Session Information
Date: Monday, October 22, 2018
Title: Systemic Lupus Erythematosus – Etiology and Pathogenesis Poster II
Session Type: ACR Poster Session B
Session Time: 9:00AM-11:00AM
Background/Purpose: Innate Lymphoid Cells (ILCs) are a novel group of innate immune cells, according to the cytokine profile, they were divided into three major subsets: ILC1(Lin¨CIL7R+NKp46+ILCs),ILC2(Lin¨CIL7R+CRTH2+ILCs) and ILC3(Lin¨CIL7R+CRTH2¨CCD117+ILCs). Little research on ILC in the pathogenesis of systemic lupus erythematosus. Our purpose is to explore the function and role of innate lymphoid cells(ILCs) in the pathogenesis of systemic lupus erythematosus at different disease activity levels.
Methods: 40 patients with SLE were included, according to the SLEDAI-2K, patients were divided into active group(n=20) and remission group(n=20), 15 age-matched healthy non-immune-related diseases controls. The frequency of ILCs, B cells, CD4+T and CD8+T cells from PBMCs was detected by flow cytometry. Analysis the subsets of ILCs in each group which compared with B cells and T cell subsets respectively and correlated with clinical serologic markers. Analyze the level of IL-4, IL-33 and IFN-¦Ã in each group by ELISA.
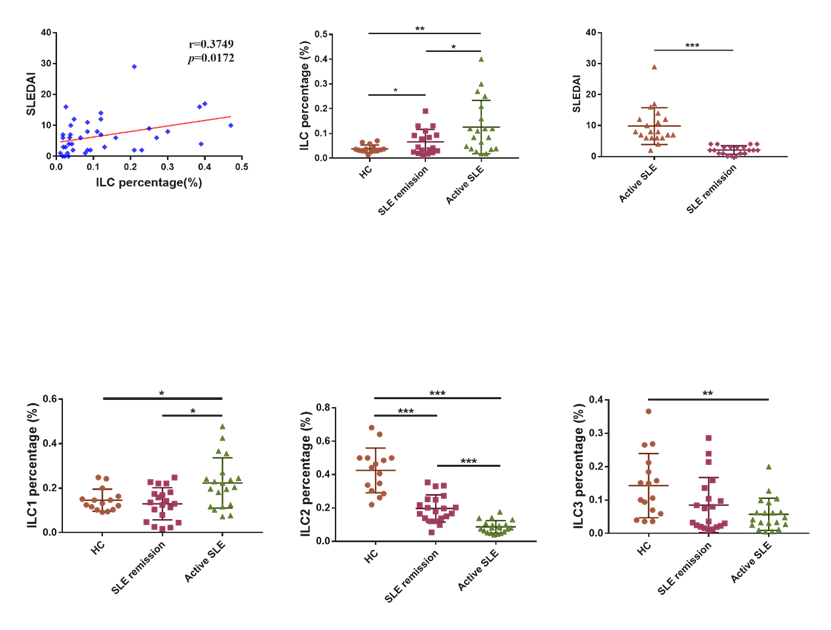
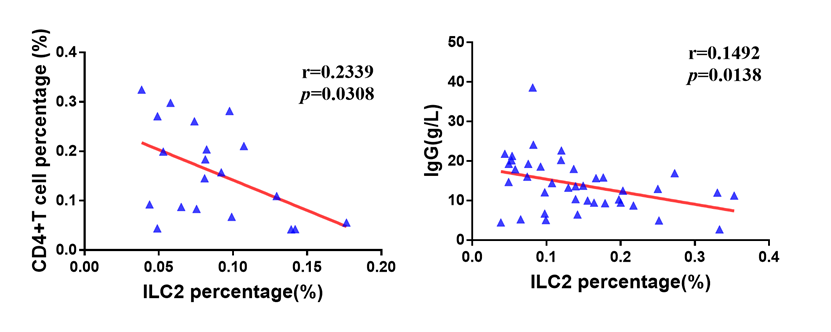
Results: Compared with the control group, ILC1 percentage was significantly increased in SLE active group(P=0.0181);ILC2 was decreased significantly in both remission(P<0.0001) and active groups(P<0.0001);ILC3 was decreased significantly in active group(P=0.0013). The frequency of ILCs in all patients positively correlated with SLEDAI score(P=0.0172). The frequency of ILCs in the remission(P=0.0462)and activity group (P=0.0037) are both increased significantly (Figure1). Moreover, the frequency of ILC2 in active group was negatively correlated with CD4+T cells(P=0.0308), and the serum IgG in patients was negatively correlated with ILC2 of all patients (P=0.0138) (Figure2). Compared with either control group or the remission group ,the levels of IFN-¦Ã (P=0.0001)and IL-4 (P=0.0047)in active group were remarkable higher. However, IL-33 was significantly reduced in active group(P=0.0027)(Figure3). (*,p<0.05; **,p<0.01; ***,p<0.001).
Conclusion: The frequency of ILCs is related to disease activity, and ILCs play a "double-edged" role in the pathogenesis of SLE. Its function and mechanism are worth further exploration.
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Chu H, Li X, Tan Z, Wu R, Li X, Fang X, Zhen X, Wang G. Changes of Innate Lymphoid Cells in Peripheral Blood of Patients with Systemic Lupus Erythematosus and Its Correlations with Clinical Markers [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2018; 70 (suppl 9). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/changes-of-innate-lymphoid-cells-in-peripheral-blood-of-patients-with-systemic-lupus-erythematosus-and-its-correlations-with-clinical-markers/. Accessed .« Back to 2018 ACR/ARHP Annual Meeting
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/changes-of-innate-lymphoid-cells-in-peripheral-blood-of-patients-with-systemic-lupus-erythematosus-and-its-correlations-with-clinical-markers/