Background/Purpose
To identify circulating proteins that distinguish between active vasculitis and remission in giant cell arteritis (GCA), Takayasu’s arteritis (TAK), polyarteritis nodosa (PAN) and eosinophilic granulomatosis with polyangiitis (EGPA, Churg-Strauss), using a panel of markers known to be elevated in ANCA-associated vasculitis.
Methods
22 serum proteins (MMP-3, NGAL, ACE, sIL-6R, osteopontin, PAI-1, PDGF-AB, RANTES, sICAM-1, TIMP-1, BCA-1, G-CSF, GM-CSF, IFNγ, IL-15, IL-18, IL-18BPa, sIL-2Ra, IL-6, IL-8, IP-10, and sTNFRII) linked to possible pathways relevant to vasculitis were measured using a microarray platform. Disease activity during the past 28 days was classified by physician global assessment (PGA), where remission is indicated by PGA=0 and active disease by PGA 1-10. Spearman’s correlation was used to study the association between serum proteins and ESR. To compare marker values between active disease and remission, mixed models were used to account for repeated measures with unequal spacing between visits. Prednisone and immunosuppressive treatments were included as independent variables. Fold-change (FC) in marker values between active and mean remission values was used as the measure of effect.
Results
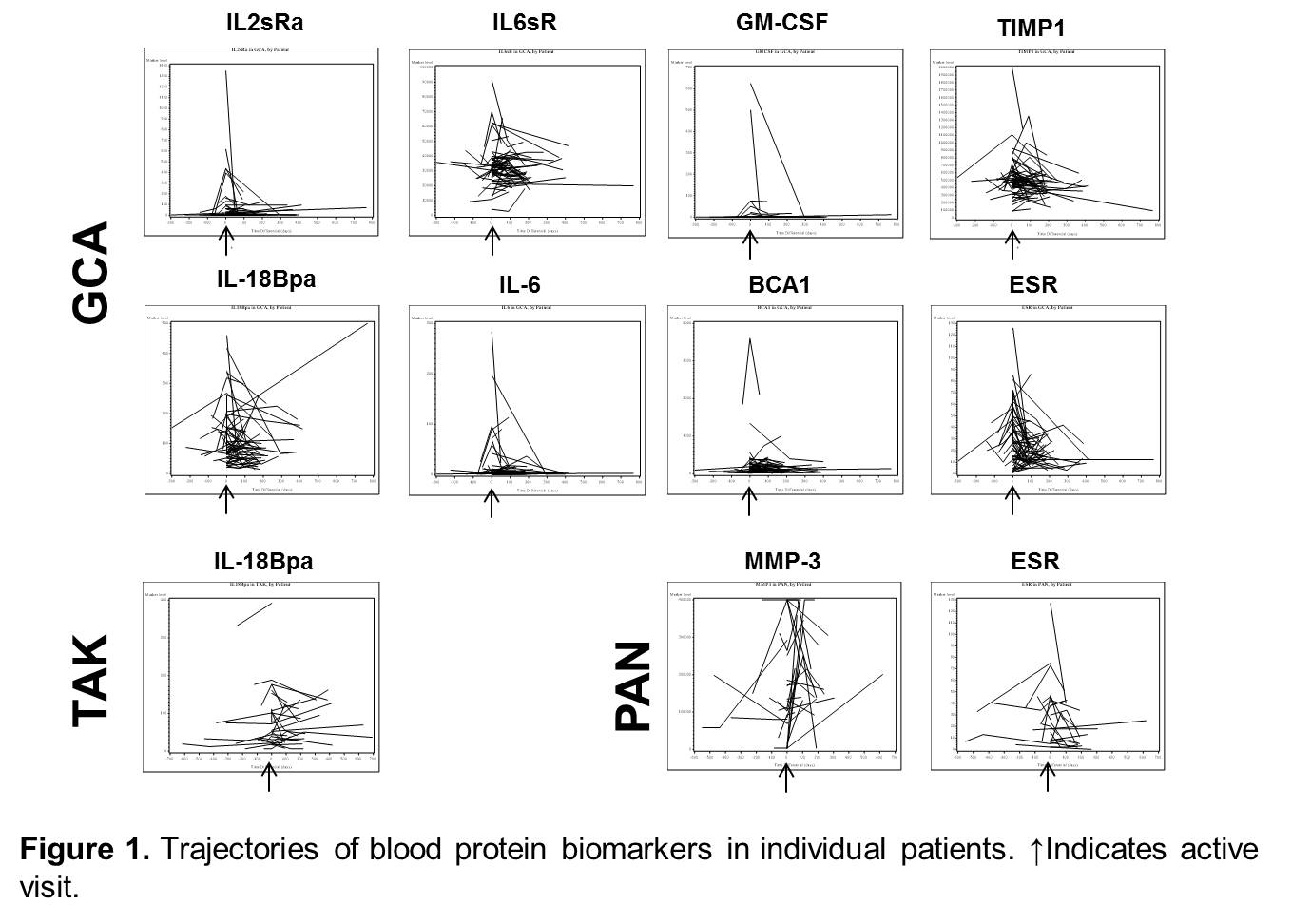
479 samples from 174 patients (66 GCA, 35 TAK, 31 PAN, 42 EGPA, with 1 active visit and 1-3 remission visit samples per patient) were tested. 440 samples (92%) were obtained while the patient was on treatment. Disease activity ranged from PGA 1 to 9. In GCA, sIL-6R (FC 1.1, p=0.024), BCA-1 (FC 2.08, p=0.008), GM-CSF (FC 32.5, p=0.04; 7 patients with FC>2), IL-18BPa (FC 1.16, p=0.026), sIL-2Ra (FC 2.03, p=0.018), IL-6 (FC 2.54, p=0.032), and TIMP-1 (FC 1.18, p=0.034) were significantly higher in active than remission samples; in TAK, only IL-18BPa was higher in active than in remission samples (FC 