Session Information
Date: Saturday, November 12, 2022
Title: Plenary I
Session Type: Plenary Session
Session Time: 11:30AM-1:00PM
Background/Purpose: Adult-onset idiopathic inflammatory myopathy (IIM) is associated with increased cancer risk (lung, ovarian, colorectal, lymphoma, breast, and naso-pharyngeal among the most common) within the three years prior to or following IIM onset. Evidence and consensus-based recommendations for IIM-associated cancer screening could potentially improve outcomes.
Methods: The International Myositis Assessment and Clinical Studies Group (IMACS) formed a Steering Group to develop recommendations for IIM-associated cancer screening. A modified Delphi Method approach using a series of online surveys was utilised for recommendation formation. Draft recommendations were sent to an international group (79 members located across 22 countries) with expertise in IIM and cancer screening. Surveys asked respondents to rate their level of agreement with each draft recommendation on a 1-9 numerical rating scale (1 = complete disagreement, 9 = complete agreement). The median vote rating for each draft recommendation was calculated and defined as disagreement (median 1-3), uncertainty (median 4-6), and consensus (median 7-9). Recommendations were assigned a strength of recommendation (strong, conditional); “strong” recommendations are made when the benefits are deemed to clearly outweigh risks, whereas “conditional” recommendations are made when benefits are more clearly balanced. Recommendations were assigned a quality of supporting evidence: high, moderate, low, or very low, according to Grading of Recommendations, Assessment, Development, and Evaluations (GRADE) methodology.
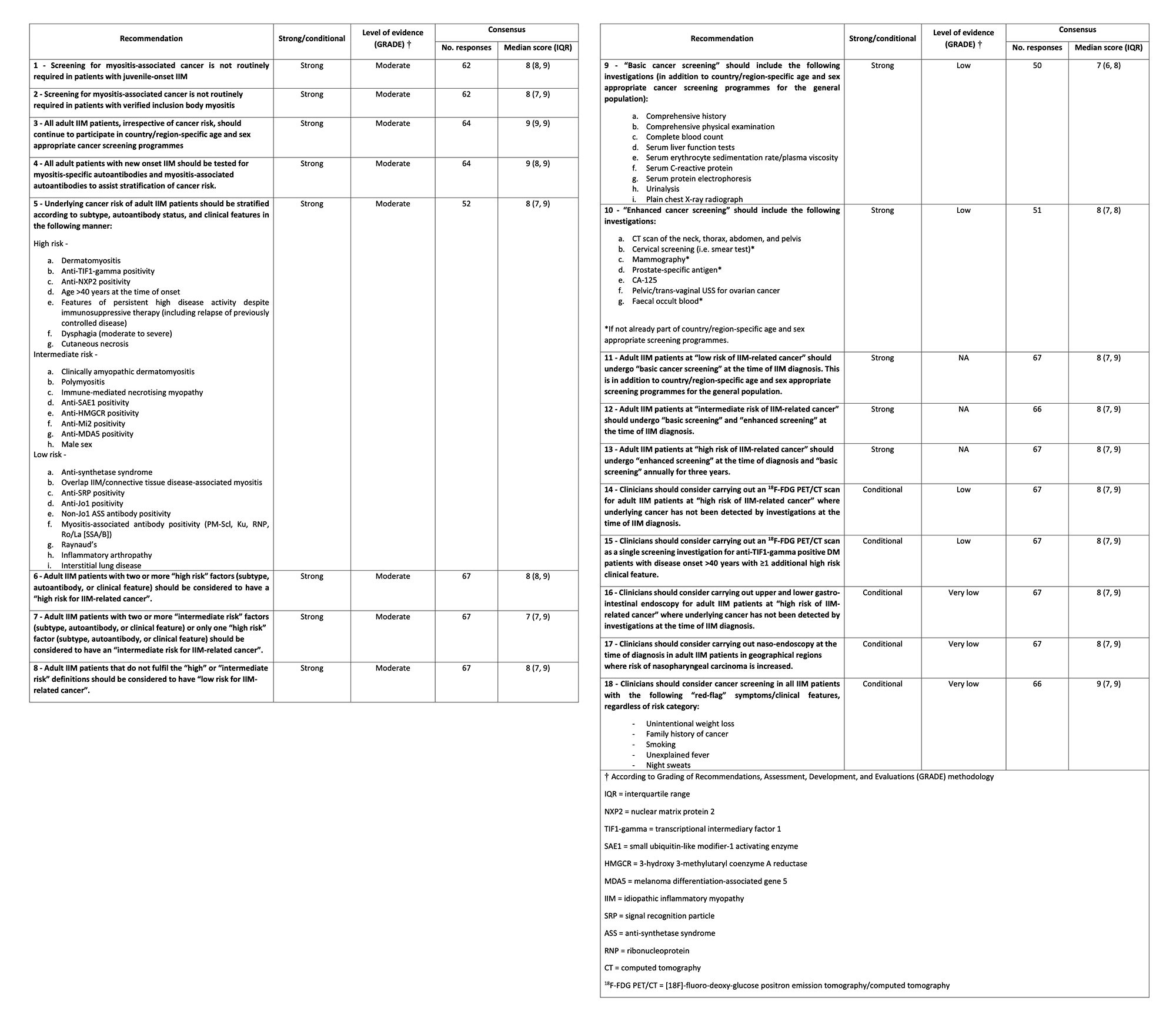
Results: A total of 18 final recommendations were generated (Table 1). Regarding strength of recommendation, 13 recommendations were strong and five were conditional. Quality of supporting evidence was moderate for 8 recommendations, low for four, and very low for three; three further recommendations had no corresponding evidence base and were formed via expert consensus only.
