Session Information
Session Type: Poster Session B
Session Time: 9:00AM-10:30AM
Background/Purpose: Immunocompromised patients with immune mediated inflammatory diseases (IMIDs) undergoing therapy with B cell depleting agents (BCDT) are among the most vulnerable to severe COVID-19 infection as well as the most likely to respond sub-optimally to SARS-CoV-2 vaccines. However, little is known about the frequency or severity of breakthrough infection in this population. We retrospectively analyzed a large group of vaccinated IMIDs patients undergoing B cell depleting therapy in order to identify the presence of breakthrough COVID-19 infections and assess their outcomes.
Methods: In this retrospective cohort study, the pharmacy records and COVID-19 registry at the Cleveland Clinic were searched using specific ICD-10 codes in order to identify patients with IMIDs who (1) were treated with B cell depleting monoclonal antibodies, (2) were vaccinated against SARS-CoV-2, and (3) experienced breakthrough infections. Each EMR record was reviewed to extract clinical data and outcomes. Univariate and multivariable logistic/proportional-odds regression models were used to examine the risk factors for severe outcomes. In addition a cohort of patients undergoing BCDT but not vaccinated against COVID-19 were identified over the same time period and examined using the same methodology as a comparator group to assess vaccine effectiveness for both incidence and severity of infection.
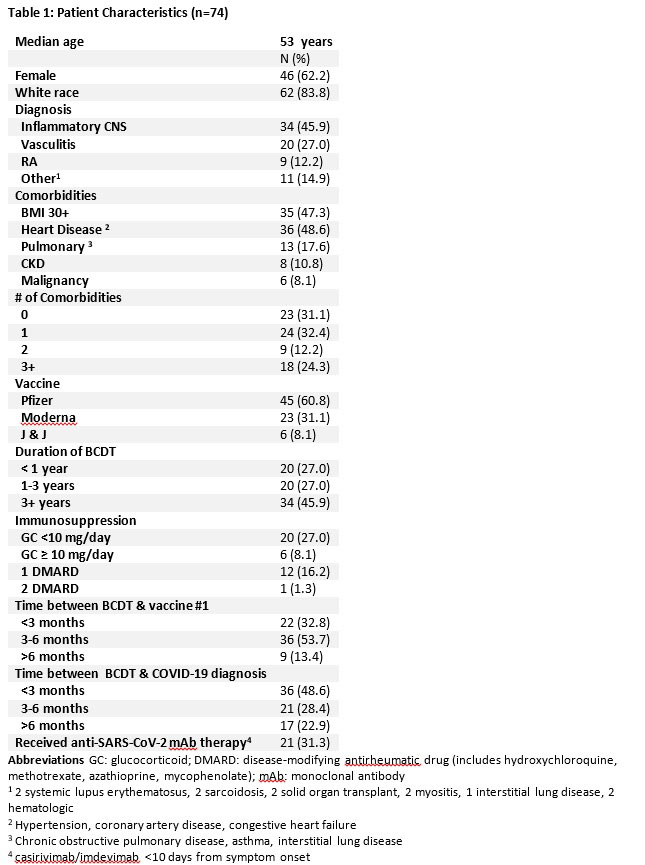
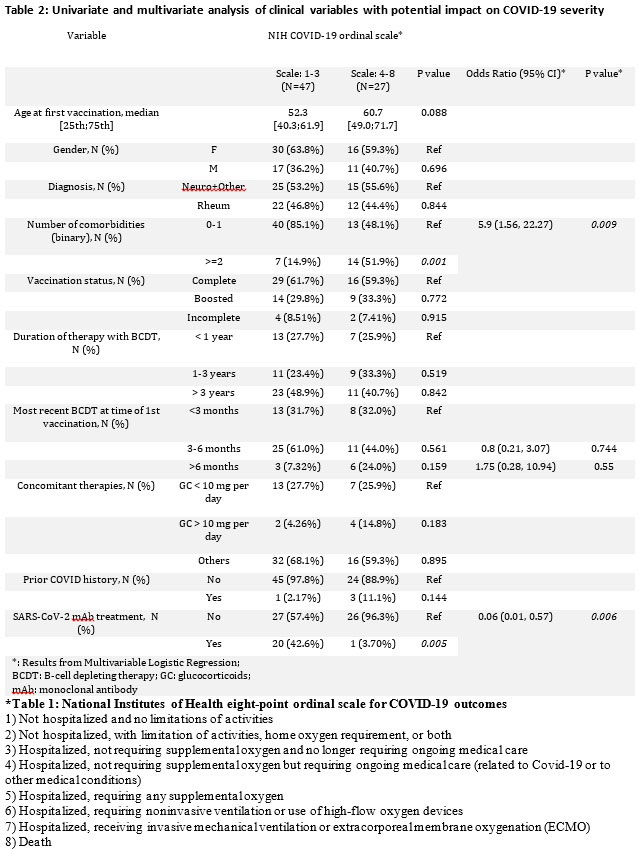
Results: Of 1696 vaccinated IMIDs patients on BCDT, 74 developed breakthrough COVID-19 prior to December 16th, 2021 (Table 1). Outcomes were severe with 29 (39.2%) patients hospitalized, 11 (14.9%) requiring critical care, and 6 (8.1%) deaths (Table 2). Anti-SARS-CoV-2 monoclonal antibodies were used on an outpatient basis to treat 21 with only a single patient requiring hospitalization and no deaths. An additional exploratory analysis was performed examining the incidence and severity of COVID-19 in 1437 unvaccinated patients identified via the same search strategy as a comparator group. Among these, 57 were diagnosed with COVID-19 for a crude incidence of 3.9%. In terms of severity as measured by the NIH ordinal scale, 29 patients (50.9%) fit the criteria for groups 1-3, and 28 patients were in groups 4-8 (49.1%);7 (12.2%) patients died.
Conclusion: In IMIDs patients on BCDT breakthrough infections appear frequent and associated with severe outcomes. Based on our exploratory analysis it appears that patients on BCDTs regardless of vaccine status are at risk for serious and fatal COVID-19. Outpatient use of anti-SARS-CoV-2 monoclonal antibody therapy appeared to be associated with enhanced clinical outcomes.
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Calabrese C, Kirchner E, Husni M, Moss B, Fernandez A, Jin Y, Calabrese L. Breakthrough SARS-CoV-2 Infections in Immune Mediated Disease Patients Undergoing B Cell Depleting Therapy: A Retrospective Cohort Analysis [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2022; 74 (suppl 9). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/breakthrough-sars-cov-2-infections-in-immune-mediated-disease-patients-undergoing-b-cell-depleting-therapy-a-retrospective-cohort-analysis/. Accessed .« Back to ACR Convergence 2022
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/breakthrough-sars-cov-2-infections-in-immune-mediated-disease-patients-undergoing-b-cell-depleting-therapy-a-retrospective-cohort-analysis/