Session Information
Date: Sunday, November 5, 2017
Title: Rheumatoid Arthritis – Clinical Aspects Poster I: Treatment Patterns and Response
Session Type: ACR Poster Session A
Session Time: 9:00AM-11:00AM
Background/Purpose: Fatigue is an important problem that impairs life quality in patients with rheumatic diseases. Although fatigue is often associated with disease activity, only a modest effect of anti-TNFs on fatigue was observed in patients with RA (1). We aimed to determine the efficacy of different doses of certolizumab pegol (CZP) in chronic inflammatory rheumatic diseases by a meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials.
Methods: A systematic literature search including patients with rheumatic diseases who received CZP was performed. We searched PubMed for all randomized controlled trials with CZP up to May 2017 without any restrictions. Studies that assessed fatigue in any rheumatic disease using the fatigue assessment scale (FAS) and reported the FAS score and/or the proportion of patients who met the minimum clinically important difference (MCID) for FAS score were included. The MCID for FAS is 1 over a scale of 0 to 10 where higher scores show increased severity of fatigue. The CZP 200 mg and CZP 400 mg arms of trials were pooled for comparison with the placebo arms.
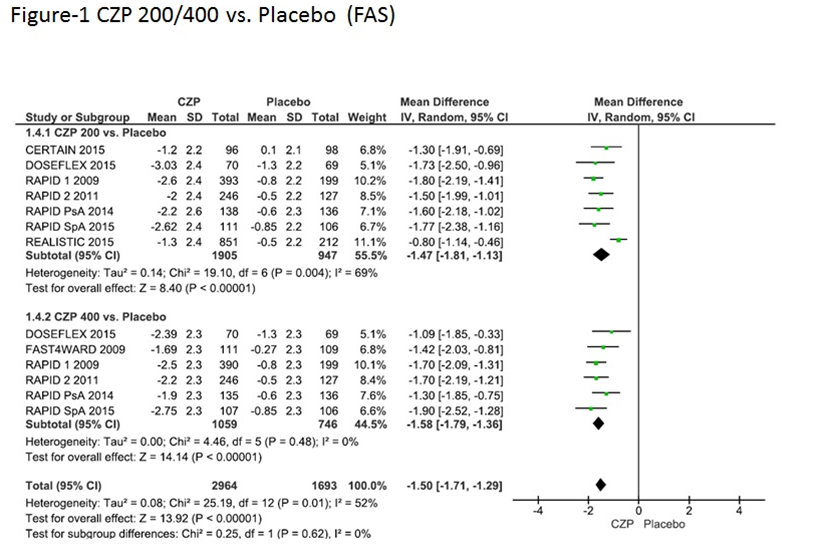
Results: The literature search yielded 68 articles. 55 articles were excluded after evaluating the title and abstract, 5 were excluded after reading the full-text. Among the 8 RCTs that were selected , the study population was RA in 6 RCTs, and psoriatic arthritis and axial spondyloarthritis in 1 RCT each. Overall, there were 2964 patients treated with CZP and 1056 with placebo. Table summarizes the included studies.
An improvement in the FAS score and an increase in the proportion of patients who met the MCID for FAS were observed in all the included trials regardless of the underlying disease (Figure-1, 2). The pooled results showed that CZP significantly improved fatigue compared to placebo (FAS: MD = -1.50, 95% CI:-1.71- -1.29, p <0.0001, MCID: RR=2.53, 95% CI: 1.74-3.68).
Conclusion: This meta-analysis showed that CZP may be an effective treatment modality for fatigue in rheumatic diseases.
Reference:
1) Druce KL, Bhattacharya Y, Jones GT, Macfarlane GJ, Basu N. Most patients who reach disease remission following anti-TNF therapy continue to report fatigue: results from the British Society for Rheumatology Biologics Register for Rheumatoid Arthritis. Rheumatology (Oxford). 2016 Oct;55(10):1786-90
|
Table 1. Characteristics of randomized controlled studies included in the meta-analysis |
||||||||
|
First author, year |
Disease state |
Inclusion criteria |
Intervention arm |
Comparator arm |
Number of patients (M/W) |
Study duration (weeks) |
||
|
CZP 400 |
CZP 200 |
Placebo |
|
|||||
|
Fleischman, 2017 |
RA |
Active disease despite ≥1 DMARD |
CZP 400 |
Placebo every 4 weeks
|
111 (24/87) |
NA |
109 (12/97) |
24 |
|
Furst, 2015 |
RA |
Active disease despite MTX |
CZP 400 CZP 200 |
Placebo every 2 weeks |
70 (12/58) |
70 (23/49) |
69 (14/56) |
34 |
|
Pope, 2015 |
RA |
Active disease despite ≥1 DMARD |
CZP 200 |
Placebo every 2 weeks |
NA |
851 (NR) |
221 (NR) |
12 |
|
Smolen, 2017 |
RA |
Low/moderate active despite ≥1 DMARD |
CZP 200 |
Placebo every 2 weeks |
NA |
96 (15/81) |
98 (23/75) |
24 |
|
Strand, 2009 |
RA |
Active disease despite MTX |
CZP 400 CZP 200 |
Placebo every 2 weeks |
390 (64/326) |
393 (69/324) |
199 (32/167) |
52 |
|
Strand, 2011
|
RA |
Active disease despite MTX |
CZP 400 CZP 200 |
Placebo every 2 weeks |
246 (54/192) |
246 (42/206) |
127 (20/107) |
24 |
|
Gladman, 2014 |
pSA |
Active disease despite ≥1 DMARD* |
CZP 400 CZP 200 |
Placebo every 2 weeks |
135 (62/73) |
138 (64/74) |
136 (57/79) |
24 |
|
Sieper, 2015 |
axial SpA |
Active disease despite ≥1 NSAID* |
CZP 400 CZP 200 |
Placebo every 2 weeks |
107 (68/39) |
111 (67/44) |
107 (65/43) |
24 |
|
*An history of an anti-TNF failure was not an exclusion criterion DMARD: disease modifying anti-rheumatic drug; pSA; psoriatic arthritis; SpA: spondyloarthritis; MTX methotrexate, NSAID: non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs; CZP: certolizumab pegol; NA: not applicable; NR: not reported
|
||||||||
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Ozguler Y, Esatoglu SN, Karatemiz G, Unal AU, Guzelant G, Dincses E, Erdogan M, Kaymaz Tahra S, Hatemi G. Certolizumab Pegol for Fatigue in Chronic Inflammatory Rheumatic Diseases: A Meta-Analysis [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2017; 69 (suppl 10). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/certolizumab-pegol-for-fatigue-in-chronic-inflammatory-rheumatic-diseases-a-meta-analysis/. Accessed .« Back to 2017 ACR/ARHP Annual Meeting
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/certolizumab-pegol-for-fatigue-in-chronic-inflammatory-rheumatic-diseases-a-meta-analysis/