Session Information
Date: Sunday, November 7, 2021
Title: Measures & Measurement of Healthcare Quality Poster (0623–0659)
Session Type: Poster Session B
Session Time: 8:30AM-10:30AM
Background/Purpose: Up to 83% of SLE patients are nonadherent to hydroxychloroquine (HCQ) which can result in up to 8-fold higher risk of early death. Yet, adherence is never assessed during routine SLE visits. Current adherence tools are time-consuming and offer no guidance to clinicians for adherence discussions. Our prior study reported feasibility of using an adapted seven-item Assessing Medication Adherence & Tailoring Intervention in Clinic (A-MATIC) process that identifies nonadherence and facilitates tailored adherence discussions in 2.6 mins. This study examined the impact and sustainability of using A-MATIC during SLE visits.
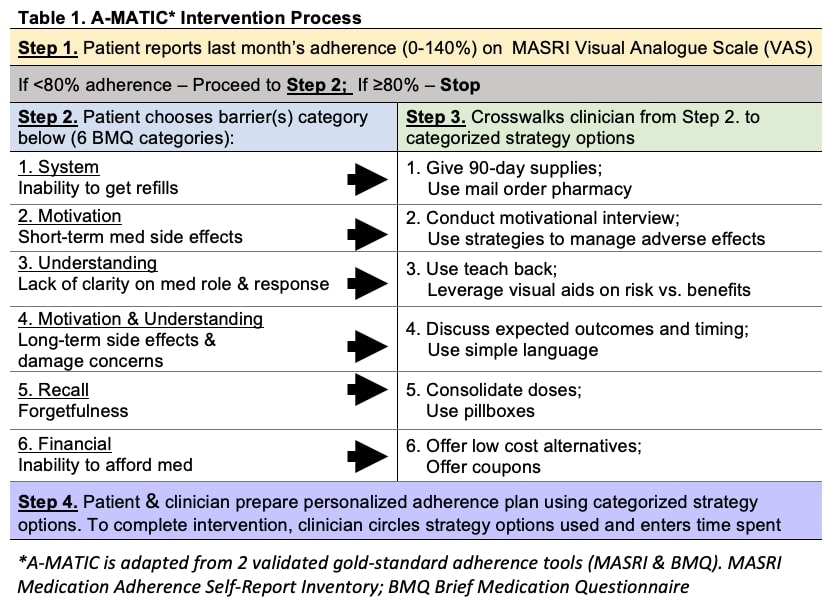
Methods: Our study included all patients seen at the UW SLE Clinic between 3/2019-5/2021. A-MATIC intervention is adapted from two standard adherence tools, Medication Adherence Self-Report Inventory (MASRI) and Brief Medication Questionnaire (BMQ), and includes 4 steps (Table 1): Step 1, assesses adherence using 0-140% MASRI visual analogue scale (VAS). The tool prompts patients reporting adherence < 80% to proceed to Step 2. Step 2, has 6-items BMQ-derived to identify key barriers. Step 3, contains adherence planning strategies that crosswalks from Step 2 barriers. Using these strategies, clinician can tailor an adherence plan based on patient choices in Step 4. Last, the clinician circles strategies used and time spent.
To assess impact, we examined the change in adherence across 3 follow-up (f/u) visits after patients participated in tailored patient-clinician discussions using A-MATIC compared to baseline adherence. We calculated the mean difference in adherence and examined the trend of adherence over time. To assess sustainability, we calculated the mean time spent and percentage of intervention completed at baseline, 1st, 2nd, 3rd f/u visits. Intervention completion was defined as patients and clinicians completing all steps.
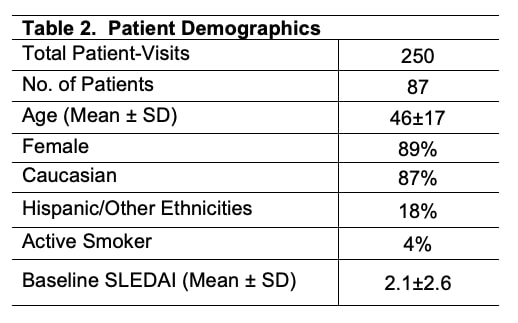
Results: In study period there were 250 visits of 87 SLE patients with demographics shown in Table 2.
