Session Information
Date: Sunday, November 13, 2022
Title: Systemic Sclerosis and Related Disorders – Clinical Poster II
Session Type: Poster Session C
Session Time: 1:00PM-3:00PM
Background/Purpose: Patients with systemic autoimmune rheumatic diseases (AIRDs) are considered more susceptible to break through infection (BI) following vaccination due to their immunosuppressed status and associated co-morbid conditions. Data on BI in patients with systemic sclerosis (SSc) is scarce. These patients are at higher risks of adverse outcomes from COVID-19 due to high prevalence of interstitial lung disease and cardiovascular co-morbidities.
Methods: Data on respondents with SSc, non-SSc AIRDs and healthy controls (HCs) was extracted from the COVAD database, an international self-reported SurveyMonkey platform based online survey that captured respondent demographics, comorbidities, AIRD characteristics, COVID-19 infection history, and COVID-19 Vaccination details. Fully vaccinated patients (completed 2 doses of vaccine) who did not report COVID-19 prior to vaccination were included. BI was defined as per the CDC definition. Frequency of BI, symptoms, duration of illness, and severity (hospitalization or supplementary oxygen) were compared between the groups.
The survival analysis included Kaplan Meier curves with log-rank tests. Cox proportionate regression was used to assess the association of age, gender, ethnicity and immunosuppressive drugs at the time of vaccination on BI.
Results: Of 10900 respondents in the COVAD database, 6836 fulfilling inclusion criteria [SSc (n=427), other AIRDs (n=2934) and HCs (n=3475)] were analysed. BI were reported in 27 (6.3%) of SSc, 202 (6.9%) non-SSc AIRD and 560 (16.1%) of HCs during a median follow up of 100 days (IQR: 60-137) since the first dose of vaccination.
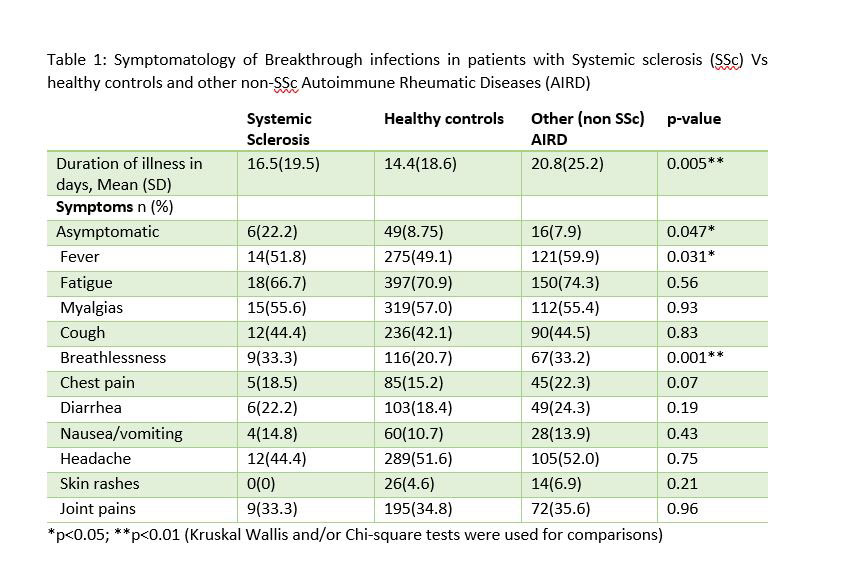
The duration and symptomatology of BI is compared between the three groups in Table-1. Hospitalization [SSc:4 (14.8%); HC:37 (6.61%); non SSc AIRD: 32(15.8%)] and the need for oxygenation [SSc:1 (25%); HC:17 (45.9%); non SSc AIRD: 13(40.6%)] were statistically same between the groups.