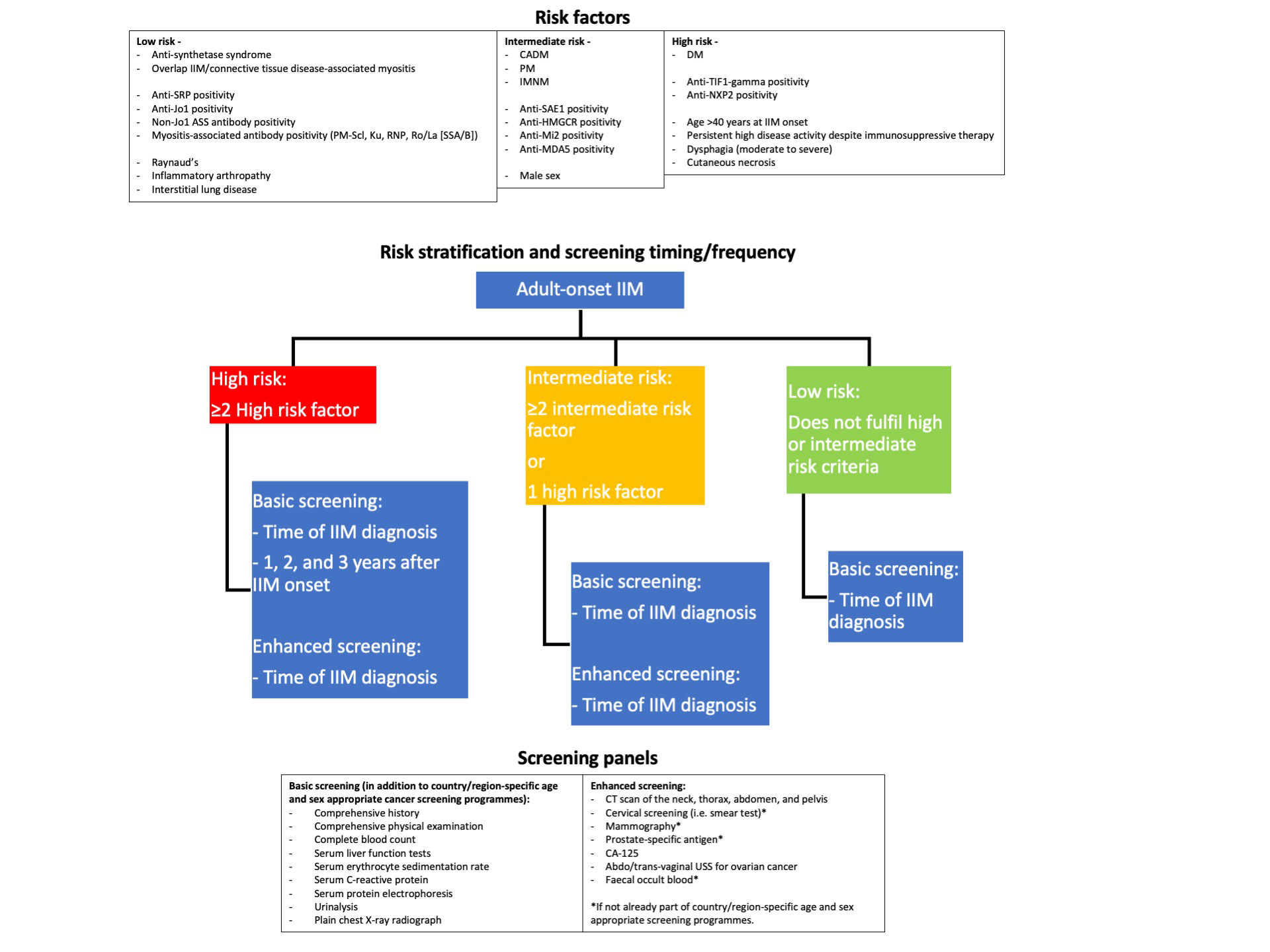
Firstly, recommendations allow a patient’s individual IIM-associated cancer risk to be stratified into low, intermediate, and high risk according to subtype, autoantibody status, and clinical features. Secondly, recommendations outline a “basic” screening panel (including chest X-ray radiography, basic laboratory blood tests) and an “enhanced” screening panel (including computed tomography, tumour markers). Thirdly, recommendations advise on the timing and frequency of screening via basic and enhanced panels, according to low/intermediate/high risk status (Figure 1). Recommendations also advise consideration of upper/lower gastro-intestinal endoscopy, naso-endoscopy, and 18F-FDG PET/CT scanning in specific populations.
Conclusion: The 2022 IIM-associated cancer screening guideline provides, for the first time, recommendations addressing individual patient risk stratification, cancer screening modalities, and screening frequency. Implementation of the recommendations aim to facilitate earlier IIM-associated cancer detection, especially in those with high risk, thus potentially improving outcomes, including survival.
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Oldroyd A, Callen J, Chinoy H, Chung L, Fiorentino D, Gordon P, Machado P, McHugh N, O’Callaghan A, Schmidt J, Tansley S, Vleugels R, Werth V, Aggarwal R. Cancer Screening Recommendations for Patients with Idiopathic Inflammatory Myopathy [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2022; 74 (suppl 9). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/cancer-screening-recommendations-for-patients-with-idiopathic-inflammatory-myopathy/. Accessed .« Back to ACR Convergence 2022
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/cancer-screening-recommendations-for-patients-with-idiopathic-inflammatory-myopathy/