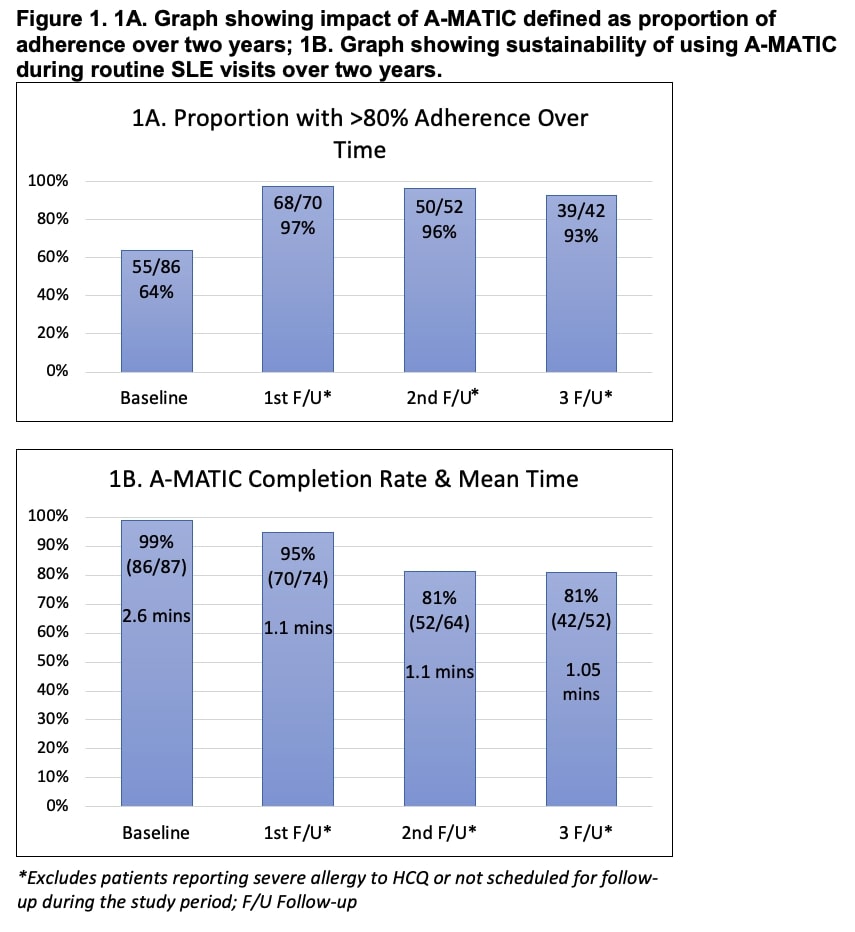
Impact – We found 36% (31/87) of the patients reported nonadherence at baseline. All patients reporting nonadherence participated in tailored adherence planning with their clinician. During the 1st f/u, 96% of these patients reported >80% HCQ adherence and resolution of underlying barriers; these patients reported HCQ adherence on their subsequent f/u. We found 93% lower odds of reported nonadherence after completing the A-MATIC intervention and participating in adherence discussions (OR 0.07, CI 0.01-0.24, p < 0.001). Significant improvement in adherence was noted over time (Mean diff. 27%, CI 16%-38%, p < 0.001) (Fig. 1A). Finally, over 2 years, 95% of patients reported >80% adherence compared to 64% at baseline.
Sustainability – Over 2 years, the mean time to complete the intervention was 2.6±1 mins, 1.1±0.2 mins, 1.1±0.2 mins, 1.05±0.2 mins. during baseline, 1st, 2nd, 3rd f/u; the intervention was completed during 99%, 95%, 81%, 81% of the baseline, 1st, 2nd, 3rd f/u visits. (Fig. 1B).
Conclusion: A-MATIC intervention is a sustainable and impactful way to assess and facilitate adherence discussions between a patient and clinician, and helps sustain adherence over time. Next study will examine A-MATIC’s role in targeting nonadherence in diverse SLE clinics.
*A-MATIC is adapted from 2 validated gold-standard adherence tools (MASRI & BMQ). MASRI Medication Adherence Self-Report Inventory; BMQ Brief Medication Questionnaire
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Garg S, Chewning B, Gomez S, Bartels C. Brief Tailored Clinic Intervention (A-MATIC) Targets Nonadherence During SLE Visits: Two-year Sustainability and Outcomes [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2021; 73 (suppl 9). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/brief-tailored-clinic-intervention-a-matic-targets-nonadherence-during-sle-visits-two-year-sustainability-and-outcomes/. Accessed .« Back to ACR Convergence 2021
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/brief-tailored-clinic-intervention-a-matic-targets-nonadherence-during-sle-visits-two-year-sustainability-and-outcomes/