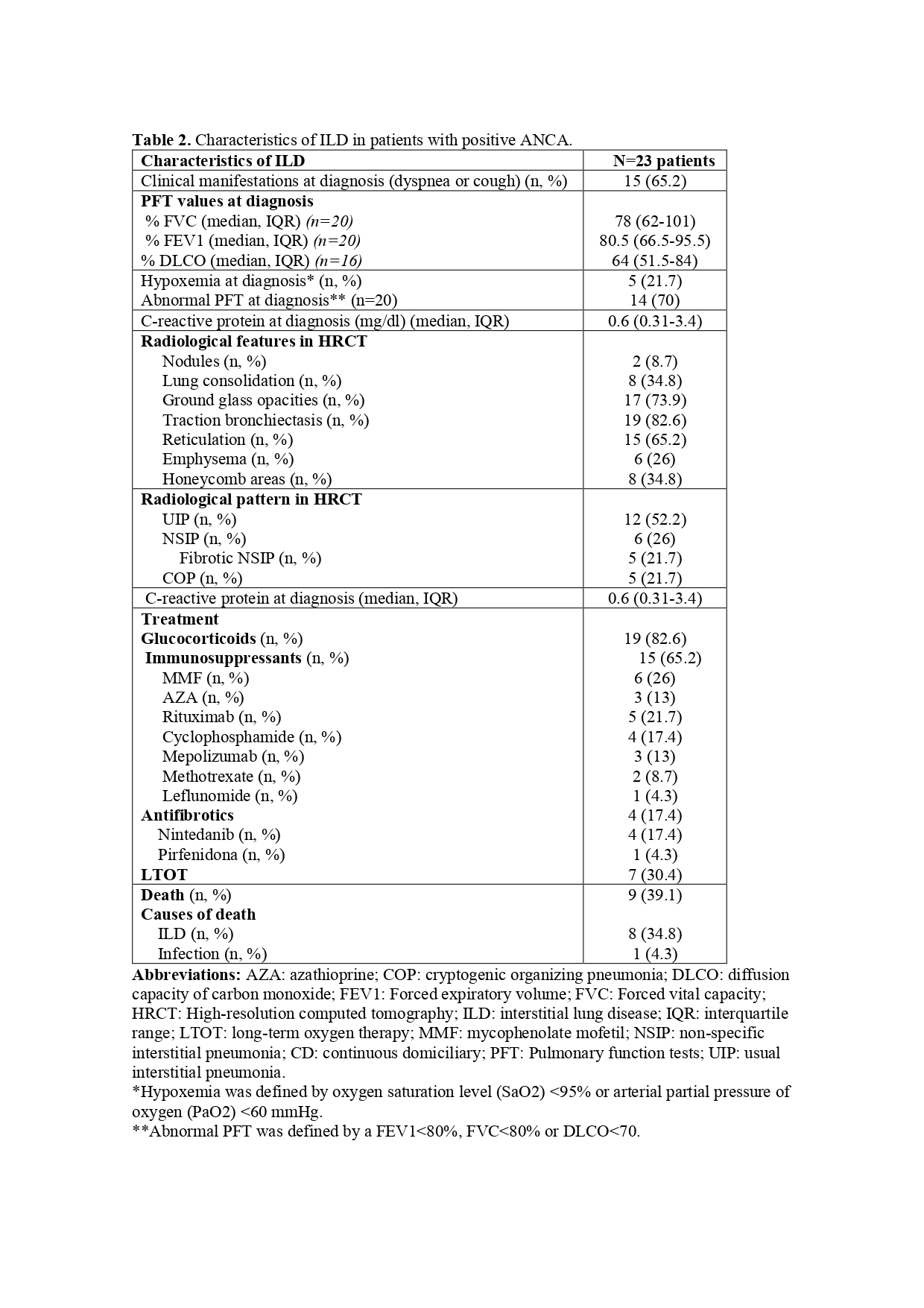
The most frequent radiological findings (Table 2) included bronchiectasis (82.6%) or ground-glass opacities (73.9%). The predominant radiological pattern was fibrotic in 17 patients (73.9%), mostly UIP (51.2%). At diagnosis, 70% of patients had abnormal PFTs, which were associated with a fibrotic pattern (p=0.014), UIP subtype (p=0.029) or baseline hypoxemia (p=0.05).
Treatment involved glucocorticoids (n=19; 82.6%; 9/13 with AAV) and immunosuppressants (n=15; 65.2%; 5/13 with AAV), with mycophenolate and rituximab as the most frequently used drugs. Antifibrotics were used in four cases.
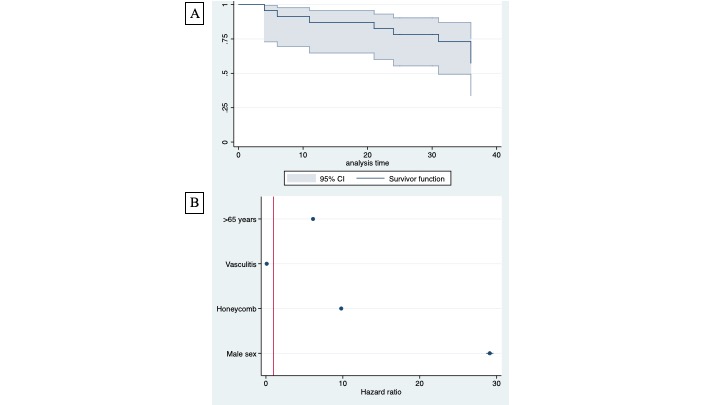
Death rate was high (n=9, 39.1%), and the main cause was ILD (8/9, 88.8%). The presence of honeycomb was associated with a greater mortality due to ILD in the logistic regression analysis (OR 17.9±2.9, p=0.036). (Figure 1), The cumulative patient 1-year survival rate (Figure 1) was 86.7% (95% CI: 64-95%). Risk factors associated with death in the Cox regression analysis were male sex (HR 29.1±37.3, p=0.009) and honeycomb (HR 9.7±9, p=0.048) with a non-significant tendence for age >65 years (HR 6.12±6.4, p=0.084),. The presence of AAV was protective (HR 0.09±0.1, p=0.02). The use of immunosuppressants in patients without AAV was associated with a lower ILD induced mortality (n=1/5; 20%), compared to untreated patients (n=3/8; 37.5%), but this difference did not reach statistical significance (p=0.490).
Conclusion: In our cohort, patients with ILD and ANCA mostly presented with a fibrotic pattern, concomitant AAV in half of the cases, and with a high and early mortality rate. Larger studies are needed to confirm these results, which would also reinforce the inclusion of ANCA in the IPAF criteria.
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Valero C, Valenzuela C, Martínez-Besteiro E, Quiroga Colina P, Alfranca A, Vicente-rabaneda E, Castañeda S, García-Vicuña R. Characteristics of a Cohort of Patients with Interstitial Lung Disease and ANCA Positivity in a University Hospital [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2024; 76 (suppl 9). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/characteristics-of-a-cohort-of-patients-with-interstitial-lung-disease-and-anca-positivity-in-a-university-hospital/. Accessed .« Back to ACR Convergence 2024
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/characteristics-of-a-cohort-of-patients-with-interstitial-lung-disease-and-anca-positivity-in-a-university-hospital/