Session Information
Session Type: Abstract Submissions (ACR)
Background/Purpose: Elevated levels of cell bound complement activation products (CBCAPS) have been established as valuable biomarkers in the diagnosis of Systemic Lupus Erythematosus (SLE). In this study, we compared the sensitivity of CBCAPS to reduced complement C3 and C4 proteins levels in SLE. We also evaluated the relationship between elevated CBCAPS, reduced complement levels and SLE disease activity.
Methods: A total 288 SLE patients (mean age 41±1 years, 92% females) all meeting the 1982 American College of Rheumatology SLE classification criteria were enrolled. Serum complement C3 and C4 protein levels were determined using immunoturbidimetry while complement C4d fragment deposited on erythrocytes (EC4d) and B-lymphocytes (BC4d) were determined using flow cytometry (and expressed as net mean fluorescence intensity [MFI]). A group of 476 subjects comprising 274 patients with other rheumatic diseases and 202 healthy subjects was used to establish the cutoffs yielding 95% specificity for C3, C4, EC4d and BC4d. Among SLE subjects, disease activity was determined using the Systemic Lupus Erythematosus Disease Activity Index SELENA Modification (SELENA-SLEDAI) subscore (without low complement and anti-dsDNA reactivity components). Difference in sensitivity (while controlling for similar specificity) was evaluated using χ2 test.
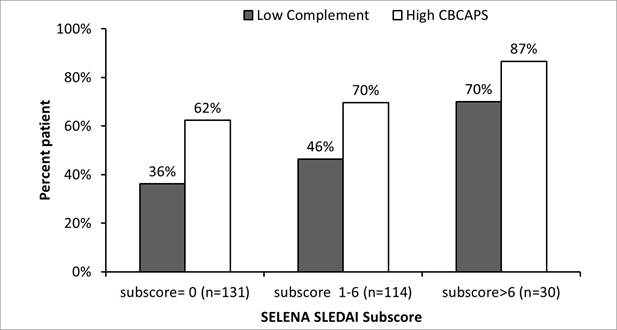
Results : Reduced C3 or C4 were both 32% sensitive for SLE (95% specific). In contrast, EC4d at a cutoff above 14 net MFI yielded 45% sensitivity (95% specific) while BC4d above 60 net MFI yielded 54% sensitivity (95% specific) (p<0.002). Elevated EC4d or BC4d (above their respective cutoffs as above) yielded a 22% higher sensitivity (66%) than reduced C3 or C4 (44%). Among 273 SLE patients with evaluable SELENA-SLEDAI subscores, the median subscore was 1 (range 0-23). Higher level of disease activity resulted in a higher proportion of patients testing positive for elevated CBCAPS (p=0.027) and reduced complement (p=0.002) (Figure). Among SLE with less active disease (SELENA-SLEDAI subscore=0) the difference in sensitivity was 26% greater for elevated CBCAPS (62%) than for reduced complement C3 or C4 (36%) (p<0.001). The difference in sensitivity remained higher (17%) for CBCAPS compared to low complement among SLE having a SELENA-SLEDAI subscore greater than 6 points but without reaching statistical significance (p=0.21).
Conclusion : Among all SLE patients, elevated CBCAPS have higher sensitivity than reduced C3 or C4. The higher sensitivity of CBCAPS is particularly significant among SLE with less active disease, and this supports the diagnostic utility of these markers for SLE
Disclosure:
R. Ramsey-Goldman,
None;
R. Furie,
Exagen,
2;
C. Putterman,
Exagen,
2,
Exagen,
5;
A. Askanase,
Exagen,
2;
J. P. Buyon,
Exagen,
2;
K. Kalunian,
Exagen,
2,
Exagen,
5;
W. W. Chatham,
None;
E. Massarotti,
None;
K. A. Kirou,
None;
A. Weinstein,
Exagen,
1,
Exagen,
6,
EXagen,
5;
P. Chitkara,
Exagen,
8;
S. Manzi,
EXagen,
5,
Exagen,
7;
J. Ahearn,
Exagen,
5,
Exagen,
7;
L. Wolover,
Exagen,
3;
J. Conklin,
Exagen,
3;
T. O’Malley,
Exagen,
3;
C. Ibarra,
Exagen,
3;
D. Barken,
Exagen,
3;
T. Dervieux,
Exagen,
3.
« Back to 2014 ACR/ARHP Annual Meeting
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/cell-bound-complement-activation-products-have-higher-sensitivity-than-serum-c3-and-c4-levels-in-systemic-lupus-erythematosus/