Session Information
Session Type: Poster Session A
Session Time: 8:30AM-10:30AM
Background/Purpose: Many studies linking vasculitis to the development of malignancy based on chronic inflammation, cytotoxicity, emergence of vasculitis as a paraneoplastic disease. Even previous studies emphasize the role of cyclophosphamide, recent AAV cohort studies, where cumulative cyclophosphamide is lower than the historical cohorts, do not show such associations with cancer. The objective was to identify characteristics of adult AAV patients having a history of cancer and compare with AAV patients with no history of cancer.
Methods: In this nationwide study we used Turkish Vasculitis Study Group Registry (TRVaS)-a newly established, multicenter, and e-database of Turkey. Among 517 AAV patients, data regarding cancer was available in 373 (72%) patients. Demographics, clinical characteristics, medications, smoking data were analyzed. Retrospective analysis of patients that presented cancer before AAV diagnosis or after AAV diagnosıs was done. Regarding malignancies, type of cancer, clinical or pathological stage, treatment response were also recorded. AAV patients were groupped according to having cancer after AAV diagnosis or no cancer history. Groups were compared in terms of demographic, clinical features, and medications. Relative risk was measured using the standardized incidence ratio (SIR), which was calculated by the ratio of cancer cases except non-melanoma skin cancer among AAV patients to the expected cases for the background population. The expected number of cases was calculated by multiplying the measured person-years by the incidence rate of cancer in Turkey. Cancer data were obtained from the GLOBOCAN 2020 estimates of new cases in Turkey.
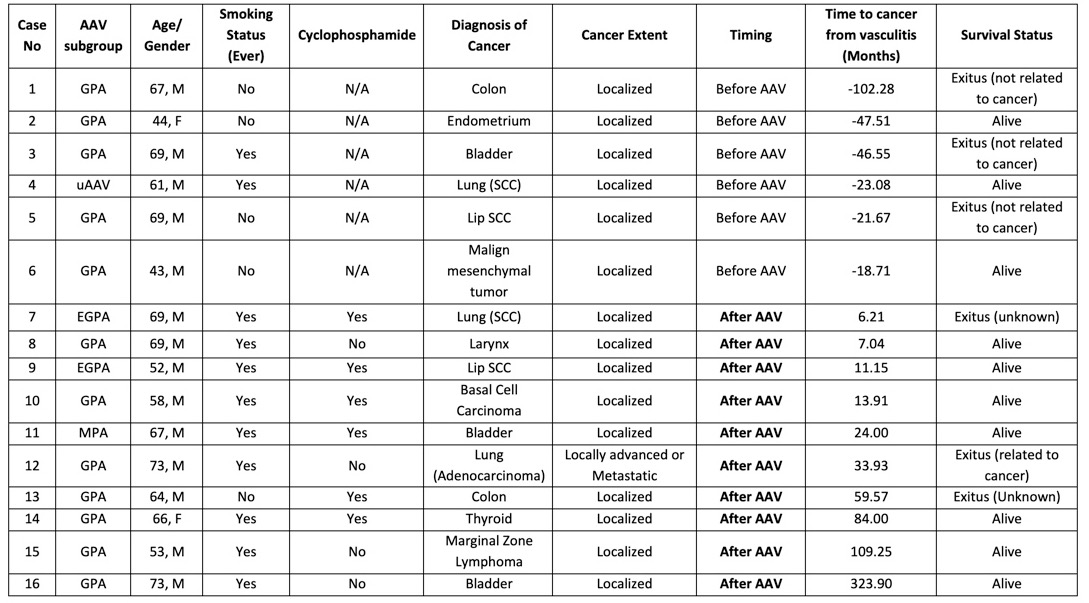
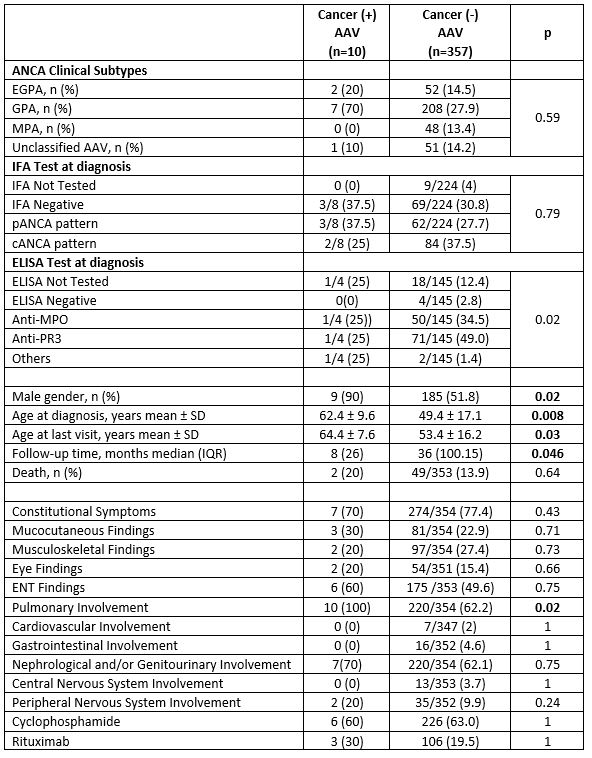
Results: Totally 16 patients had ever cancer history before AAV diagnosis in 6 and after AAV diagnosis in 10 patients. Distribution of cancer diagnosis were lung cancer (n=3), bladder (n=3), skin (n=3), colon (n=2), endometrium, lymphoma, thyroid, larynx, and malign mesenchymal tumor (Table 1). Patients with cancer history were older and male predominant (Table 2). Smoking history was present in 90% of the patients with cancer. In the comparison of AAV patients with cancer after AAV diagnosis with AAV patients with no cancer history, no difference was found in terms of clinical features of AAV except for pulmonary involvement(Table-2). Cyclophosphamide usage and dosages were similar between groups. Cancer risk was found to be over 2 times higher than the general population for the analysis of AAV patients who developed cancer after the diagnosis (SIR: 2.3, 95% CI: 1.2-4.1, P=0.02).
Conclusion: It seems AAV patients have an increased risk for overall malignancies as in European cohorts (1). Smoking was the most seen and preventable risk factor. Cyclophosphamide usage with lower doses in recent years decrease the importance of cyclophosphamide-related cancer. Cancer was more seen in AAV patients not only after AAV diagnosis but also before AAV diagnosis. Further studies required to better understand of which came first, the chicken or the egg?
Reference: 1. Heijl C, Westman K, Höglund P, et al. Malignancies in Patients with Antineutrophil Cytoplasmic Antibody-associated Vasculitis: A Population-based Cohort Study. J Rheumatol. 2020 Aug 1;47(8):1229-1237.
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Ediboglu E, Kardas R, bolek E, Yildirim R, Guven D, Kilickap S, Dizdar O, Yalcin Mutlu M, Icacan O, Ayan G, Bilgin E, Yasar Bilge N, Kilic L, Kasifoglu T, Bes C, Akar S, Karadag O. Cancer in Patients with ANCA-associated Vasculitis: Which Came First, the Chicken or the Egg? [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2021; 73 (suppl 9). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/cancer-in-patients-with-anca-associated-vasculitis-which-came-first-the-chicken-or-the-egg/. Accessed .« Back to ACR Convergence 2021
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/cancer-in-patients-with-anca-associated-vasculitis-which-came-first-the-chicken-or-the-egg/