1.16, p=0.029); and in PAN, only MMP-3 was significantly different, being higher in remission samples (FC 0.71, p=0.045). ESR was significantly elevated in active GCA (FC 1.43, p=0.001) and PAN (FC 1.45, p=0.013), and no differences were observed in TAK or EGPA. The correlation of ESR with the majority of the protein markers was weak; the highest correlation was observed in GCA with IL-6 (r=0.34, p<0.0001). FC and p-values were similar when use of prednisone and other immune-suppressive drugs were included in the models. The majority of the samples were obtained while the patients were on prednisone (81.2% of the active and 79.1% of the remission samples). Trajectories of selected markers are shown in Figure 1.
Conclusion
This study identifies several potential biomarkers of disease activity in GCA, although effect sizes were modest in this partially-treated cohort. Promising markers included several cytokines (IL-6, GM-CSF, BCA-1), soluble cytokine receptors (sIL-6R, IL-18BPa), and the metalloproteinase inhibitor TIMP-1. Larger studies are needed to test the utility of these biomarkers for disease monitoring.
Disclosure:
A. Rodriguez-Pla,
None;
R. L. Warner,
None;
D. Cuthbertson,
None;
S. Carette,
None;
G. S. Hoffman,
Roche Pharmaceuticals,
9;
N. A. Khalidi,
None;
C. L. Koening,
None;
C. A. Langford,
None;
K. Maksimowicz-McKinnon,
None;
L. W. Moreland,
None;
C. Pagnoux,
None;
P. Seo,
None;
U. Specks,
None;
K. J. Warrington,
None;
S. R. Ytterberg,
None;
P. A. Merkel,
Genentech and Biogen IDEC Inc.,
2,
Bristol-Myers Squibb,
2,
GlaxoSmithKline,
2,
Actelion Pharmaceuticals US,
2,
Actelion Pharmaceuticals US,
5,
Sanofi-Aventis Pharmaceutical,
5,
Chemocentryx,
5;
K. J. Johnson,
None;
P. A. Monach,
None;
F. the Vasculitis Research Consortium,
None.
« Back to 2014 ACR/ARHP Annual Meeting
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/biomarkers-of-disease-activity-in-vasculitis/