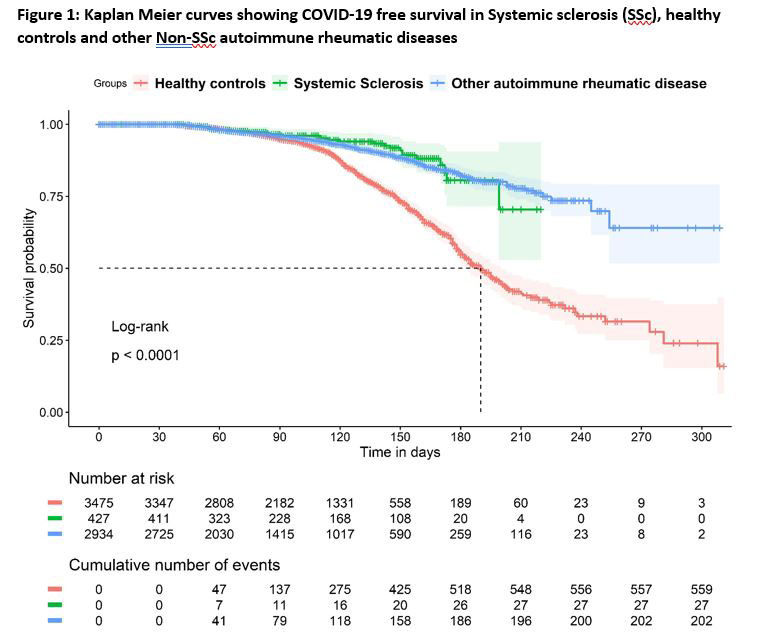
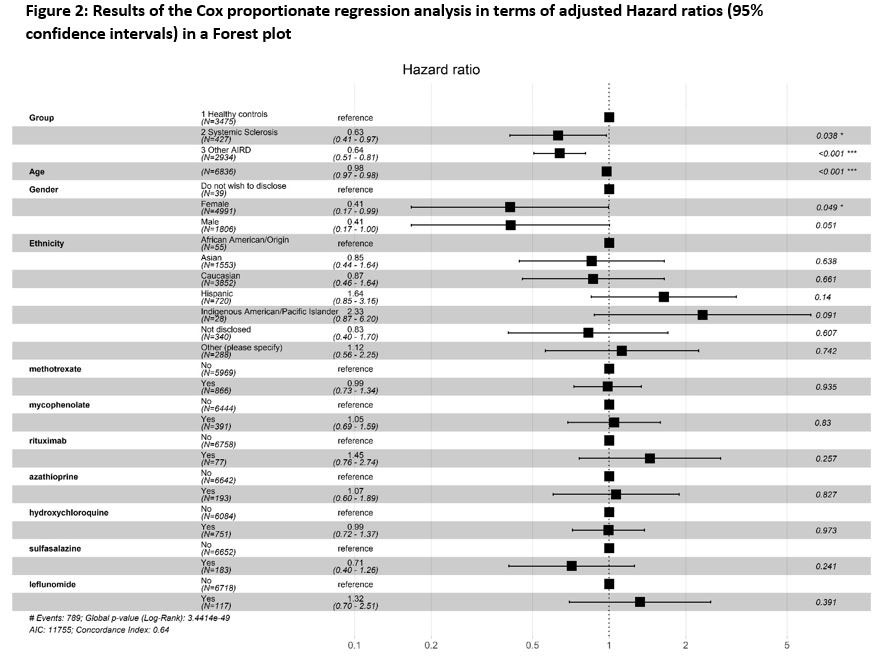
The incidence of BI in SSc was lower than that of HC, but comparable to non-SSc AIRD [Figure-1]. SSc had lower risk for BI [Hazard ratio (HR): 0.56 (95%CI: 0.46-0.74)]. BIs were associated with age [HR: 0.98 (0.97-0.98)] but not ethnicities or immunosuppressive drugs at the time of vaccination [Figure 2].
Conclusion: Patients with SSc had lower risk for BI as compared to HC, but similar to that in non-SSc AIRD. This may indicate that people with SSc and other AIRDs have continued to take effective precautions against contracting COVID-19. Severity of BI was not different between groups. Advancing age, but not ethnicity or immunosuppressive medication were associated with BIs.
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Ahmed S, R N, Pauling J, Thakare D, Wincup C, Del Papa N, Sambataro G, Atzeni F, PARISI S, Govoni M, Bartoloni Bocci E, Sebastiani G, Fusaro E, Sebastiani M, Quartuccio L, Franceschini F, Sainaghi P, Orsolini G, De Angelis R, Giovanna Danielli M, Venerito V, Sen P, Kim M, Gracia-Ramos A, Yoshida A, Lilleker J, Agarwal V, Kardes S, Day J, Joshi M, Milchert M, Gheita T, Salim B, Parodis I, O’Callaghan A, Nikiphorou E, Chatterjee T, Tan A, Nune A, Cavagna L, Shinjo S, Ziade N, Knitza J, Chinoy H, Distler O, Kuwana M, Aggarwal R, Gupta L, Agarwal V, Makol A. Breakthrough Infections in COVID-19 Vaccinated Patients with Systemic Sclerosis: A Survival Analysis from a Multicenter International Patient-Reported Survey [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2022; 74 (suppl 9). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/breakthrough-infections-in-covid-19-vaccinated-patients-with-systemic-sclerosis-a-survival-analysis-from-a-multicenter-international-patient-reported-survey/. Accessed .« Back to ACR Convergence 2022
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/breakthrough-infections-in-covid-19-vaccinated-patients-with-systemic-sclerosis-a-survival-analysis-from-a-multicenter-international-patient-reported-survey/