Session Information
Date: Monday, November 9, 2020
Title: RA – Diagnosis, Manifestations, & Outcomes Poster IV: Lifespan of a Disease
Session Type: Poster Session D
Session Time: 9:00AM-11:00AM
Background/Purpose: Past studies have examined associations between BMI and disease activity [1, 2, 3], but few studies have characterized BMI trajectory over the disease course of RA, and there are no known prior studies assessing BMI variability over time in RA patients. We compared BMI trends and variability over time between RA and matched non-RA subjects.
Methods: The study population comprised residents of a geographically defined area with incident RA (age ≥18 years, 1987 ACR criteria met in 1995-2009) and non-RA subjects from the same underlying population with similar age, sex and calendar year of index. All subjects were followed until death, migration, or 01/July/2019. Follow-up was truncated for comparability. Visit-to-visit BMI variability was defined as the within-subject standard deviation (SD) for BMI. Generalized additive models with smoothing splines and random effects to account for multiple measurements per subject were used to illustrate trends in BMI measurements over time.
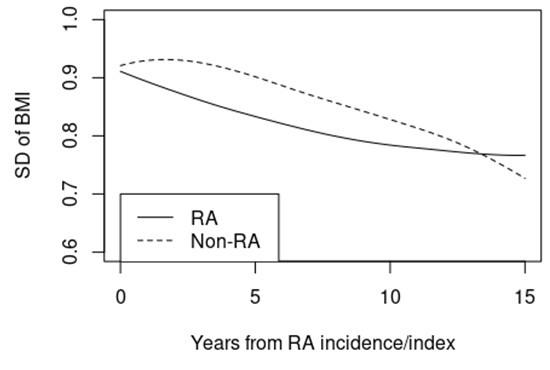
Results: The study included 558 patients with RA (mean age 55.6 years; 69% female) and 556 patients without RA (mean age 55.7 years, 69% female). Mean (±SD) BMI of patients with incident RA (28.8 ±6.4 kg/m2) was not significantly different from that of non-RA subjects (28.9 ±6.8 kg/m2, p=0.94). Models of time trends in BMI demonstrated no significant change in BMI over time for the non-RA subjects (-0.01 kg/m2 per year, 95% CI:-0.05, 0.5, p=0.58) and a non-significant decline over time for the RA (-0.05 kg/m2 per year, 95% CI: -0.10, 0.0, p=0.058). Among patients with RA, no differences were found for BMI trend according to sex (p=0.93) or RF/CCP-positivity (p=0.32). There was no evidence of higher variability of BMI measurements over time in patients with RA compared to subjects without RA (SD of random effects: 6.5 RA vs 6.7 non-RA). The figure shows the trends in within-subject SD for RA and non-RA based on consecutive sets of 6 BMI measures.
Conclusion: Our findings demonstrate a minimal decline in BMI over time in the RA population, perhaps reflecting the phenomenon of rheumatoid cachexia. While we were surprised that the RA population did not demonstrate higher BMI variability over time compared to the non-RA population due to weight variation secondary to corticosteroid use, further studies are needed to understand the reasons and implications of these trends.
REFERENCES:
[1] Liu Y, Hazlewood GS, Kaplan GG, et al. The Impact of Obesity on Remission and Disease Activity in Rheumatoid Arthritis: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Arthritis Care Res Published Online First: 9 May 2016.
[2] Sandberg MEC, Bengtsson C, Källberg H, et al. Overweight decreases the chance of achieving good response and low disease activity in early rheumatoid arthritis. Annals of the Rheumatic Diseases 2014;73:2029-2033.
[3] Sparks JA, et al. Impact of Bariatric Surgery on Patients with Rheumatoid Arthritis. Arthritis Care Res (Hoboken). 2015;67(12):1619–1626.
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Challener G, Myasoedova E, Crowson C, Giblon R, Davis J. Body Mass Index Trajectory and Variability in Rheumatoid Arthritis [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2020; 72 (suppl 10). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/body-mass-index-trajectory-and-variability-in-rheumatoid-arthritis/. Accessed .« Back to ACR Convergence 2020
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/body-mass-index-trajectory-and-variability-in-rheumatoid-arthritis/