Session Information
Date: Sunday, November 5, 2017
Title: Systemic Sclerosis, Fibrosing Syndromes and Raynaud's – Clinical Aspects and Therapeutics Poster I
Session Type: ACR Poster Session A
Session Time: 9:00AM-11:00AM
Background/Purpose:
Pulmonary arterial hypertension (PAH) is one of the leading death causes in SSc patients. To gain a better prognosis, screening methods are needed to provide an early diagnosis and intervention. The DETECT algorithm is a highly sensitive tool, however it presents a very low positive predictive value. To reduce the number of unnecessary right heart catheterizations (RHC), we evaluated the predictive performance of cardiopulmonary exercise testing (CPET) in a DETECT positive SSc population.
Methods:
Two-hundred-fifty-eight adult SSc consecutive patients attending our Scleroderma Unit were considered. Among those, the DETECT algorithm was applied to the subjects responding to the application criteria (ACR criteria for SSc, DLco < 60%, disease duration ≥ 3 years). DETECT positive patients underwent CPET and RHC. CPET was performed on a COSMED Quark-B2 equipment, on a cycle ergometer with an incremental work rate between 5 and 15 watts per minute up to the patients’ maximum tolerance.
Pearson’s correlation was used to evaluate linear associations between CPET parameters and mean pulmonary pressure (mPAP); the difference between PAH vs non-PAH patients for the best parameter was assessed by means of Student’s t-test. Finally, the sensitivity/specificity trade-off of this parameter was evaluated by ROC analysis.
Results:
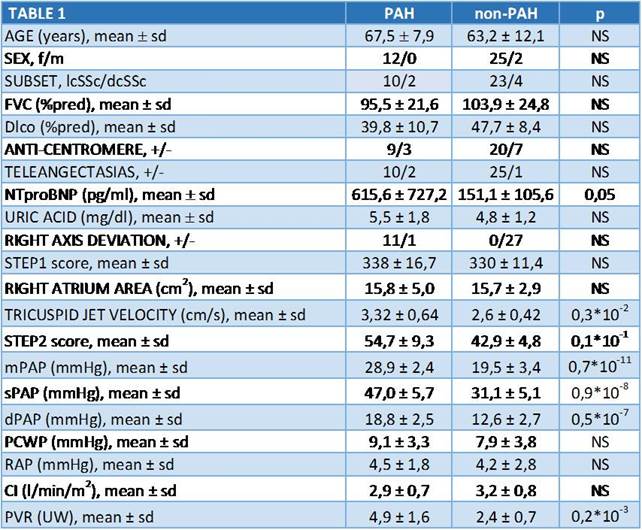
The enrolment flow chart is reported in Figure 1. Overall 81 patients were eligible for DETECT screening, 39 were positive and underwent CPET and RHC (Figure 1). The patients’ clinical characteristics are reported in Table 1. RHC found 12 cases of PAH (30.7%), 1 case of PH due to left heart disease (2.6%) and non-PH in 26 subjects (66.7%).
We found the following significant correlation:
– mPAP-PetCO2@lt (r 0.74, p 0.7*10-7)
– mPAP-VE/VCO2@lt (r 0.8, p 0.1*10-8)
– mPAP-VE/VCO2 slope (r 0.85, p 0.7*10-11)
The VE/VCO2 slope was selected for further investigation.
VE/VCO2 slope statistically differed between PAH and non-PAH patients (mean ± DS: 45.5 ± 4.95 vs 35.11 ± 5.04; p 0.5 *10-5). ROC analysis showed a remarkable performance of the VE/VCO2 slope in detecting PAH in the DETECT population (AUC 0.955, p 0.7*10-5). A single cut-point value equal to 38.5 of the VE/VCO2 slope was capable of discriminating PAH and non-PAH patients with a 100% sensitivity and 82% specificity.
Conclusion:
This study shows that CPET can fruitfully be applied to patients screened with the DETECT improve its specificity. The VE/VCO2 slope determination allows to significantly reduce the number of useless invasive RHC (from 39 to 17), without increasing missed diagnosis rate.
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Casella R, Santaniello A, Vicenzi M, Beretta L. Cardiopulmonary Exercise Testing to “Detect” Pulmonary Arterial Hypertension in Systemic Sclerosis [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2017; 69 (suppl 10). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/cardiopulmonary-exercise-testing-to-detect-pulmonary-arterial-hypertension-in-systemic-sclerosis/. Accessed .« Back to 2017 ACR/ARHP Annual Meeting
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/cardiopulmonary-exercise-testing-to-detect-pulmonary-arterial-hypertension-in-systemic-sclerosis/