Session Information
Date: Sunday, November 10, 2019
Title: RA – Diagnosis, Manifestations, & Outcomes Poster I: Risk Factors, Predictors, & Prognosis
Session Type: Poster Session (Sunday)
Session Time: 9:00AM-11:00AM
Background/Purpose: Pain of rheumatoid arthritis (RA) is thought to be nociceptive. However, recent studies indicate that RA pain also includes the mechanism of central sensitization (CS). Therefore, we examined the prevalence of CS among RA patients and these patients’ clinical characteristics.
Methods: The central sensitization inventory (CSI) was used to evaluate in 240 outpatients (63 Male, 177 Female) with RA from May 2017 to September 2018. The disease activity was evaluated using the disease activity score of 28 joint (DAS28), clinical disease activity index (CDAI), and simplified disease activity index (SDAI). The following parameters were evaluated: swollen joint count on 28 joints (SJC), tender joint count on 28 joints (TJC), patient global assessment (PGA), estimator global assessment (EGA), pain visual analogue scale (PainVAS), serum C-reactive protein (CRP), and ESR. Physical function was evaluated using mHAQ-DI. Health-related quality of life (HRQOL) was evaluated using short-formed 36-Item health survey (SF-36). Fibromyalgia was evaluated using the fibromyalgia activity score 31 (FAS-31). Neuropathic-like pain was evaluated using the painDETECT questionnaire. Depression and anxiety were evaluated using the hospital anxiety and depression scale (HADS). We compared the clinical parameters between the patients with CS (CSI ≧ 40) and without CS (CSI < 39).
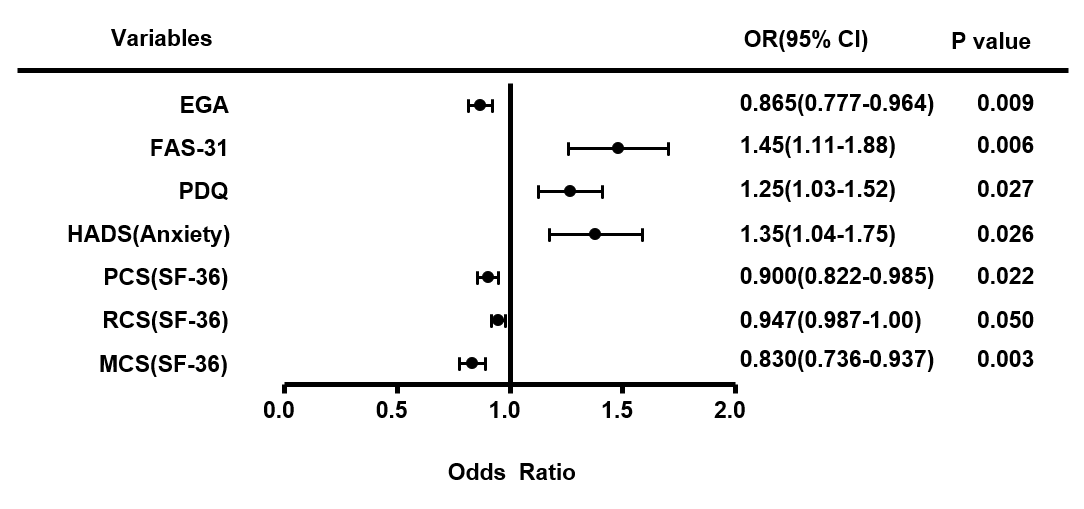
Results: Eighteen (7.5 %) of 240 patients had CS according to the CSI. In patients with CS, EGA, PainVAS, mHAQ-DI, FAS-31, HADS scores, physical component summary scores (PCS), and mental component summary scores (MCS) on the SF-36 were significantly higher than in patients without CS. Multivariate analysis of clinical parameters contributing CS showed significant differences in EGA (p = 0.009, OR 0.865), PDQ (p = 0.027, OR 1.25), FAS-31 (p = 0.006, OR 1.45), HADS(Anxiety) (p = 0.026, OR 1.35), PCS (p = 0.022, OR 0.900) and MCS (p = 0.003, OR 0.830) on the SF36.
Conclusion: CS in RA patients was associated with neuropathic-like symptoms, fibromyalgia, anxiety, and decrease of HRQOL. Neuropathic-like symptoms in RA may be helpful to detect CS. Proper treatment of CS in RA patients may improve HRQOL.
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Noda K, Saitou M, Ukichi T, Oto Y, Yoshida K, Kurosaka D. Central Sensitization in Patients with Rheumatoid Arthritis Using the Central Sensitization Inventory [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2019; 71 (suppl 10). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/central-sensitization-in-patients-with-rheumatoid-arthritis-using-the-central-sensitization-inventory/. Accessed .« Back to 2019 ACR/ARP Annual Meeting
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/central-sensitization-in-patients-with-rheumatoid-arthritis-using-the-central-sensitization-inventory/