Session Information
Date: Sunday, October 21, 2018
Title: Systemic Lupus Erythematosus – Clinical Poster I: Clinical Manifestations and Comorbidity
Session Type: ACR Poster Session A
Session Time: 9:00AM-11:00AM
Cerebrospinal Fluid Biomarkers for Diagnosing Neuropsychiatric SLE:
A Systematic Review and Meta-analysis
Background/Purpose: Current guidelines recommend that in suspected neuropsychiatric SLE (NPSLE), the initial diagnostic workup should be similar to that in non-SLE patients presenting with the same manifestations. We aimed to synthesize the current best evidence regarding whether any additional cerebrospinal fluid (CSF) biomarker could be particularly beneficial in diagnosing patients with suspected NPSLE.
Methods: We completed a comprehensive search within PubMed, Embase, and CINAHL. We used a highly-sensitive search strategy comprising 67 keywords representing NPSLE and its 19 syndromes as well as CSF biomarkers. We also carried out forward and backward citation checking of the included studies and the relevant reviews using the Web of Knowledge Science Citation Index. We included the studies of the diagnostic test accuracy of any CSF biomarker for diagnosing NPSLE among patients with SLE, in which they used the ACR case definitions or other validated tools as their reference standards. Two investigators (SFA, GZ) independently replicated data extraction by using a standard form, which included an assessment of study quality as well as participant-level data to populate 2×2 contingency tables (true positives, true negatives, false positives and false negatives).
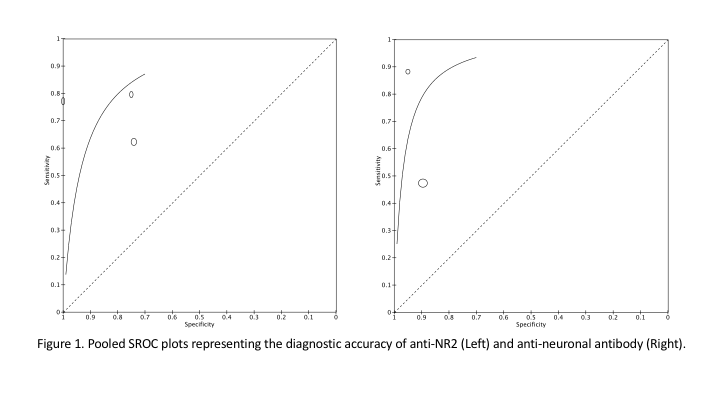
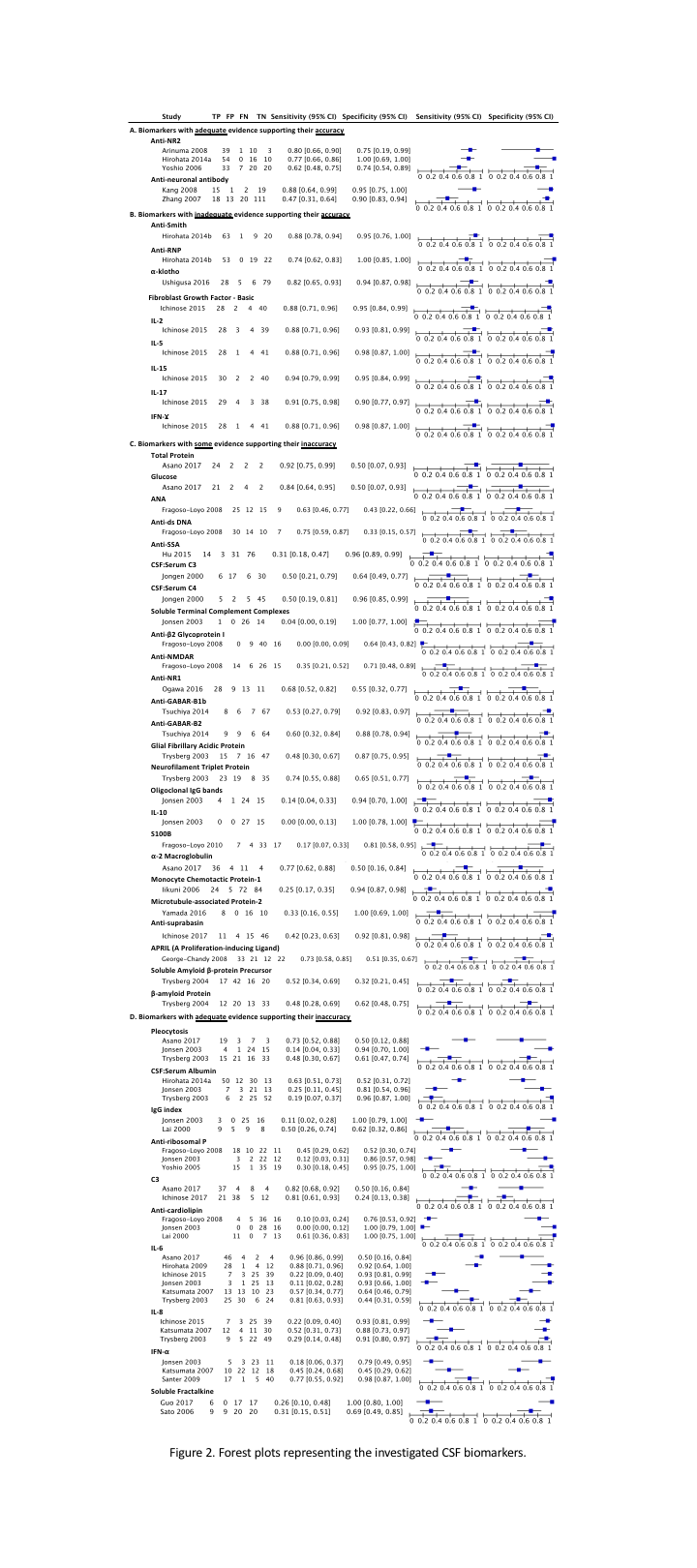
Results: We screened 2851 records and eventually included the data from 30 studies. Among the investigated 46 CSF biomarkers, only anti-NR2 and anti-neuronal antibody were shown to be highly accurate by more than one study (Figure 1). Also, anti-Smith, anti-RNP, α-klotho, fibroblast growth factor, IFN-γ, and interleukins 2, 5, 15, and 17 were each suggested to be highly accurate by a single study. The other CSF biomarkers were shown to be inaccurate by one study or more (Figure 2).
Conclusion: The CSF anti-NR2 and anti-neuronal antibody may be valuable additions to the routine initial workup done for suspected neuropsychiatric SLE. As these studies are both sensitive and specific, they can effectively change the post-test probability of NPSLE over a wide range or pre-test probabilities. Other biomarkers such as anti-Smith may have substantial diagnostic accuracy as well. However, their routine use requires more support by strong evidence.
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Ahmadi SF, Zahmatkesh G, Majed M, Desai S. Cerebrospinal Fluid Biomarkers for Diagnosing Neuropsychiatric SLE: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2018; 70 (suppl 9). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/cerebrospinal-fluid-biomarkers-for-diagnosing-neuropsychiatric-sle-a-systematic-review-and-meta-analysis/. Accessed .« Back to 2018 ACR/ARHP Annual Meeting
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/cerebrospinal-fluid-biomarkers-for-diagnosing-neuropsychiatric-sle-a-systematic-review-and-meta-analysis/