Session Information
Session Type: Poster Session B
Session Time: 10:30AM-12:30PM
Background/Purpose: The characteristics of brain impairment in different subtypes of systemic sclerosis (SSc) (dcSSc, diffuse cutaneous SSc; lcSSc, limited cutaneous SSc) remain unclear. This study aimed to characterize cerebral structure and perfusion changes in different subtype of SSc patients using magnetic resonance (MR) imaging.
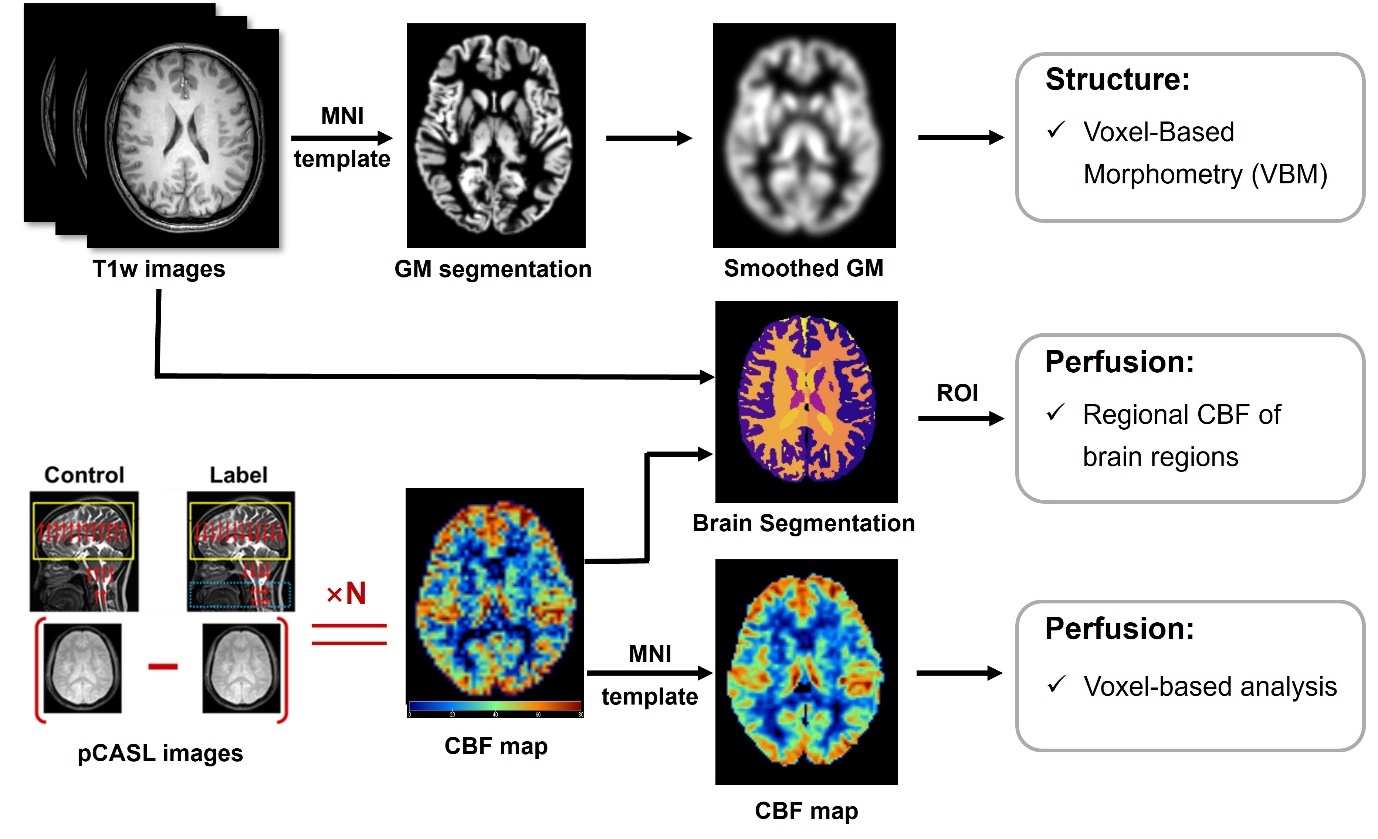
Methods: Seventy SSc patients (46.0±11.7 years, 62 females) and 30 age- and sex-matched healthy volunteers (44.8±13.7 years, 24 females) were recruited and underwent brain MR imaging and Montreal Cognitive Assessment (MoCA) test. Gray matter (GM) volumes were measured using voxel-based morphometry analysis on T1-weighted images. Voxel-based and regional cerebral blood flow (CBF) was calculated on arterial spin labeling images. The cerebral structural and perfusion measurements by MR imaging were compared among dcSSc, lcSSc and healthy subjects using one-way ANOVA. The correlations between clinical characteristics and MR imaging measurements were also analyzed.
