Session Information
Date: Saturday, November 16, 2024
Title: Vasculitis – Non-ANCA-Associated & Related Disorders Poster I
Session Type: Poster Session A
Session Time: 10:30AM-12:30PM
Background/Purpose: Giant cell arteritis (GCA) is the most common form of systemic vasculitis in the elderly and involves the large and medium-sized vessels. Cerebrovascular accidents (CVA) are one of the most feared ischemic complications, but its prevalence and associated factors remains understudied.
Our aim is to determine the prevalence and predictive factors of CVA in a large registry of patients with GCA.
Methods: ARTESER is a large Spanish multicentre registry supported by the Spanish Society of Rheumatology. It includes patients with GCA from across the entire country diagnosed between June 2013 and March 2019. The variables collected at diagnosis were demographics, clinical manifestations (including the occurrence and type of CVA), laboratory, temporal artery biopsy, and imaging findings (ultrasound, FDG-PET/CT, MRI, angiography, CT angiography). Patients with and without CVA were compared in a bivariate analysis. Multivariate logistic regression was performed to determine potential predictive factors of CVA.
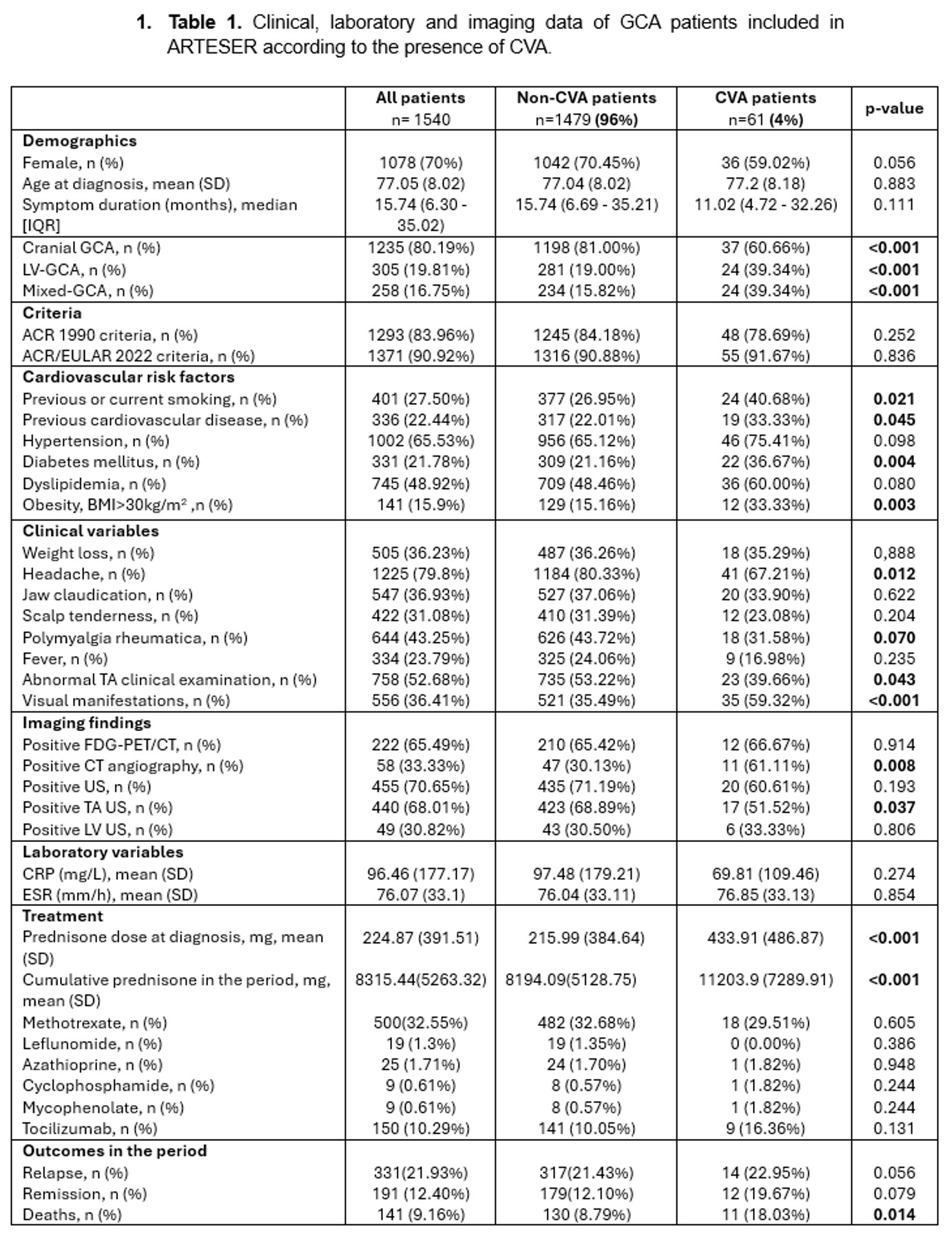
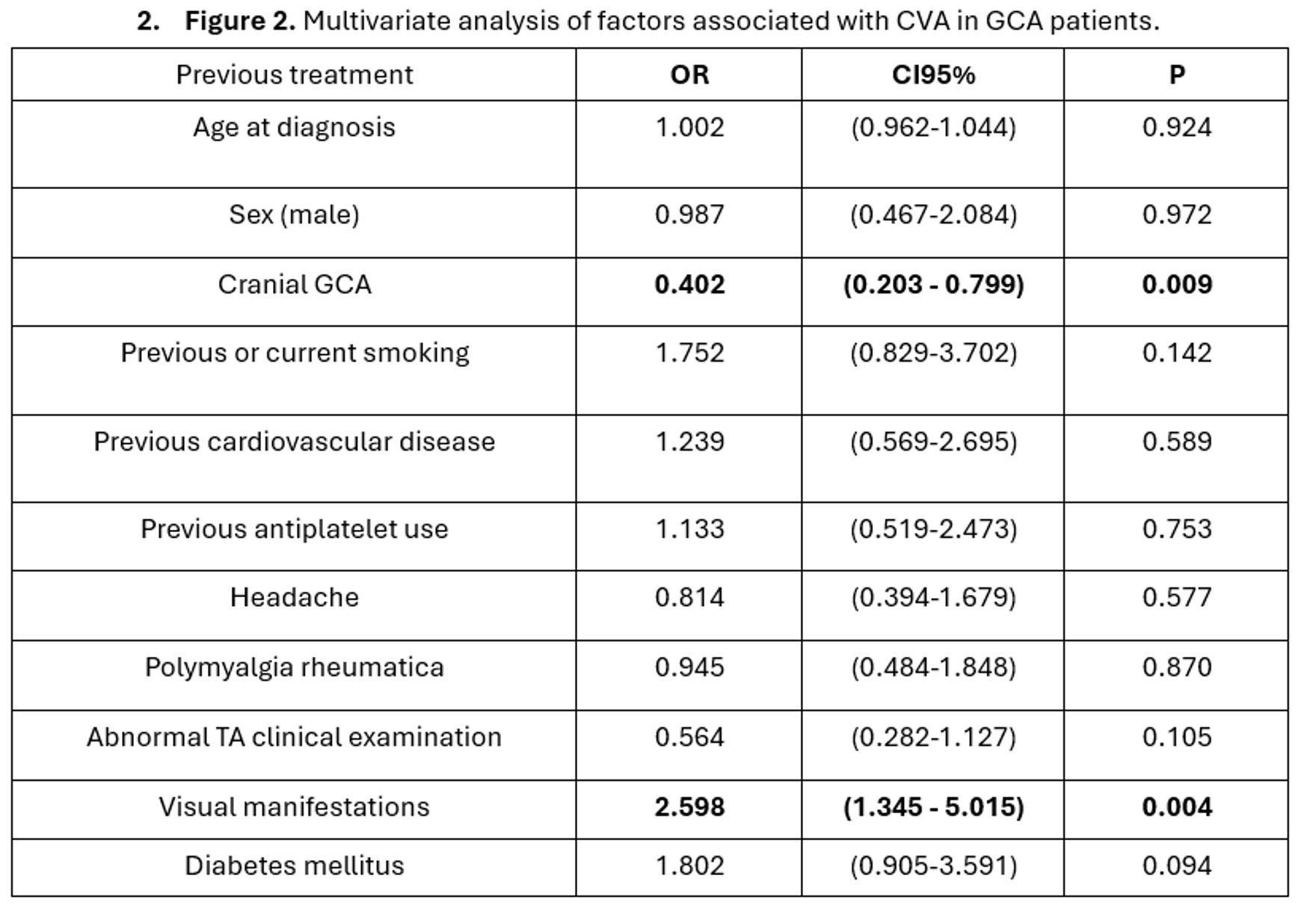
Results: A total of 1540 patients with GCA were included for analysis (mean age 77.1 years, 70% females). CVA occurred in 61 (3.96%), of whom 21 (34.4%) involved the carotid territory and 38 (62.3%) the vertebrobasilar territory. Demographics, clinical and imaging findings in patients with and without CVA is shown in Figure 1. The risk of death during follow-up was significantly higher in patients with CVA (18% vs 