Session Information
Session Type: ACR Poster Session C
Session Time: 9:00AM-11:00AM
Background/Purpose: Patients with rheumatoid arthritis (RA) have higher healthcare utilization (HCU) and costs than patients without RA1.
Evidence is mixed as to the impact of biologic treatment on HCU. The purpose of this study was to evaluate HCU before and after etanercept (ETN) initiation.Methods: We conducted a retrospective cohort study using claims data. Adult RA patients newly exposed to ETN from January 1, 2010 through December 31, 2013 were included. Patients were required to have at least 1 inpatient or outpatient claim for RA (ICD-9-CM 714.0) in the primary position, and at least 1 ETN medication claim; the earliest ETN claim served as index date. Patients were excluded if they had exposure to a biologic DMARD or had a claim for psoriasis, psoriatic arthritis, ankylosing spondylitis, or juvenile idiopathic arthritis. The proportion of days covered (PDC) was calculated and used as a measure of ETN compliance. The primary outcome was the change in HCU (both overall and RA-related) in the year before and after ETN initiation. McNemar’s test and paired t-test were used to determine statistical significance for dichotomous and continuous variables, respectively. To compare the HCU across ETN compliance groups, F-test and Chi-square test were used for categorical and continuous variables, respectively.
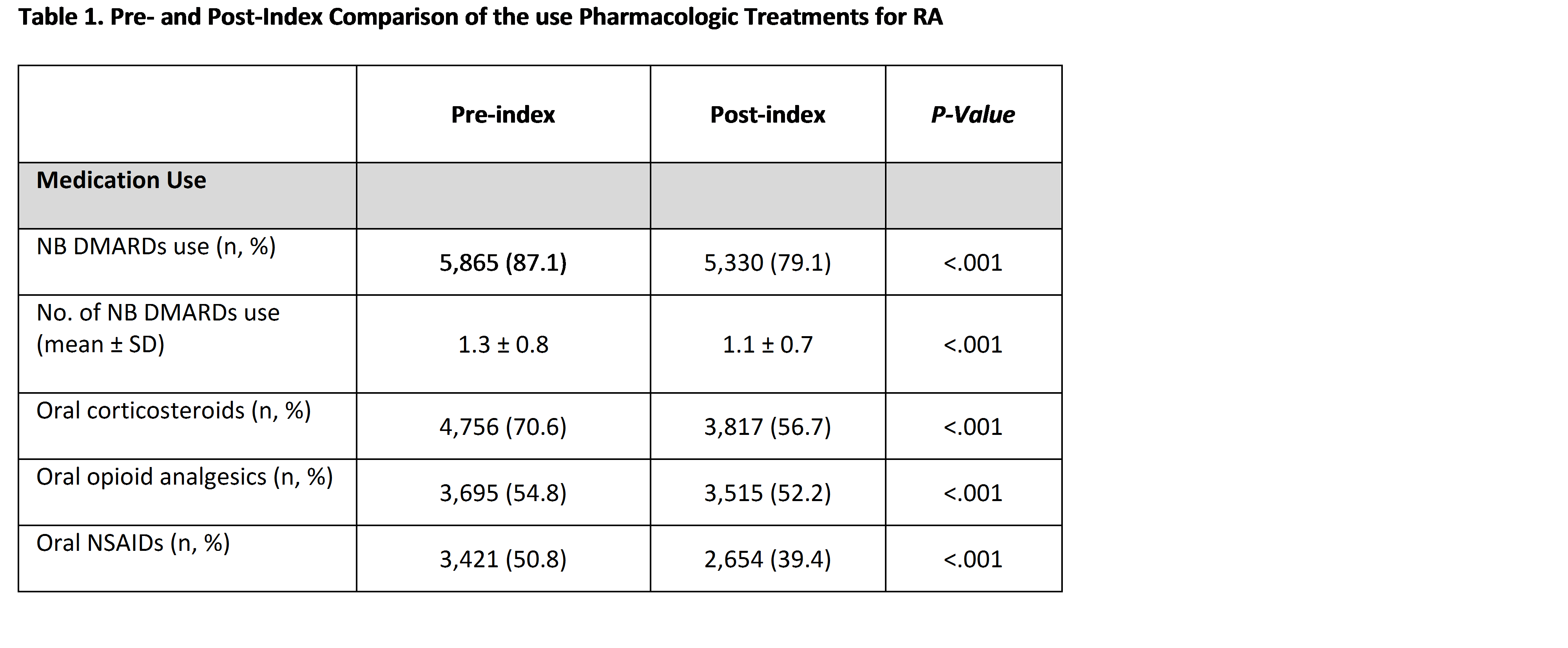
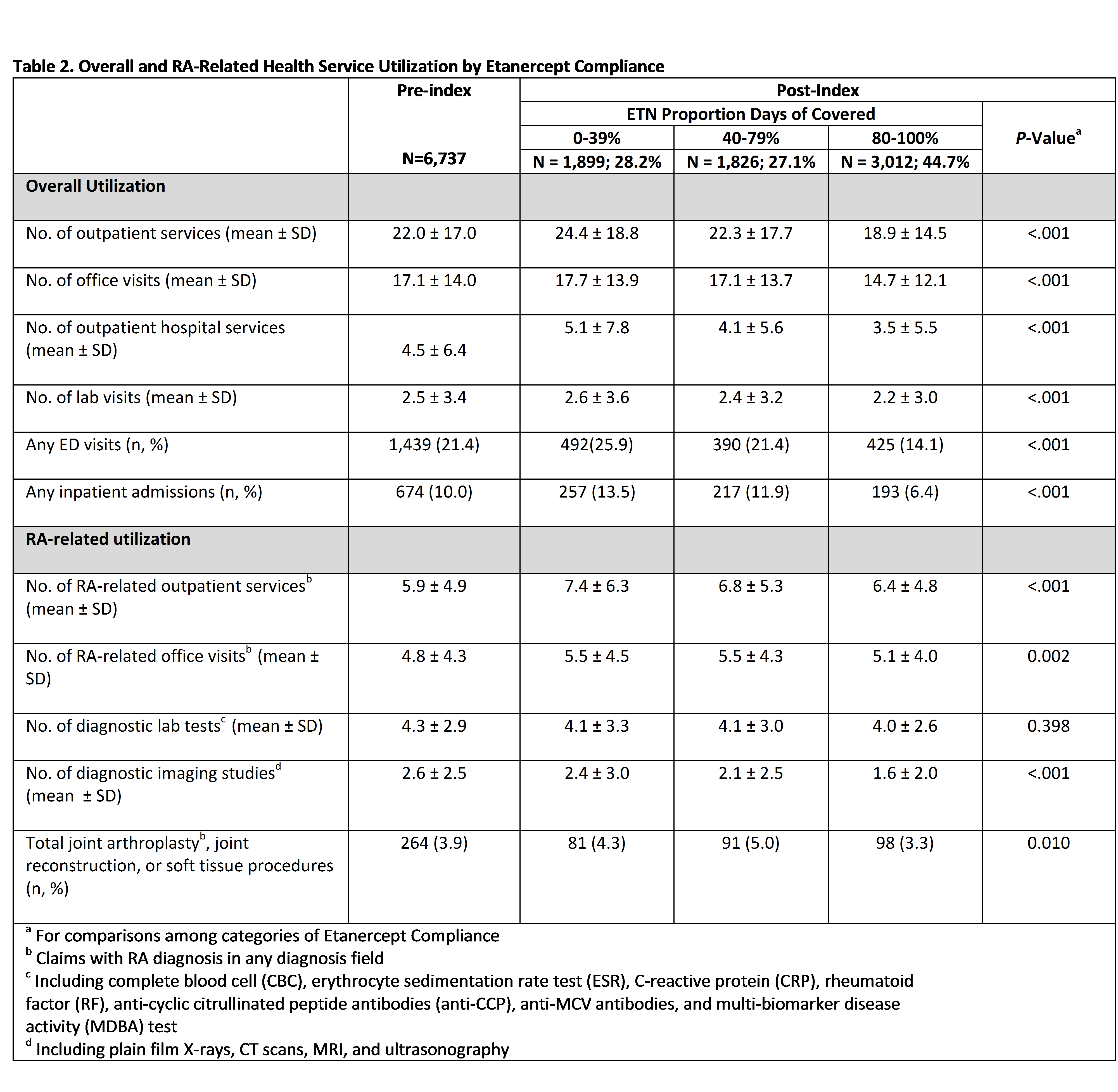
