Session Information
Date: Sunday, November 17, 2024
Title: Muscle Biology, Myositis & Myopathies – Basic & Clinical Science Poster II
Session Type: Poster Session B
Session Time: 10:30AM-12:30PM
Background/Purpose: Idiopathic inflammatory myopathies (IIM) are associated with increased morbidity, mortality, and economic health burden compared to the general population despite advancements in overall disease management. However, the long-term trends in cause-specific mortality in IIM are lacking.
Methods: This retrospective cohort study utilized the Multiple Cause of Death files from the CDC’s National Center for Health Statistics to analyze IIM mortality data. The dataset includes US resident death certificates detailing demographics, a primary cause of death, and up to 20 contributory causes. We examined trends in proportionate cardiovascular mortality (PCM), respiratory mortality (PRM), infectious mortality (PIM), and neoplastic mortality (PNM), defined as the number of cause-specific deaths divided by all-cause mortality in IIM patients from 1999 to 2020. Linear regression and Chi-square tests were used for comparisons.
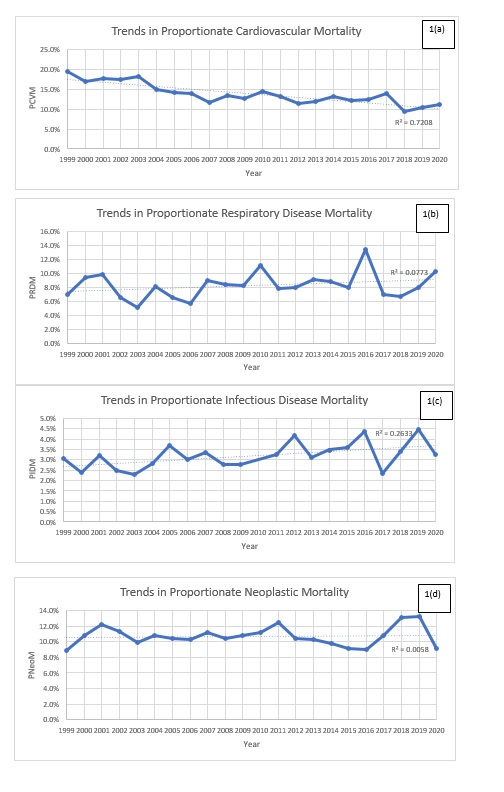
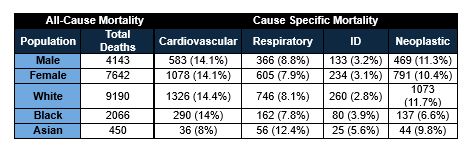
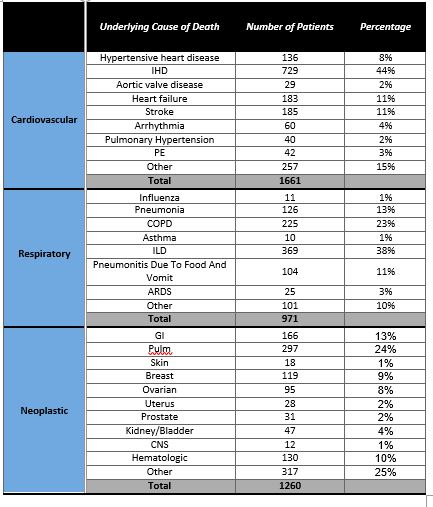
Results: During the study period, 11,785 deaths occurred in IIM patients. The mean age of patients with cardiovascular (CV) mortality was 73.5 + 14.07 years, with a total of 1661 deaths. PCM significantly decreased from 19.5% in 1999 to 11.3% in 2020 (p< 0.01), Figure 1(a). Ischemic heart disease (IHD) was the most common cause of CV mortality in IIM (44%). The mean age of death from respiratory causes was 69.0 + 12.31 years, with interstitial lung disease as the most common underlying cause (38%) from a total of 971 deaths. The PRM was 7.0% in 1999 and 10.3% in 2020 (p=0.20), Figure 1(b). A total of 358 deaths occurred from infectious causes, PIM showed a minor increase in trend from 3.0% to 3.3% (p< 0.01) Figure 1(c). With 1260 deaths from neoplasms, the PNM was 8.8% in 1999 to 9.2% in 2020(p=0.73), Figure 1(d). There was no gender-based difference in mortality from these causes. (Table 1)
Conclusion: The study provides nationwide insights into mortality trends from four major causes of death in IIM. CV mortality remained highest in IIM patients, although mortality trends have significantly improved over the last two decades. The impact on mortality from respiratory diseases and malignancies remained relatively constant, whereas death from infections was the lowest among the studied causes of mortality.
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Daoud A, Shamim M, Dweik L, Chaudhary H. Cause-Specific Proportionate Mortality Trends in Idiopathic Inflammatory Myopathies [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2024; 76 (suppl 9). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/cause-specific-proportionate-mortality-trends-in-idiopathic-inflammatory-myopathies/. Accessed .« Back to ACR Convergence 2024
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/cause-specific-proportionate-mortality-trends-in-idiopathic-inflammatory-myopathies/