Session Information
Date: Wednesday, November 11, 2015
Title: Rheumatoid Arthritis - Clinical Aspects VII: Disease Activity and Updates in Measurement
Session Type: ACR Concurrent Abstract Session
Session Time: 11:00AM-12:30PM
Background/Purpose:
Fatigue is a major burden among patients with rheumatoid arthritis (RA). The identification of reliable biomarkers
would greatly enhance research in this challenging field. Diffusion tensor magnetic resonance imaging
(DTI) brain studies have previously reported fatigue specific abnormalities in
the white matter integrity of patients with other autoimmune conditions. These studies were however cross-sectional
and underpowered. We present the first
study to evaluate brain white matter integrity in RA. We specifically aimed to
evaluate the responsiveness of this putative biomarker to changing fatigue
levels over time in a large sample.
Methods: Consecutive
clinic attending RA patients fulfilling ACR/EULAR 2012 criteria were recruited if
they reported problems with fatigue >3 months and scored >3 on the Chalder Fatigue Scale (CFS, binary scoring). All participants underwent DTI scanning on 2
occasions, 6 months apart, during which time they received standard care. At
both visits they were clinically characterised. This included an evaluation of
disease activity (DAS28), depressive symptoms (Hospital Anxiety &
Depression Scale), pain (numerical rating scale) and sleep disturbance (Jenkin’s scale).
DTI data was acquired by a 3 Tesla, 8 channel phased array
head coil and presented as fractional anisotropy (FA) values, where decreased
FA reflects reduced white matter structural integrity and raised FA reflects
the opposite. Participants were split into 2 groups: those who reported a
clinically significant improvement in their fatigue levels (2 point reduction
in CFS) and those who did not. Within-group
differences between the time-points were analysed using paired Tract-Based
Spatial Statistics and corrected for multiple comparisons.
Results: Of the
54 participants who attended both visits (76% female, mean age 55.2 years, mean
disease duration 11.35 months at baseline), 22 (40.7%) reported a clinical
improvement in fatigue at 6 months (mean 2.64 point reduction in CFS) and 32
(60.3%) reported unchanged fatigue (-0.13 change in CFS). Within the fatigue
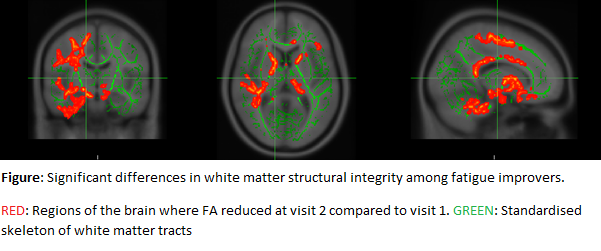
improver group, statistically significantly reduced FA levels were observed at
visit 2 compared to visit 1. The regions
of change were diffuse, but much greater in the right hemisphere and
specifically the periventricular, internal capsule, thalamus, inferior frontal
and parietal areas (figure). The regions were unchanged after adjusting
individually for disease activity or sleep, although became focalised following
adjustment of depression or pain.
In contrast, no significant differences in FA levels were
observed between visits within the fatigue non-improver group.
Conclusion: The
striking disparity in white matter integrity changes between the fatigue improver
and non-improver groups provides preliminary evidence to support the role of
DTI as a future biomarker of RA related fatigue.
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Basu N, Alsyedalhashem M, D'Allesandro M, Murray AD, Clauw DJ, Waiter GD. Brain White Matter Integrity: A Future Biomarker for Rheumatoid Arthritis Related Fatigue? [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2015; 67 (suppl 10). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/brain-white-matter-integrity-a-future-biomarker-for-rheumatoid-arthritis-related-fatigue/. Accessed .« Back to 2015 ACR/ARHP Annual Meeting
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/brain-white-matter-integrity-a-future-biomarker-for-rheumatoid-arthritis-related-fatigue/