Results: We identified 6,737 ETN initiators. The mean age was 49.8 years and 77.3% were female. Frequency of medication use for oral corticosteroids, opioid analgesics, NSAIDS and NB-DMARDS decreased significantly from the pre-index to post-index period (Table 1). There was a significant decrease in overall outpatient services, ED visits and hospitalizations from the pre-index to post-index period (data not shown). In the post-index period, there was a statistically significant decrease in HCU factors with increasing ETN compliance (Table 2).
Conclusion: Health care utilization, including medication use, outpatient services and inpatient admissions decreased after ETN initiation. Patients who were the most compliant with their medication experienced significantly lower utilization than non-compliant patients. The reduction in HCU is consistent with a reduction in disease activity as shown in clinical trials of ETN.2 1. Michet CJ, et al. Hospitalization Rates and Utilization Among Patients With Rheumatoid Arthritis: A Population-Based Study From 1987 to 2012 in Olmsted County, Minnesota. Mayo Clinic Proceedings. 2015;90:176–183.
2. Moreland LW, et al. Etanercept therapy in rheumatoid arthritis: a randomized, controlled trial. Annals of internal medicine. 1999 Mar 16;130(6):478-86.
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Accortt N, Schenfeld J, Chang E, Papoyan E, Broder MS. Change in Health Care Utilization after Etanercept Initiation in Patients with Rheumatoid Arthritis [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2016; 68 (suppl 10). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/change-in-health-care-utilization-after-etanercept-initiation-in-patients-with-rheumatoid-arthritis/. Accessed .« Back to 2016 ACR/ARHP Annual Meeting
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/change-in-health-care-utilization-after-etanercept-initiation-in-patients-with-rheumatoid-arthritis/