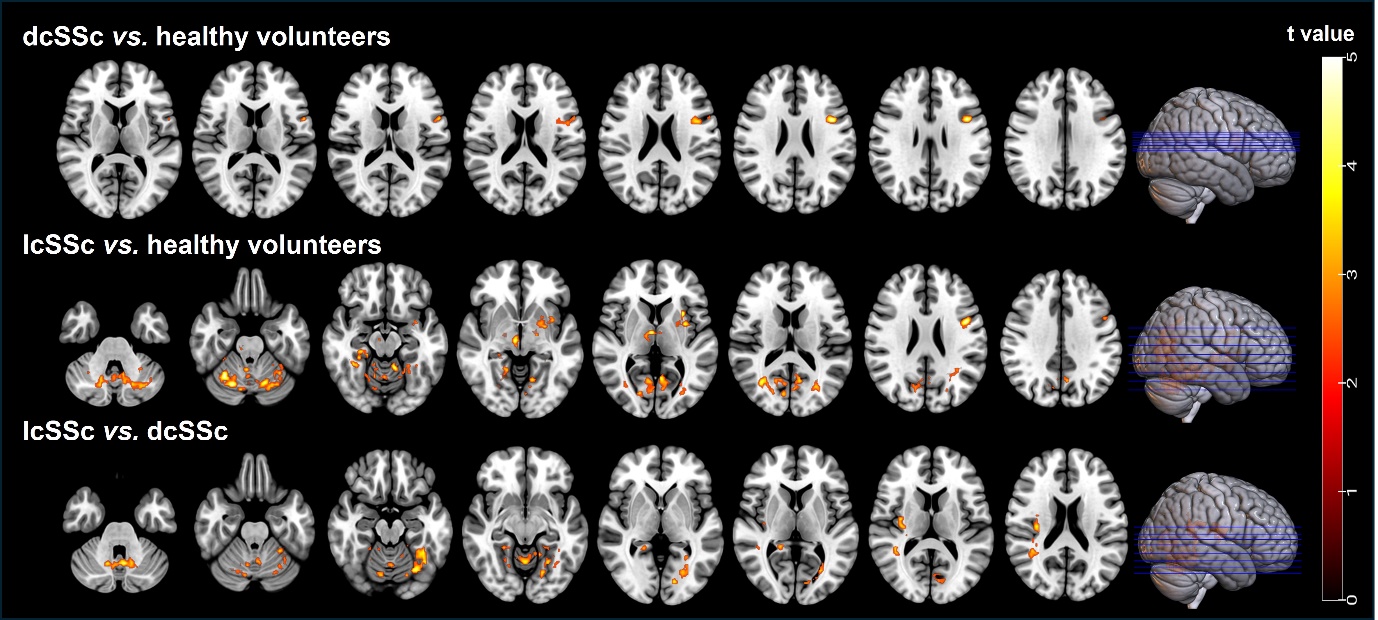
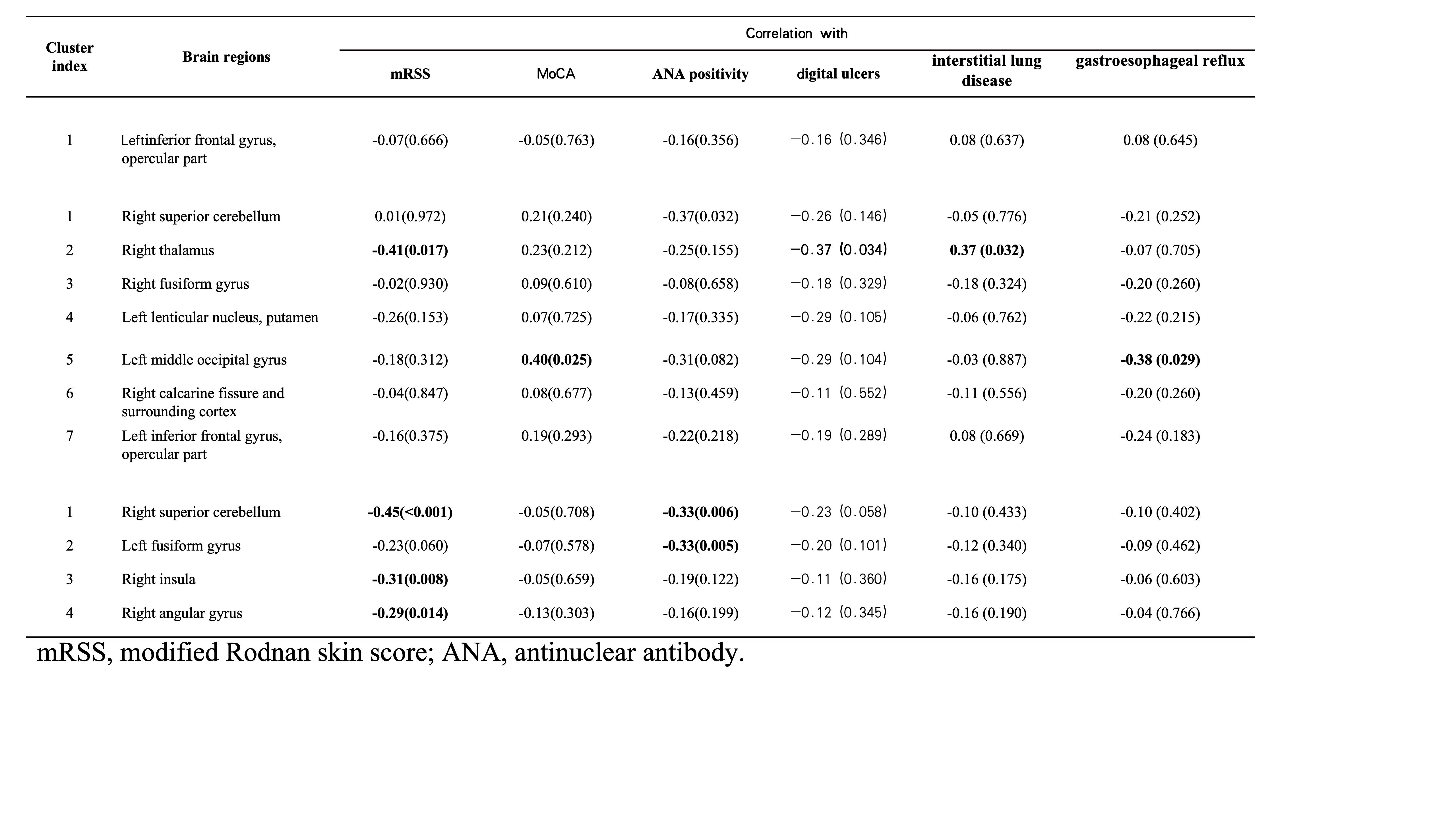
Results: The dcSSc patients exhibited a significant reduction in GM volume in the para-hippocampal region (cluster P< 0.01, FWE corrected) compared to healthy volunteers. Whereas, SSc patients, particularly lcSSc patients, showed elevated CBF in cerebellum, insula, cerebral cortex, and subcortical structures (regional analyses: all P< 0.05; voxel-based analyses: cluster P< 0.01, FWE corrected). Furthermore, clinical characteristics of modified Rodnan skin score (mRSS) (r value ranged from -0.29 to -0.45), MoCA scores (r=0.40) and antinuclear antibody (ANA) positivity (r=-0.33) were significantly associated with CBF in some regions (all P< 0.05).
Conclusion: The manifestations of brain involvement vary among different subtypes of SSc. In addition, severe skin sclerosis may indicate higher risk of brain involvement in SSc patients.
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Tong X, He H, Xu S, Ning Z, Shen R, Zeng X, wang q, Xu D, zhao X, He Z. Changes of Cerebral Structure and Perfusion Vary in Different Subtypes of Systemic Sclerosis: A Brain Magnetic Resonance Imaging Study [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2024; 76 (suppl 9). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/changes-of-cerebral-structure-and-perfusion-vary-in-different-subtypes-of-systemic-sclerosis-a-brain-magnetic-resonance-imaging-study/. Accessed .« Back to ACR Convergence 2024
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/changes-of-cerebral-structure-and-perfusion-vary-in-different-subtypes-of-systemic-sclerosis-a-brain-magnetic-resonance-imaging-study/