8.8%; p=0.014) and patients with CVA received significantly higher mean prednisone (mg) dose at diagnosis (433.9 vs 216; p< 0.001) and cumulative prednisone dose during follow-up (11203.9 vs 8194.1; p< 0.001. In the multivariate analysis (Figure2) the presence of concomitant visual manifestations (OR 2.598; 95% CI 1.345 – 5.015) was the only clinical variable associated with CVA. On the other hand, the cranial-GCA phenotype (OR 0.402; 95% CI 0.203 – 0.799) was associated with a reduced risk of CVA.
Conclusion: The prevalence of CVA in patients with GCA is low, but increases the risk of mortality. Visual manifestations were the only clinical factor associated with increased risk of CVA, whereas the cranial-GCA phenotype is associated with a reduced risk of CVA.
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Martín-Gutiérrez A, Molina-Collada J, Domínguez-Álvaro M, Melero-Gonzalez R, Fernández-Fernández: E, Silva-Diaz M, Valero J, Gonzalez I, Sánchez-Martín J, Narvaez-García J, Calvo I, Aldasoro V, Abasolo Alcazar l, RUIZ ROMAN A, Loricera J, Castañeda S, Molina Almela C, Alcalde Villar: M, Juan-Mas A, Blanco-Alonso R. Cerebrovascular Accidents (CVA) in Giant Cell Arteritis: Identification of Predictive Factors from the ARTESER Registry [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2024; 76 (suppl 9). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/cerebrovascular-accidents-cva-in-giant-cell-arteritis-identification-of-predictive-factors-from-the-arteser-registry/. Accessed .« Back to ACR Convergence 2024
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/cerebrovascular-accidents-cva-in-giant-cell-arteritis-identification-of-predictive-factors-from-the-arteser-registry/