Session Information
Date: Sunday, November 10, 2019
Title: 3S084: Systemic Sclerosis & Related Disorder – Clinical I: Therapeutics & Outcomes (863–868)
Session Type: ACR Abstract Session
Session Time: 2:30PM-4:00PM
Background/Purpose: The Combined Response Index in Systemic Sclerosis (CRISS) is a composite outcome measure provisionally endorsed by the American College of Rheumatology for use in systemic sclerosis (SSc) clinical trials. In two early, diffuse SSc trials, skin histologic change within patients was evaluated at baseline and 52-weeks. The purpose of this study is to determine if change in skin histologic severity correlates with CRISS.
Methods: Paired baseline and 52-week post-treatment clinical data and forearm skin histology were examined from patient specimens in the Nilotinib (n=6) and Belimumab (n=18) trials. During these trials, a dermatopathologist (CM), blinded to clinical response, evaluated global histologic severity (pathologist overall impression on hematoxylin and eosin stain), infiltrate intensity, collagen density, and alpha-smooth muscle actin (aSMA) and CD34 staining intensity on a semi-quantitative scale (0-3), and measured thickness (epidermis to subcutis) and follicle count. The validation of these methods is presented separately. CRISS was calculated using 52-week change in physician and patient global assessment (0-10), % predicted forced vital capacity (FVC), health assessment questionnaire disability index (HAQ-DI), and modified Rodnan skin score (MRSS). Patients were assessed for criteria that renders CRISS score zero (scleroderma renal crisis, FVC decline >15% predicted, new heart failure, or new pulmonary arterial hypertension treatment). Wilcoxon rank sum or Kruskal-Wallis tests were performed to evaluate differences in CRISS according to histologic change. Spearman correlation was used to evaluate the correlation between histologic change and CRISS.
Results: 24 diffuse SSc patients contributed baseline and 52-week biopsies. Most were female (79%) and Caucasian (75%) with median [IQR] disease duration of 0.9 [0.6, 1.2] years. 54% were RNA polymerase III positive. Baseline median [IQR] MRSS was 24 [22, 29] and physician global assessment was 5.8 [5.0, 6.8]. Mean (SD) patient global assessment was 3.2 (2.53) and HAQ-DI was 0.85 (0.59). Interstitial lung disease was present in 7 of 24 (29%). Mean (SD) baseline % predicted FVC was 86 (16). Median [IQR] CRISS was 0.93 [0.47, 1.00].
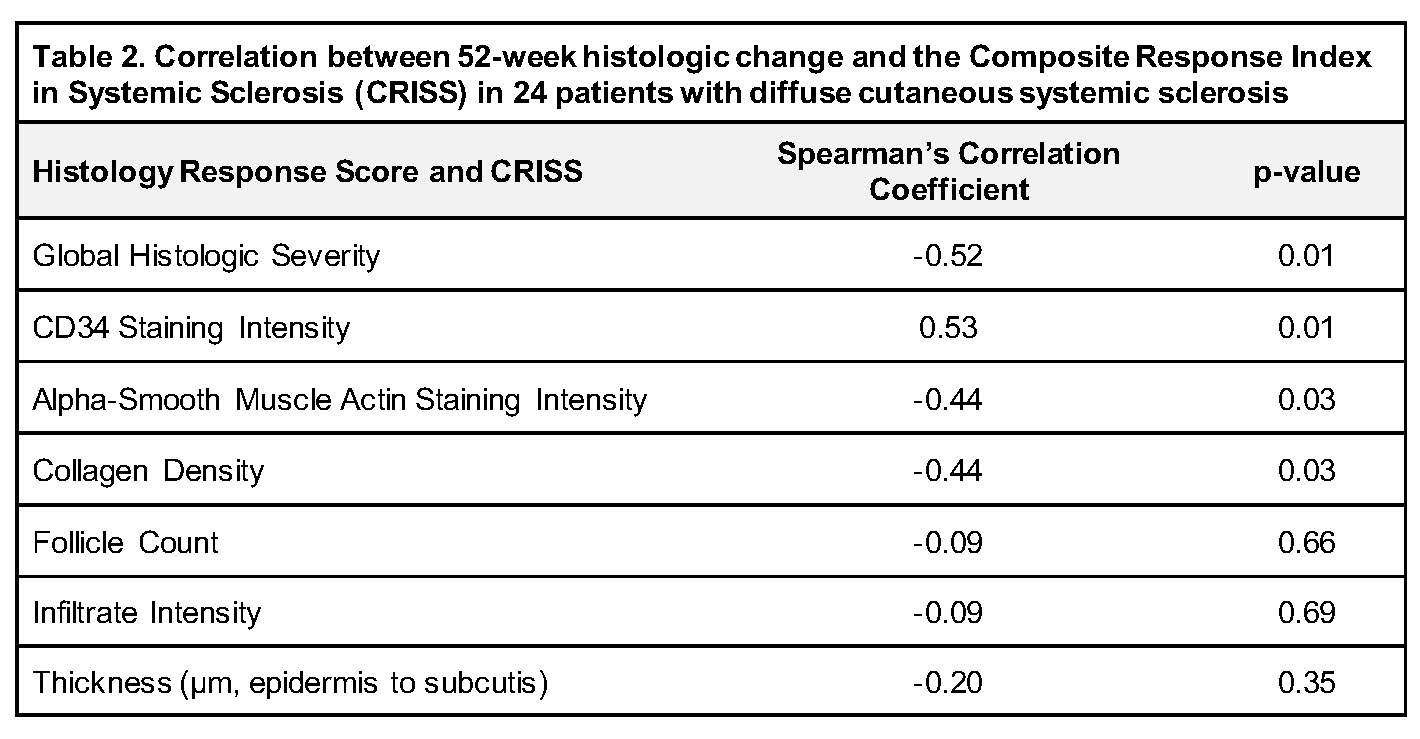
Treatment response, measured by median CRISS, was higher (improved) in those with decreased global histologic severity (p=0.02) and increased CD34 staining intensity (p=0.01) (Table 1). CRISS correlated negatively with change (decreased, stable, or increased) in global histologic severity (r=-0.52, p=0.01), aSMA staining intensity (r=-0.44, p=0.03), and collagen density (r=-0.44, p=0.03), and correlated positively with change in CD34 staining intensity (r=0.53, p=0.01) (Table 2).
Conclusion: Improved CRISS is associated with decreased global histologic severity, aSMA staining intensity, and collagen density, and increased CD34 staining intensity, suggesting these histologic features are treatment responsive and provide clinically meaningful information. Median CRISS in those with global histologic worsening was below the threshold of 0.6 that defines CRISS improvement in SSc trials. Future work may determine if baseline histologic features predict clinical response, measured by CRISS.
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Showalter K, Spiera R, Orange D, Magro C, Zhang Y, Finik J, Gordon J. Change in Scleroderma Skin Histology Correlates with the Combined Response Index in Systemic Sclerosis (CRISS) in Patients with Early, Diffuse Cutaneous Systemic Sclerosis [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2019; 71 (suppl 10). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/change-in-scleroderma-skin-histology-correlates-with-the-combined-response-index-in-systemic-sclerosis-criss-in-patients-with-early-diffuse-cutaneous-systemic-sclerosis/. Accessed .« Back to 2019 ACR/ARP Annual Meeting
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/change-in-scleroderma-skin-histology-correlates-with-the-combined-response-index-in-systemic-sclerosis-criss-in-patients-with-early-diffuse-cutaneous-systemic-sclerosis/